A planet-forming disk with mysterious ripples
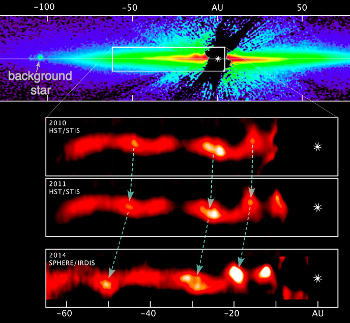
The mysteries of science: Astronomers have detected ripples and blobs moving outward through the dust disk surrounding a nearby star, and have no idea what is causing them.
The images reveal a train of wave-like arches, resembling ripples in water. After spotting the features in the SPHERE data the team turned to earlier Hubble images of the disk, taken in 2010 and 2011. The wave-like nature of some of these features were not recognized in the initial Hubble observations. But once astronomers reprocessed the Hubble images they not only identified the features but realized that they had changed over time. The researchers report that these ripples are moving — and they are moving very fast. “We ended up with enough information to track the movement of these strange features over a 3- to 4-year period,” explained team member Christian Thalmann of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, Switzerland. “By doing this, we found that the arches are racing away from the star at speeds of up to 10 kilometers per second (22,000 miles per hour)!” Co-investigator Carol Grady of Eureka Scientific in Oakland, California, added, “Because nothing like this has been observed or predicted in theory we can only hypothesize when it comes to what we are seeing and how it came about.”
The one theory that is still not refuted is that the star’s flaring activity, which is significant, causes the ripples somehow.

The mysteries of science: Astronomers have detected ripples and blobs moving outward through the dust disk surrounding a nearby star, and have no idea what is causing them.
The images reveal a train of wave-like arches, resembling ripples in water. After spotting the features in the SPHERE data the team turned to earlier Hubble images of the disk, taken in 2010 and 2011. The wave-like nature of some of these features were not recognized in the initial Hubble observations. But once astronomers reprocessed the Hubble images they not only identified the features but realized that they had changed over time. The researchers report that these ripples are moving — and they are moving very fast. “We ended up with enough information to track the movement of these strange features over a 3- to 4-year period,” explained team member Christian Thalmann of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, Switzerland. “By doing this, we found that the arches are racing away from the star at speeds of up to 10 kilometers per second (22,000 miles per hour)!” Co-investigator Carol Grady of Eureka Scientific in Oakland, California, added, “Because nothing like this has been observed or predicted in theory we can only hypothesize when it comes to what we are seeing and how it came about.”
The one theory that is still not refuted is that the star’s flaring activity, which is significant, causes the ripples somehow.