Musk: Next Starship/Superheavy test launch in mid-March
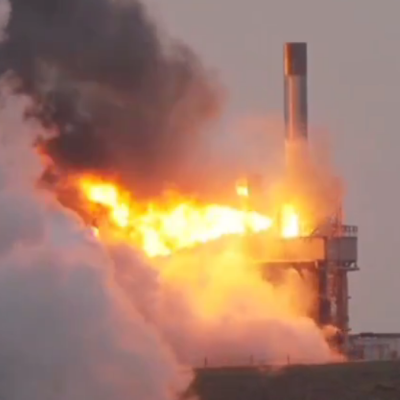
According to a recent tweet by Elon Musk , the next Starship/Superheavy test launch will occur “in 6 weeks,” placing that launch sometime in mid-March.
Musk provided no other information, but this announcement suggests the company’s engineers now understand and have corrected the issues that caused two Superheavy ruptures during two different tank tests in recent weeks. It also suggests that the launchpad repairs and upgrades will soon be completed, and that a new version 3 Superheavy prototype is ready to go, replacing one that was damaged during those tank tests.
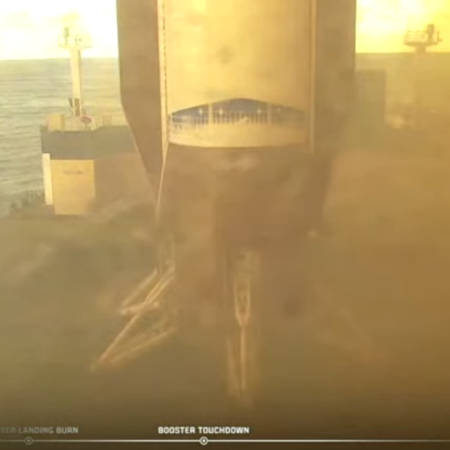
The mission specifics however remain unclear. SpaceX could repeat the flight path of the last few tests, in an orbit low enough so that the atmosphere will bring Starship down over the Indian Ocean. In such a flight the company would test refueling within Starship, restarts of its Raptor engines, and deployment of dummy or even real Starlink satellites.
It is possible however that this next test flight will go into a full orbit, and circle the Earth once or several times. SpaceX has said that in 2026 it intends to do a Starship refueling test using two Starships, launched several weeks apart. To do this more ambitious mission however it first needs to do at least one full orbital flight of Starship. Since the company has already tested on previous orbital test flights the restart of Starship’s Raptor engines — proving its capability to do a controlled re-entry — there really is no reason it can’t go for a full orbit on the next flight. There is even the possibility that Starship will come back to Boca Chica and be caught the company’s tower chopsticks, though this remains unconfirmed.
According to a recent tweet by Elon Musk , the next Starship/Superheavy test launch will occur “in 6 weeks,” placing that launch sometime in mid-March.
Musk provided no other information, but this announcement suggests the company’s engineers now understand and have corrected the issues that caused two Superheavy ruptures during two different tank tests in recent weeks. It also suggests that the launchpad repairs and upgrades will soon be completed, and that a new version 3 Superheavy prototype is ready to go, replacing one that was damaged during those tank tests.
The mission specifics however remain unclear. SpaceX could repeat the flight path of the last few tests, in an orbit low enough so that the atmosphere will bring Starship down over the Indian Ocean. In such a flight the company would test refueling within Starship, restarts of its Raptor engines, and deployment of dummy or even real Starlink satellites.
It is possible however that this next test flight will go into a full orbit, and circle the Earth once or several times. SpaceX has said that in 2026 it intends to do a Starship refueling test using two Starships, launched several weeks apart. To do this more ambitious mission however it first needs to do at least one full orbital flight of Starship. Since the company has already tested on previous orbital test flights the restart of Starship’s Raptor engines — proving its capability to do a controlled re-entry — there really is no reason it can’t go for a full orbit on the next flight. There is even the possibility that Starship will come back to Boca Chica and be caught the company’s tower chopsticks, though this remains unconfirmed.