A giant elliptical galaxy
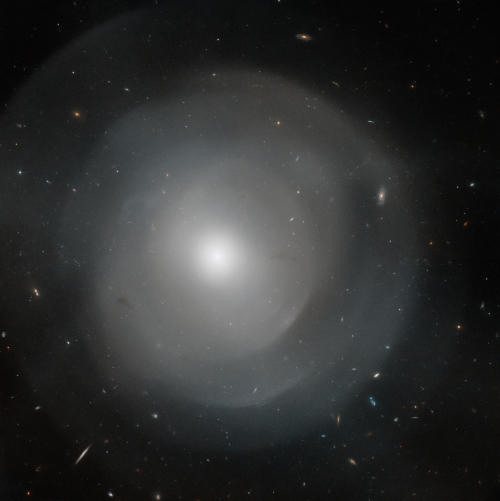
Cool image time! The image to the right, reduced to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope of the giant elliptical galaxy NGC 474.
Located some 100 million light-years from Earth, NGC 474 spans about 250,000 light-years across – that’s 2.5 times larger than our own Milky Way galaxy! Along with its enormous size, NGC 474 has a series of complex layered shells that surround its spherical-shaped core. The cause of these shells is unknown, but astronomers theorize that they may be the aftereffects of the giant galaxy absorbing one or more smaller galaxies. In the same way a pebble creates ripples on a pond when dropped into the water, the absorbed galaxy creates waves that form the shells.
About 10% of elliptical galaxies have shell structures, but unlike the majority of elliptical galaxies, which are associated with galaxy clusters, shelled ellipticals usually lie in relatively empty space. It may be that they’ve cannibalized their neighbors.
NGC 474 is no exception, also located in a relatively empty region of space.
Cool image time! The image to the right, reduced to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope of the giant elliptical galaxy NGC 474.
Located some 100 million light-years from Earth, NGC 474 spans about 250,000 light-years across – that’s 2.5 times larger than our own Milky Way galaxy! Along with its enormous size, NGC 474 has a series of complex layered shells that surround its spherical-shaped core. The cause of these shells is unknown, but astronomers theorize that they may be the aftereffects of the giant galaxy absorbing one or more smaller galaxies. In the same way a pebble creates ripples on a pond when dropped into the water, the absorbed galaxy creates waves that form the shells.
About 10% of elliptical galaxies have shell structures, but unlike the majority of elliptical galaxies, which are associated with galaxy clusters, shelled ellipticals usually lie in relatively empty space. It may be that they’ve cannibalized their neighbors.
NGC 474 is no exception, also located in a relatively empty region of space.