Curiosity looks uphill at its upcoming travels
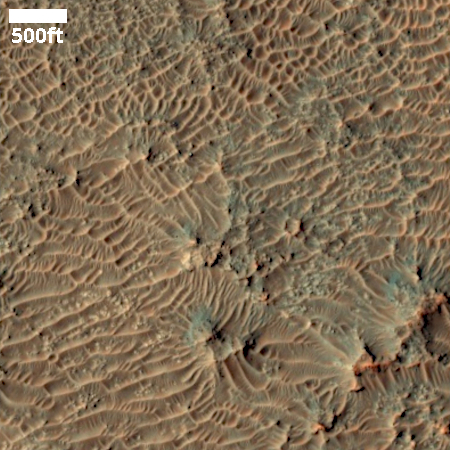
Cool image time! Since May 2025 Curiosity has been exploring in great detail the boxwork formations located on the lower slopes of Mount Sharp. It is now about to complete those investigations, with the Curiosity science team beginning their planning for moving onward and upward.
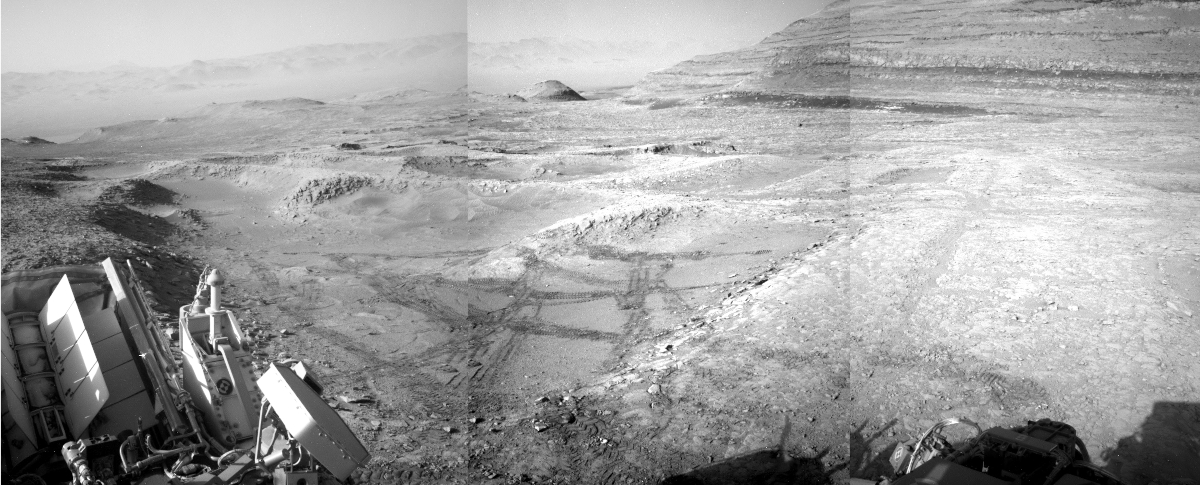
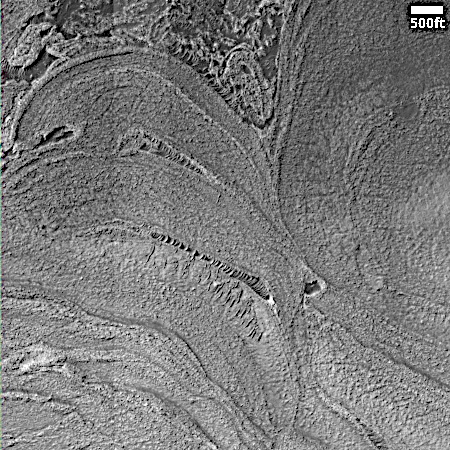
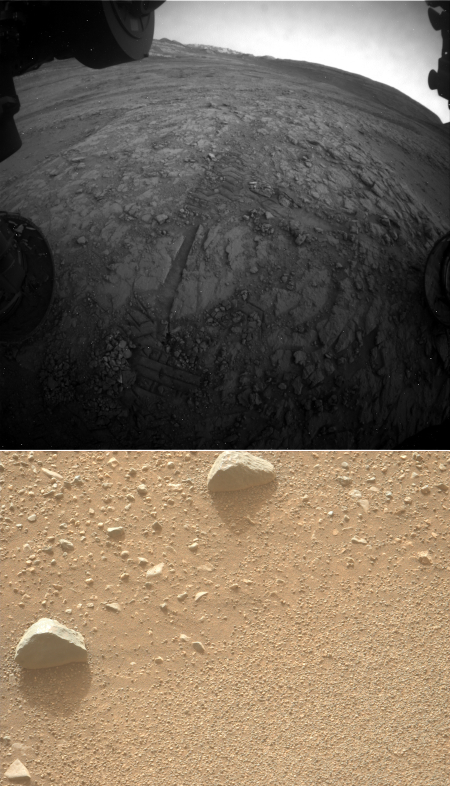
