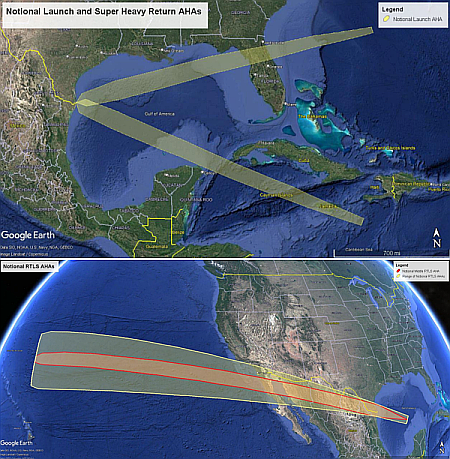
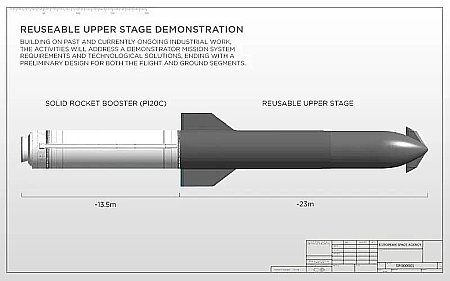
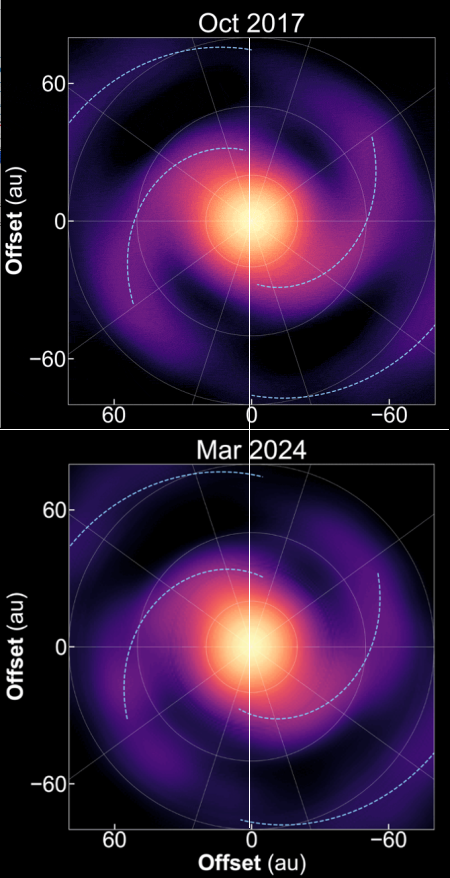
Axiom successfully tests two of its lunar spacesuits underwater

Axiom’s two spacesuits being tested underwater.
Click for original.
The space station startup Axiom this week successfully completed underwater testing of two of its lunar spacesuits, making them ready for astronaut training.
Axiom won the contract to build these suits for NASA in 2022. It speaks well of the company that only three years later the suits are now ready for use. It also shows NASA’s own incompetence, because before it awarded this contract to Axiom the agency tried to build its own suits, spending more than a billion dollars and fourteen years to produce nothing.
Furthermore, this success underlines yesterday’s NASA inspector general report that lambasted Collins Aerospace’s incompetence in maintaining the spacesuits on ISS. Collins in 2022 had won a similar spacesuit contract to build new space station suits, but two years later backed out of the deal, unable to get the job done.
For Axiom, this spacesuit success adds an essential component to its own space station plans. Though these suits are intended for the Moon, the company now has the basics down for its own space station suit. It owns this suit design, and will not only sell suits to NASA, it can market the suits to any one else.

Axiom’s two spacesuits being tested underwater.
Click for original.
The space station startup Axiom this week successfully completed underwater testing of two of its lunar spacesuits, making them ready for astronaut training.
Axiom won the contract to build these suits for NASA in 2022. It speaks well of the company that only three years later the suits are now ready for use. It also shows NASA’s own incompetence, because before it awarded this contract to Axiom the agency tried to build its own suits, spending more than a billion dollars and fourteen years to produce nothing.
Furthermore, this success underlines yesterday’s NASA inspector general report that lambasted Collins Aerospace’s incompetence in maintaining the spacesuits on ISS. Collins in 2022 had won a similar spacesuit contract to build new space station suits, but two years later backed out of the deal, unable to get the job done.
For Axiom, this spacesuit success adds an essential component to its own space station plans. Though these suits are intended for the Moon, the company now has the basics down for its own space station suit. It owns this suit design, and will not only sell suits to NASA, it can market the suits to any one else.