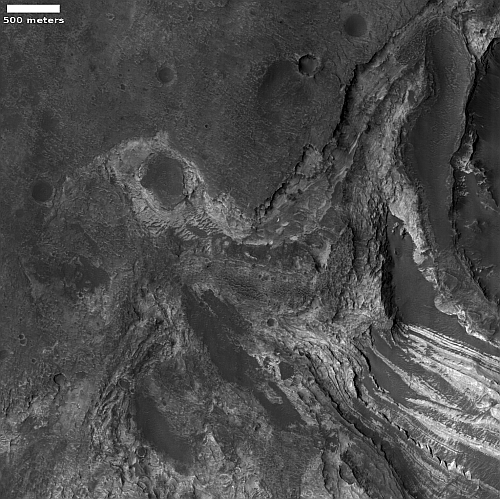
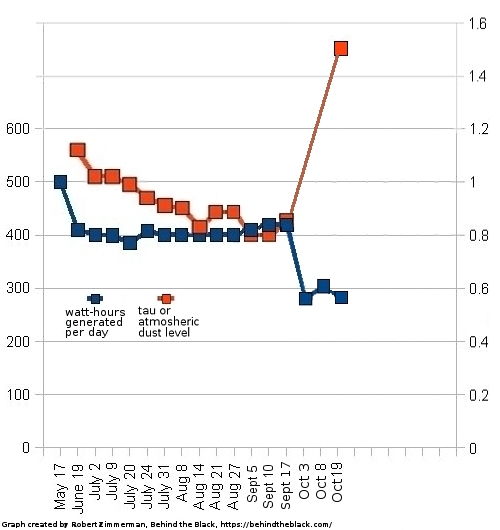
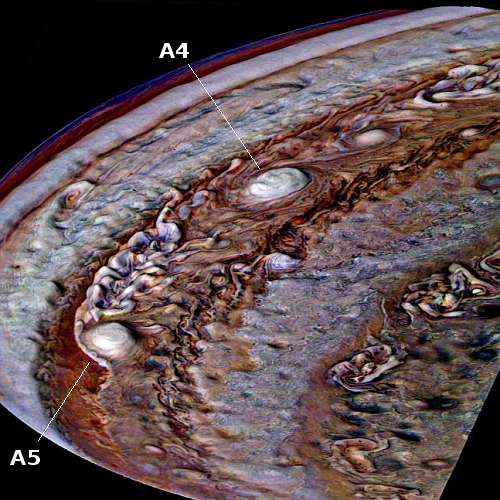
A hole in space
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and was released today as its picture of the week. From the caption:
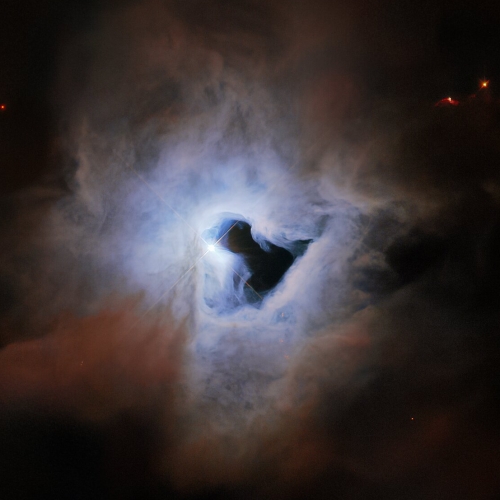
This peculiar portrait from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope showcases NGC 1999, a reflection nebula in the constellation Orion. NGC 1999 is around 1350 light-years from Earth and lies near to the Orion Nebula, the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. NGC 1999 itself is a relic of recent star formation — it is composed of detritus left over from the formation of a newborn star.
Just like fog curling around a street lamp, reflection nebulae like NGC 1999 only shine because of the light from an embedded source. In the case of NGC 1999, this source is the aforementioned newborn star V380 Orionis which is visible at the centre of this image. The most notable aspect of NGC 1999’s appearance, however, is the conspicuous hole in its centre, which resembles an inky-black keyhole of cosmic proportions.
Once astronomers thought the black area was caused by dust, blocking the light. Now, based on a lot of new data from multiple ground- and space-based telescopes, they know that it actually is a black empty void. Why it exists however is not yet understood.
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and was released today as its picture of the week. From the caption:
This peculiar portrait from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope showcases NGC 1999, a reflection nebula in the constellation Orion. NGC 1999 is around 1350 light-years from Earth and lies near to the Orion Nebula, the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. NGC 1999 itself is a relic of recent star formation — it is composed of detritus left over from the formation of a newborn star.
Just like fog curling around a street lamp, reflection nebulae like NGC 1999 only shine because of the light from an embedded source. In the case of NGC 1999, this source is the aforementioned newborn star V380 Orionis which is visible at the centre of this image. The most notable aspect of NGC 1999’s appearance, however, is the conspicuous hole in its centre, which resembles an inky-black keyhole of cosmic proportions.
Once astronomers thought the black area was caused by dust, blocking the light. Now, based on a lot of new data from multiple ground- and space-based telescopes, they know that it actually is a black empty void. Why it exists however is not yet understood.