The closest black hole: 1,000 light years away?
The uncertainty of science: Astronomers now think they have detected evidence of a stellar-mass black hole only a thousand light years away and orbiting a star system that is visible to the naked eye.
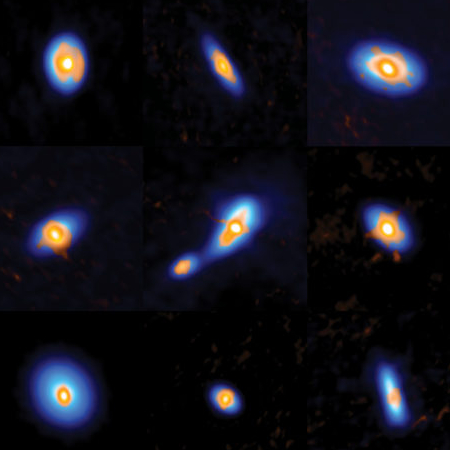
Thomas Rivinius, an astronomer with the European Southern Observatory (ESO), and his colleagues studied the unusual star system HR 6819 in this way using a 2.2-meter telescope in Chile, operated by ESO and the Max Planck Society. They thought it was a binary system, but there was an extra wobble in the periodic light shifts of one of the stars that indicated something else was asserting its presence. It turned out to be a triple system, with one star in a fast 40-day orbit with an unseen companion and another star on a more distant, slow-moving trajectory, they write today in Astronomy & Astrophysics. The invisible companion’s mass was large enough—four times the mass of the Sun—that, if it was a star, “we would have seen it,” Rivinius says.
Though there are a lot of uncertainties, this discovery is reasonable, and expected. In the coming years astronomers will surely find more such stellar-mass black holes, with some even closer to Earth.
The uncertainty of science: Astronomers now think they have detected evidence of a stellar-mass black hole only a thousand light years away and orbiting a star system that is visible to the naked eye.
Thomas Rivinius, an astronomer with the European Southern Observatory (ESO), and his colleagues studied the unusual star system HR 6819 in this way using a 2.2-meter telescope in Chile, operated by ESO and the Max Planck Society. They thought it was a binary system, but there was an extra wobble in the periodic light shifts of one of the stars that indicated something else was asserting its presence. It turned out to be a triple system, with one star in a fast 40-day orbit with an unseen companion and another star on a more distant, slow-moving trajectory, they write today in Astronomy & Astrophysics. The invisible companion’s mass was large enough—four times the mass of the Sun—that, if it was a star, “we would have seen it,” Rivinius says.
Though there are a lot of uncertainties, this discovery is reasonable, and expected. In the coming years astronomers will surely find more such stellar-mass black holes, with some even closer to Earth.