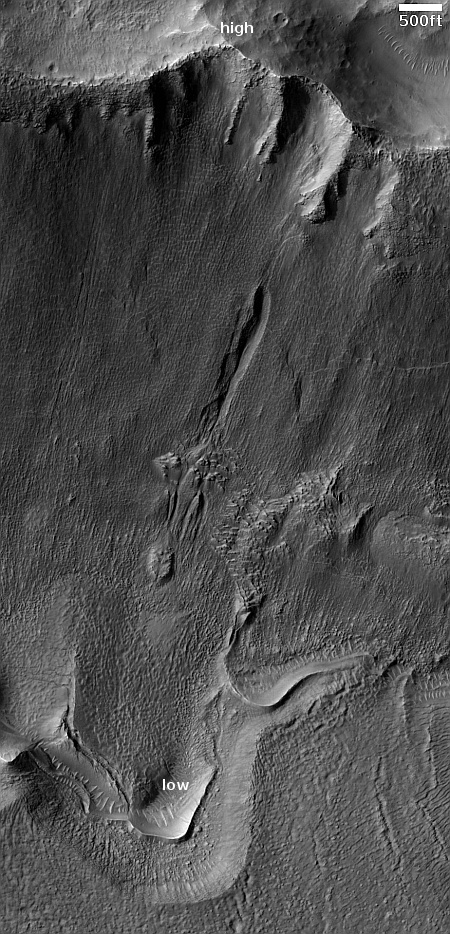
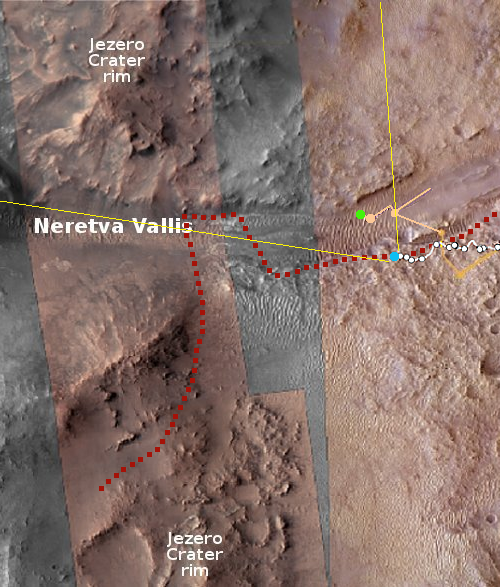
Click for original image.
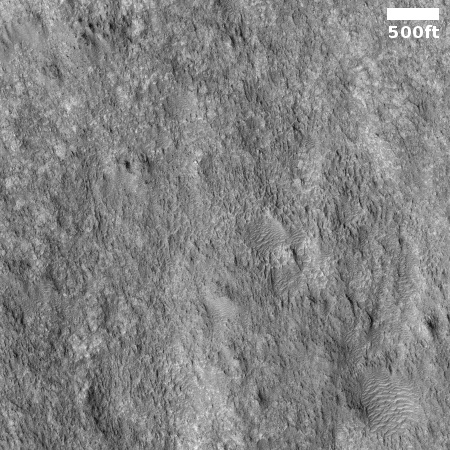
We now know why SLIM’s solar panel was not facing the Sun after the Japanese lunar lander touched down. When it was only 10 to 15 feet above the ground, preparing to land, one of its two descent engines failed, causing the spacecraft to tumble as it softly touched down. As a result, it landed softly, but upside down, thus putting the panel on its west side instead of its east side as planned.
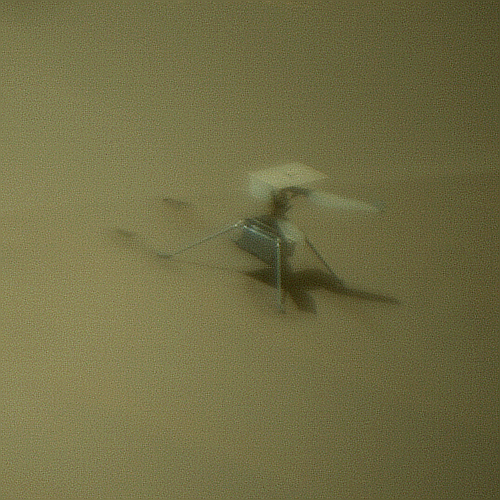
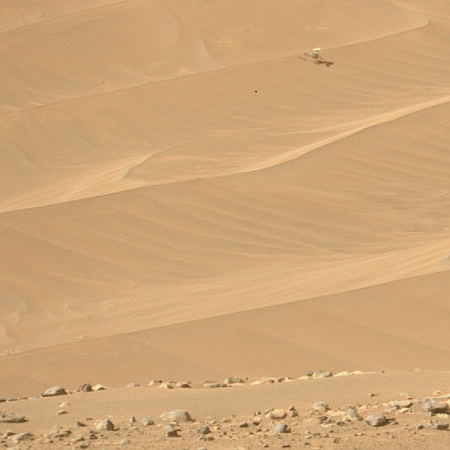
The image to the right, cropped to post here, was taken by one of the two tiny rovers released by SLIM just prior to landing. It shows SLIM upside down, but essentially undamaged.
The lander however still apparently achieved its primary goal, landing within a small zone only 300 feet across, or 100 meters.
Analysis of the data acquired before shutting down the power confirmed that SLIM had reached the Moon’s surface approximately 55m east (180 feet) of the original target landing site. The positional accuracy before the commencement of the obstacle avoidance maneuver (at around a 50m altitude) which indicates the pinpoint landing performance, was evaluated to be at approximately 10m or less, possibly about 3 – 4m.
…Under these circumstances, the SLIM onboard software autonomously identifies the anomaly, and while controlling the horizontal position as much as possible, SLIM continued the descent with the other engine and moved gradually towards the east. The descent velocity at the time of contact with the ground was approximately 1.4 m/s or less, which was below the design range., but conditions such as the lateral velocity and attitude were outside the design range, and this is thought to have resulted in a different attitude than planned.
In other words, when that engine failed, SLIM was only about 10 to 30 feet from its pinpoint landing target, but then drifted eastward as its dropped those last few feet because of the unbalanced engine burn caused by only one engine.
That the spacecraft is still operating and can communicate with Earth, even though it is upside down, is remarkable. Moreover, SLIM did achieve its main goals quite successfully. It landed within its tight target zone, it released two mini-rovers which operated successfully, and has been able to send its own pictures back to Earth. It was not able however to test its crushable landing legs, as they remain in the air.