SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket launches the Space Force’s X-37B
SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket tonight successfully launched one of the two X-37B reuseable mini-shuttles in the Space Force’s fleet, lifting off from Cape Canaveral.
This was the seventh X-37B flight. It is not clear which of the two vehicles was flying, and how many flights it has completed previously. The previous X-37B flight stayed in orbit for a record 908 days, landing safely in November 2022.
The two side boosters completed their fifth flight, landing safely back at Cape Canaveral. The center core was treated as expendable, and was not recovered.
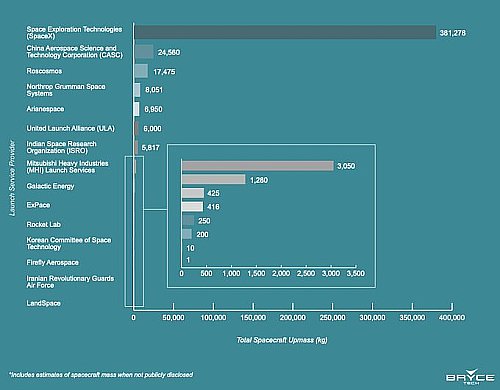
The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
95 SpaceX (with another launch scheduled later tonight)
65 China
19 Russia
8 Rocket Lab
7 India
American private enterprise now leads China in successful launches 109 to 65, and the entire world combined 109 to 102. SpaceX in turn trails the rest of the world (excluding other American companies) 95 to 102.
SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket tonight successfully launched one of the two X-37B reuseable mini-shuttles in the Space Force’s fleet, lifting off from Cape Canaveral.
This was the seventh X-37B flight. It is not clear which of the two vehicles was flying, and how many flights it has completed previously. The previous X-37B flight stayed in orbit for a record 908 days, landing safely in November 2022.
The two side boosters completed their fifth flight, landing safely back at Cape Canaveral. The center core was treated as expendable, and was not recovered.
The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
95 SpaceX (with another launch scheduled later tonight)
65 China
19 Russia
8 Rocket Lab
7 India
American private enterprise now leads China in successful launches 109 to 65, and the entire world combined 109 to 102. SpaceX in turn trails the rest of the world (excluding other American companies) 95 to 102.