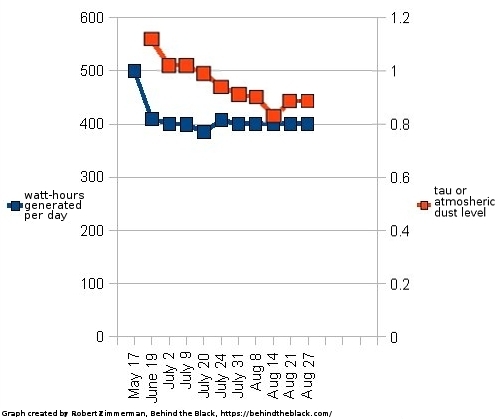
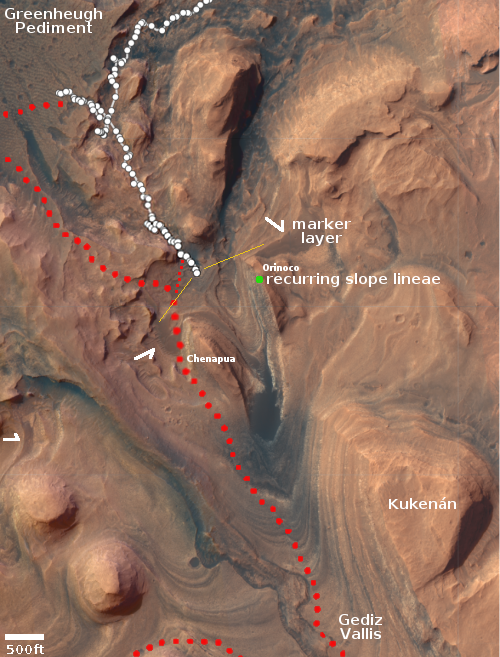
Perseverance: Evidence of both past lava and liquid water on the floor of Jezero Crater
Two new papers (here and here), published last week in Science and using data obtained during Perseverance’s first year of roving on Mars, strongly suggest that the floor of Jezero Crater was first formed by lava flows, either from impact or later flows from eruptions, followed by a period where liquid water interacted with these igneous materials to produce the chemistry seen today. From the first paper:
After emplacement of the igneous rocks on the crater floor, multiple forms of aqueous interaction modified—but did not destroy—their igneous mineralogy, composition, and texture. Evidence for alteration includes the presence of carbonate in the Séítah abrasion patches, the iron oxides in the Máaz formation abrasion patches (which we presume are due to iron mobilization and precipitation), and the deposition of salts including sulfates and perchlorate. More broadly, the appearance of possible spheroidal weathering textures suggests that aqueous alteration played a role in rock disintegration.
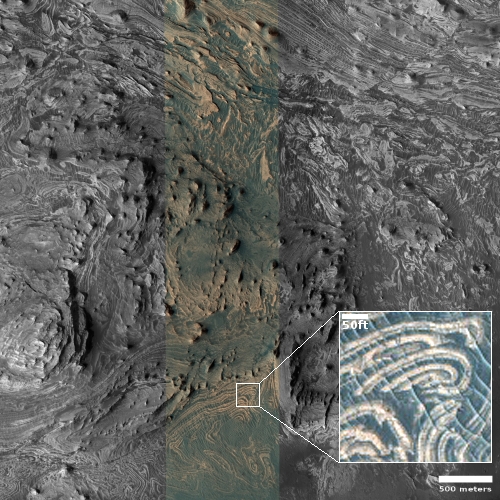
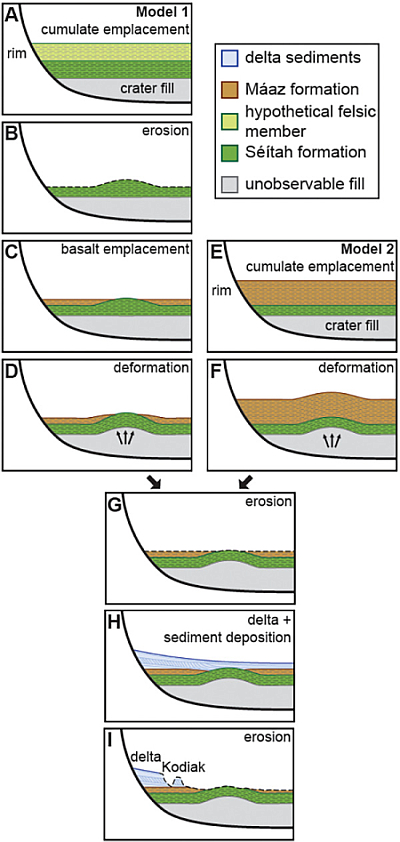
The graphic to the right, figure 6 in the first paper, shows two different models for the geological formation of the floor of Jezero Crater. “Basalt emplacement” are the lava flows.
