Curiosity

For the overall context of Curiosity’s travels, see Pinpointing Curiosity’s location in Gale Crater.
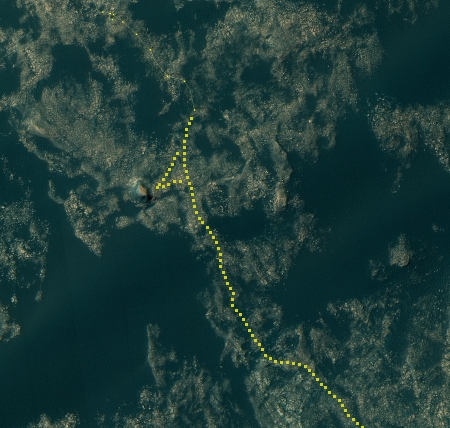
In the past month, since my last rover update on December 22, 2016, Curiosity has begun moving again, carefully picking its way through the dune-filled flats in the foothills at the base of Mount Sharp. The route taken, shown on the image on the right, corresponds to the easternmost of the possible routes I noted in my November 14, 2016 update. This route is also the most direct route, which I think is smart considering that the rover’s life on Mars certainly uncertain and the higher they can climb the more geological information they will get.
I have also annotated the likely route into the near future, including a possible side trip to the base of the mesa up ahead. It appears to me that they are now a little more than halfway through the flats, with Mt. Sharp directly ahead, as shown by the panorama below, taken near the end of December. The goal is a canyon just out of view to the right of this panorama.

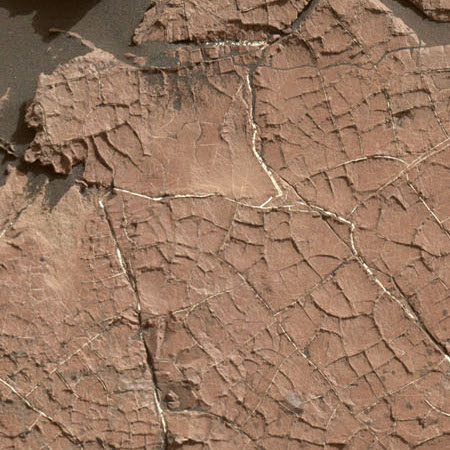
The flats the rover is presently traversing, and visible in the foreground of the panorama above, is strewn with dark sand that often piled into large sand dunes. Where the ground is exposed, it is made up of a scattering of pavement-like rocks. As noted in a press release yesterday, many of these flat rocks have polygonal cracks and boxwork similar to that seen in dried mud here on Earth, suggesting that this area was once wet and then dried. This geology helps confirm the theory of planetary scientists that Gale Crater was once filled with water that slowly evaporated away. As the rover climbs, it leaves the lakebed and begins to move through the lake’s various shores, each one older than the last.
Opportunity
For the overall context of Opportunity’s travels at Endeavour Crater, see Opportunity’s future travels on Mars.
» Read more