The coming April 8, 2024 total eclipse
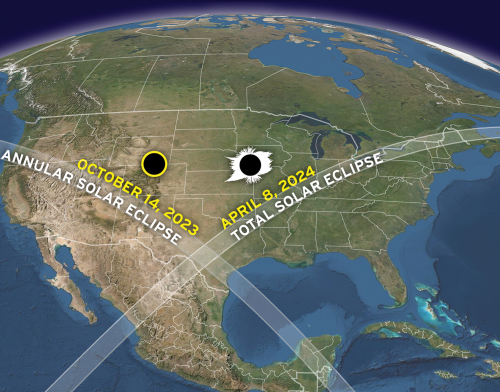
Map by Michael Zeiler (GreatAmericanEclipse.com). Click for original.
On April 8, 2024 a large swath of the United States, from Texas to Maine, will have the opportunity to witness personally a total eclipse of the Sun by the Moon.
If you have never experienced a total eclipse, then you must do whatever you can to see this event, since the next eclipse within the United States will not happen again until 2044. Diane and I made a special trip to Idaho Falls, Idaho in 2017 to see that eclipse, and without doubt it was an experience that is difficult to describe. As I wrote afterward:
Totality was amazing. I was amazed by two things. First, how quiet it became. There were about hundred people scattered about the hotel lawn, with dogs and kids playing around. The hotel manager’s husband set up speakers for music and to make announcements, but when totality arrived he played nothing. People stopped talking. A hush fell over everything. Moreover, I think we somehow imagine a subconscious roar from the full sun. Covered as it was, with its soft corona gleaming gently around it, it suddenly seemed still.
Secondly, the amazing unlikeliness of the Moon being at just the right distance and size to periodically cause this event seemed almost miraculous. Watching it happen drove this point home to me. And since eclipses themselves have been a critical event in the intellectual development of humanity, helping to drive learning and our understanding of the universe, it truly makes me wonder at the majesty of it. I do not believe in any particular religion or their rituals (though I consider the Bible, the Old Testament especially, to be a very good manual for creating a good life and society), but I do not deny the existence of a higher power. Something made this place, and set it up in this wonderous way. Today’s eclipse only served to demonstrate this fact to me again.

Map by Michael Zeiler (GreatAmericanEclipse.com). Click for original.
On April 8, 2024 a large swath of the United States, from Texas to Maine, will have the opportunity to witness personally a total eclipse of the Sun by the Moon.
If you have never experienced a total eclipse, then you must do whatever you can to see this event, since the next eclipse within the United States will not happen again until 2044. Diane and I made a special trip to Idaho Falls, Idaho in 2017 to see that eclipse, and without doubt it was an experience that is difficult to describe. As I wrote afterward:
Totality was amazing. I was amazed by two things. First, how quiet it became. There were about hundred people scattered about the hotel lawn, with dogs and kids playing around. The hotel manager’s husband set up speakers for music and to make announcements, but when totality arrived he played nothing. People stopped talking. A hush fell over everything. Moreover, I think we somehow imagine a subconscious roar from the full sun. Covered as it was, with its soft corona gleaming gently around it, it suddenly seemed still.
Secondly, the amazing unlikeliness of the Moon being at just the right distance and size to periodically cause this event seemed almost miraculous. Watching it happen drove this point home to me. And since eclipses themselves have been a critical event in the intellectual development of humanity, helping to drive learning and our understanding of the universe, it truly makes me wonder at the majesty of it. I do not believe in any particular religion or their rituals (though I consider the Bible, the Old Testament especially, to be a very good manual for creating a good life and society), but I do not deny the existence of a higher power. Something made this place, and set it up in this wonderous way. Today’s eclipse only served to demonstrate this fact to me again.