According to the press release today [pdf], the first core samples that the rover gathered for later pickup and return to Earth will likely show the following:
The salts include sulfates, similar to Epsom salts, which are common on Mars. Most importantly, high levels of chlorine-containing salts are also present, such as chlorides (“table salt”) and perchlorates. These highly soluble salts reveal that the rocks were soaked in brines, and hence contain clear evidence of liquid water.
The on-going big geological mystery of Mars remains. The data suggests liquid water once existed as some form in Jezero Crater. Other data suggests liquid water existed elsewhere on Mars as well. Yet, no model exists that anyone accepts with any confidence that makes it possible for liquid water to exist on the Martian surface. Its atmosphere has always been either too cold or thin.
To underline this conundrum, note that in the graphic above, neither model includes a time period when liquid water sat on top of these layers. Though the evidence calls for liquid water at some time, the scientists do not feel confident enough to include it in these initial models.
One possible explanation that I sense some scientists are beginning to consider is the chemical interaction of melted ice at the base of past long gone ice glaciers. The ice would be frozen, but the glacier’s movement might create pockets of liquid water at its base, which over eons might result in these chemical reactions. If Jezero Crater had once been filled with glaciers, as many Martian craters in the mid-latitudes appear to be now, this could have provided the water necessary for the chemical modifications the scientists are finding.
This theory however is entirely speculative on my part, and has not yet been proposed by any scientists, though I have seen hints of it in a number of different research papers.

Two new papers (here and here), published last week in Science and using data obtained during Perseverance’s first year of roving on Mars, strongly suggest that the floor of Jezero Crater was first formed by lava flows, either from impact or later flows from eruptions, followed by a period where liquid water interacted with these igneous materials to produce the chemistry seen today. From the first paper:
After emplacement of the igneous rocks on the crater floor, multiple forms of aqueous interaction modified—but did not destroy—their igneous mineralogy, composition, and texture. Evidence for alteration includes the presence of carbonate in the Séítah abrasion patches, the iron oxides in the Máaz formation abrasion patches (which we presume are due to iron mobilization and precipitation), and the deposition of salts including sulfates and perchlorate. More broadly, the appearance of possible spheroidal weathering textures suggests that aqueous alteration played a role in rock disintegration.
The graphic to the right, figure 6 in the first paper, shows two different models for the geological formation of the floor of Jezero Crater. “Basalt emplacement” are the lava flows.
According to the press release today [pdf], the first core samples that the rover gathered for later pickup and return to Earth will likely show the following:
The salts include sulfates, similar to Epsom salts, which are common on Mars. Most importantly, high levels of chlorine-containing salts are also present, such as chlorides (“table salt”) and perchlorates. These highly soluble salts reveal that the rocks were soaked in brines, and hence contain clear evidence of liquid water.
The on-going big geological mystery of Mars remains. The data suggests liquid water once existed as some form in Jezero Crater. Other data suggests liquid water existed elsewhere on Mars as well. Yet, no model exists that anyone accepts with any confidence that makes it possible for liquid water to exist on the Martian surface. Its atmosphere has always been either too cold or thin.
To underline this conundrum, note that in the graphic above, neither model includes a time period when liquid water sat on top of these layers. Though the evidence calls for liquid water at some time, the scientists do not feel confident enough to include it in these initial models.
One possible explanation that I sense some scientists are beginning to consider is the chemical interaction of melted ice at the base of past long gone ice glaciers. The ice would be frozen, but the glacier’s movement might create pockets of liquid water at its base, which over eons might result in these chemical reactions. If Jezero Crater had once been filled with glaciers, as many Martian craters in the mid-latitudes appear to be now, this could have provided the water necessary for the chemical modifications the scientists are finding.
This theory however is entirely speculative on my part, and has not yet been proposed by any scientists, though I have seen hints of it in a number of different research papers.