
Click for full image.
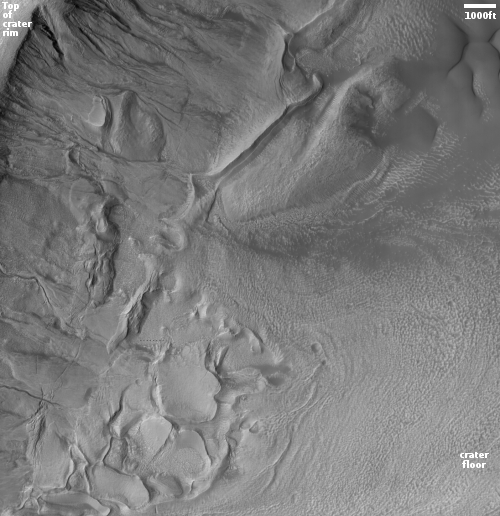
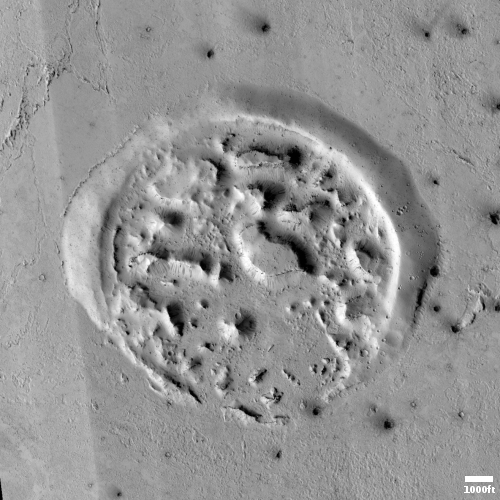
Today’s cool image provides further proof that there is ample near surface ice almost anywhere on Mars once you get above 30 degrees latitude, in either the northern or southern hemispheres. The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and annotated to post here, was taken on May 26, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows the interior slope of an unnamed 15-mile-wide crater that sits inside the much larger 185-mile-wide Newton crater, located in the cratered southern highlands of Mars.
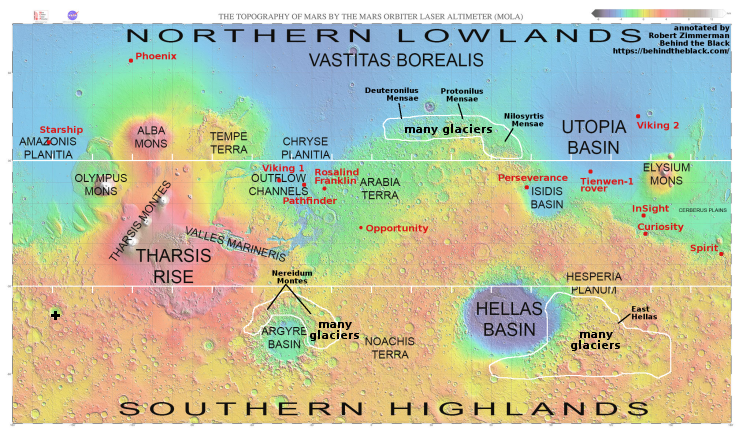
The black cross on the global map of Mars above marks the location of this crater.
The photo was taken as part of the routine monitoring planetary scientists are doing of the gullies that flow down this crater’s interior rim, a monitoring program that goes back to 2007. It is thought that those gullies might be created by seasonal frost, either water ice or dry ice, that causes erosion.
What struck me about the photo however was the glacial features on the floor of the crater. Near the bottom of the interior slope those features look broken up, as if the pressure from above pushed the ice sheets apart. Farther from the interior slope the features more resemble a typical glacial flow, slowly inching downward toward the crater’s low spot. All these glacial features also lend weight to the theory that water ice somehow caused or contributed to the formation of those gullies.
The global map above shows that this crater, while well within the 30 to 60 degrees mid-latitude band where many Martian glaciers are found, is also far from the many regions on Mars that scientists have mapped as having high concentrations of glaciers. And yet, the glacial features are here as well.
Near surface ice will not be found at every spot on Mars. However, once you get above 30 degrees latitude, the evidence increasingly suggests that you won’t have to go far or dig down deep to find it.