The long delay in Israel’s final Gaza offensive has harmed everyone except the terrorists
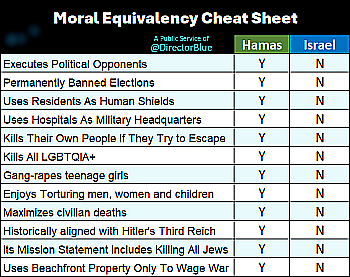
Even the Arabs recognize these facts.
Courtesy of Doug Ross.
Despite several months of delay forced on it by the Biden administration in its effort to placate the Democratic Party’s Islamic wing, Israel today began its final offensive against Hamas’s last Gazan stronghold in the southern city of Rafah.
According to the Israeli Defense Force (IDF), “The IDF is currently conducting targeted strikes against Hamas terror targets in eastern Rafah in southern Gaza.” It has also dropped leaflets throughout Rafah telling the general population to evacuate to the west and north into areas that Israel has set up to hold non-combatant refugees.
The initiation of this offensive is likely linked to Hamas’s actions this weekend. First Hamas proudly took credit for bombing the border crossing used to bring humanitarian aid to the city. That attack killed three Israeli soldiers, and put an end to the aid. Hamas also continued to stall and refuse to negotiate, and then when it was clear the offensive was about to start it suddenly announced it had accepted a ceasefire deal offered to it by Qatar and Egypt that Israel had no part in negotiating and had already rejected.
What will happen next is somewhat unclear. Israel will without doubt be able to take Rafah and likely eliminate the remaining four or so battalions of Hamas terrorists. Will it be able to do so without a large number of civilian casualties is unclear, as Hamas has a policy of using those civilians as shields. It will likely try to do so again.
The ramifications of the long delay in this offensive are however important. It occurred partly because Israel’s army wanted to regroup, but mostly because the Biden administration has been desperately trying to prevent it. The White House has threatened Israel in a number of ways if it moved forward with the attack, most recently by putting a hold on a shipment to Israel of ammo. Biden officials have also stated several times that they are considering a major change in its policy towards Israel if the Rafah offensive occurs.
Israel’s leader Benjamin Netanyahu has repeatedly made it clear that Israel has no intention of making any peace deal with Hamas. In the past month however it did appear the Israeli government was holding off on the offensive in order to placate the White House and hopefully work out a deal to get the hostages released.
In the end, the delay has served no good purpose, and in fact has had many negative consequences, against Biden, the Gazan people themselves, and the United States.
» Read more