A cliff face of volcanic erosion on Mars
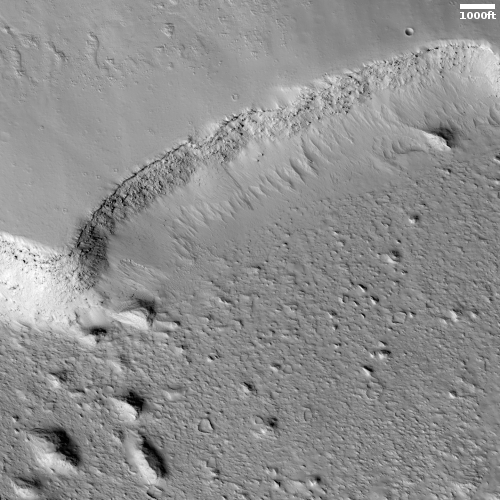
Today’s cool image is a variation of yesterday’s, showing another area on the edge of Mars’ largest volcanic ash field, dubbed the Medusae Fossae Formation and about the size of India. This time however the edge is an abrupt cliff, not the slow petering out of wind-shaped mesas.
The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on August 27, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what I very roughly estimate to be a 1,500 to 2,500 foot high cliff that appears to delineate the edge. To the north we have a plateau of intersperse layers of flood lava and ash. To the south those layers have eroded away, leaving a rough lava plain with a handful of scattered wind-sculpted mesas.
The overview map below, by providing a wider view of his region, makes its nature clearer.
» Read more
Today’s cool image is a variation of yesterday’s, showing another area on the edge of Mars’ largest volcanic ash field, dubbed the Medusae Fossae Formation and about the size of India. This time however the edge is an abrupt cliff, not the slow petering out of wind-shaped mesas.
The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on August 27, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what I very roughly estimate to be a 1,500 to 2,500 foot high cliff that appears to delineate the edge. To the north we have a plateau of intersperse layers of flood lava and ash. To the south those layers have eroded away, leaving a rough lava plain with a handful of scattered wind-sculpted mesas.
The overview map below, by providing a wider view of his region, makes its nature clearer.
» Read more