The prevailing winds in Mars’ volcano country
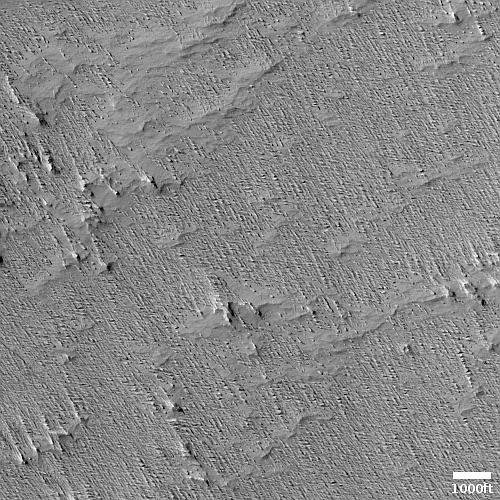
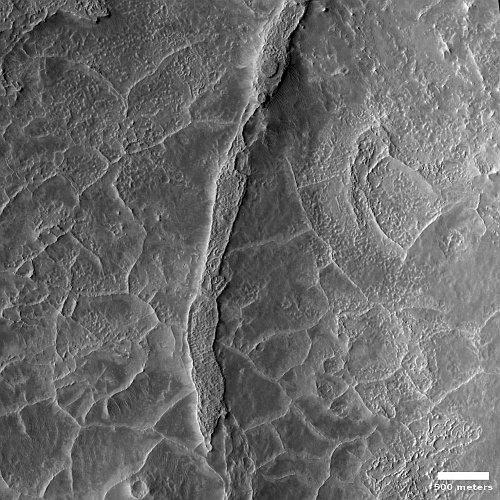
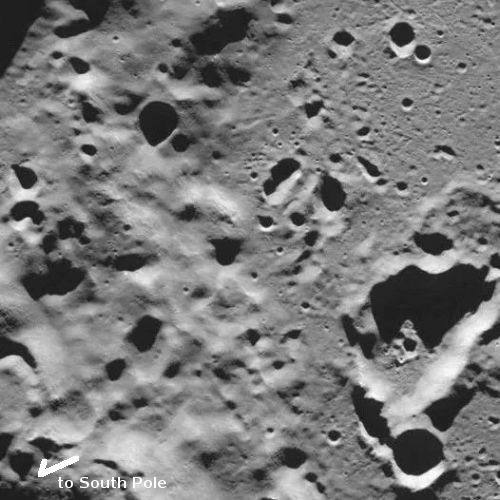
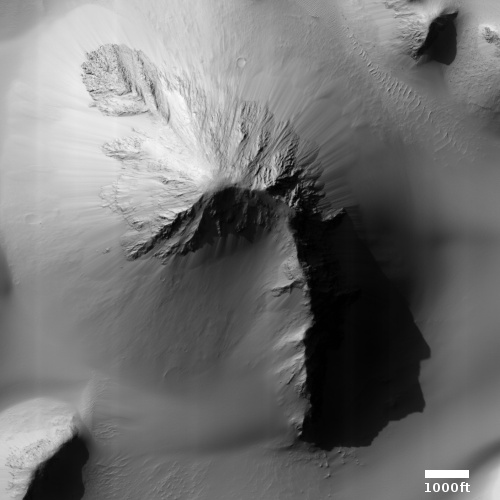
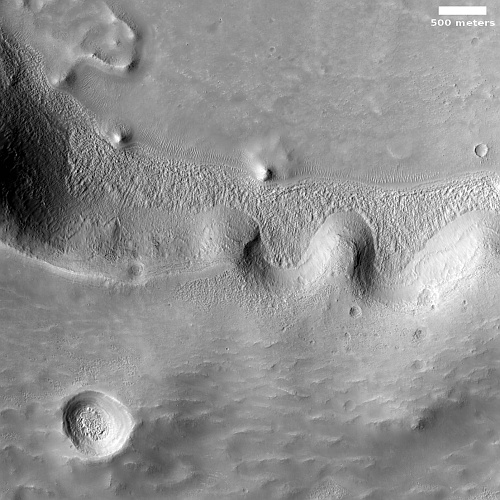
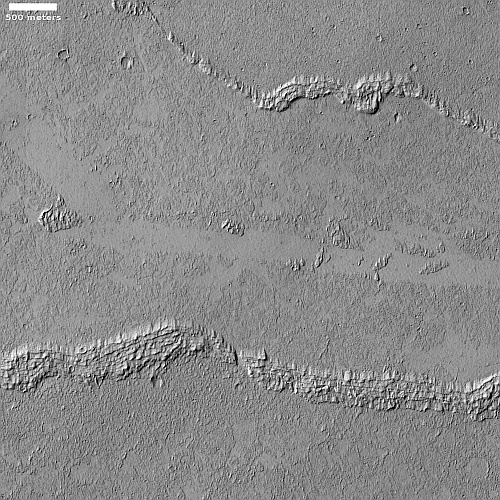
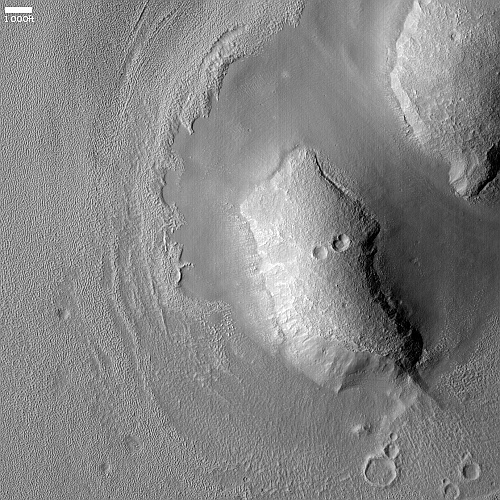
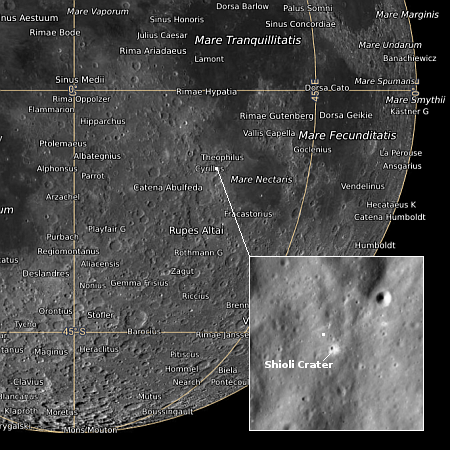
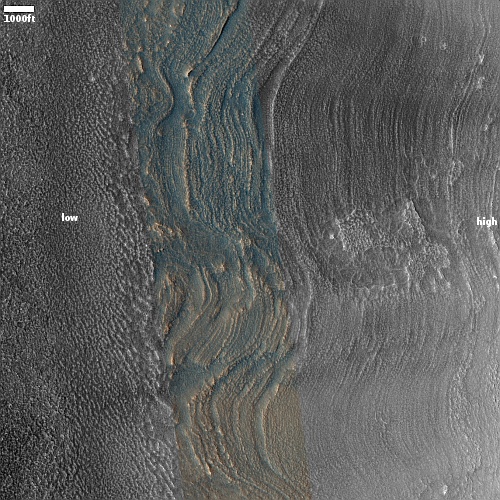
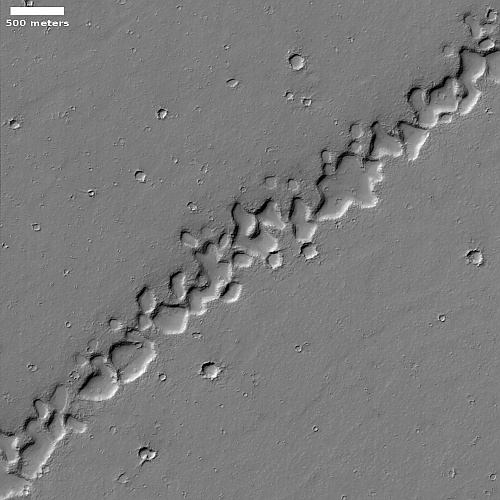
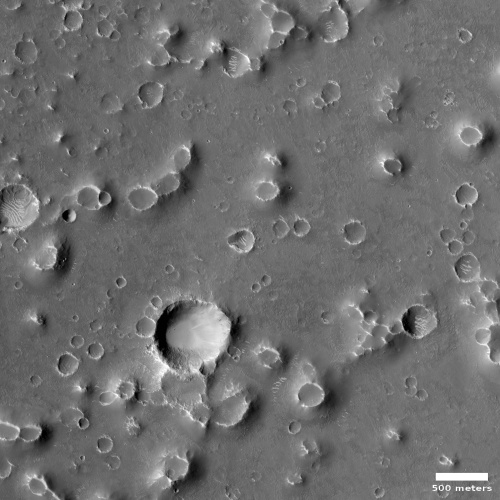
Today’s cool image is actual one new picture and four past images, which taken together reveal something about the larger wind patterns on Mars. The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on June 27, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and shows a tiny wind-swept section of the giant volcanic ash field dubbed the Medusae Fossae Formation, about the size of the subcontinent of India and thought to be source of most of the dust on Mars.
The innumerable parallel thin ridges here all suggest that the prevailing winds blow from the southeast to the northwest. As they blow, the scour the surface ash out, and sometimes reveal the underlying bedrock, which here shows up as those small peaks and a handful of northeast-to-southwest trending larger ridges. Note too that the picture shown is only a small section of the full image, which shows that this landscape continues for a considerable distance in all directions.
» Read more
Today’s cool image is actual one new picture and four past images, which taken together reveal something about the larger wind patterns on Mars. The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on June 27, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and shows a tiny wind-swept section of the giant volcanic ash field dubbed the Medusae Fossae Formation, about the size of the subcontinent of India and thought to be source of most of the dust on Mars.
The innumerable parallel thin ridges here all suggest that the prevailing winds blow from the southeast to the northwest. As they blow, the scour the surface ash out, and sometimes reveal the underlying bedrock, which here shows up as those small peaks and a handful of northeast-to-southwest trending larger ridges. Note too that the picture shown is only a small section of the full image, which shows that this landscape continues for a considerable distance in all directions.
» Read more