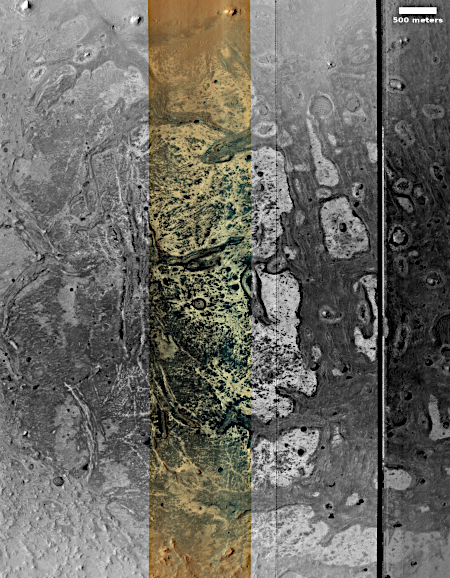
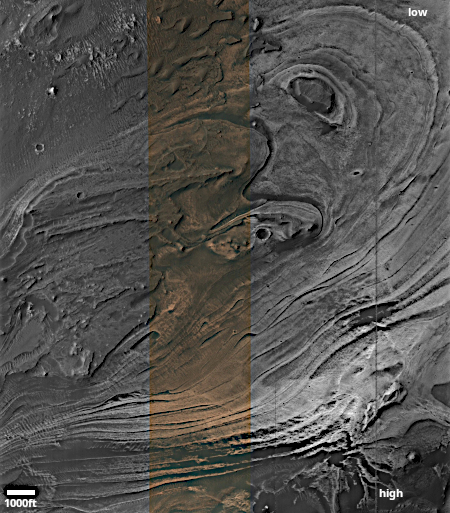
The panorama above, enhanced to post here, was taken on March 2, 2026 by the rover’s right navigation camera. It looks uphill along the valley that Curiosity is in toward the mountainous region the rover is targeting. Note that the peak of Mount Sharp is not visible, being more than 25 miles away beyond the horizon and about 15,000 feet higher up.
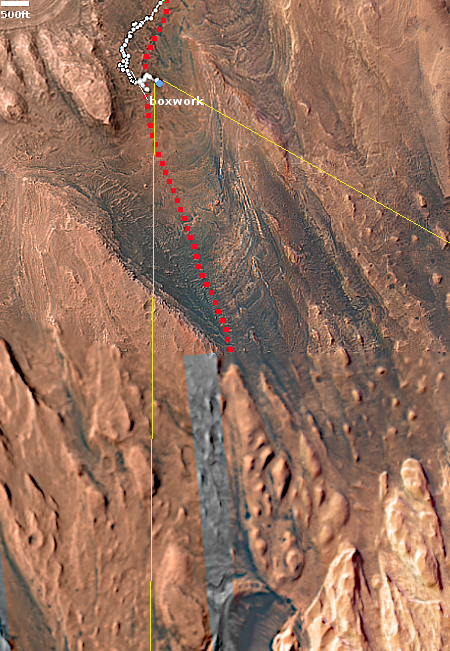
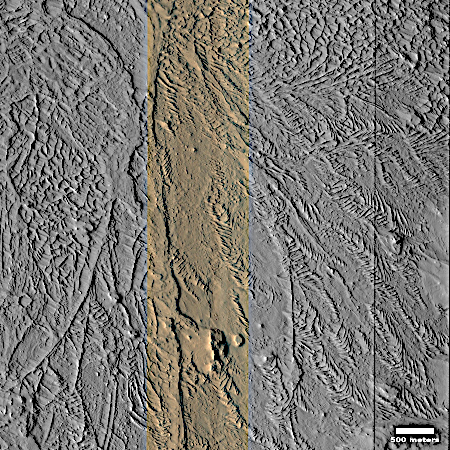
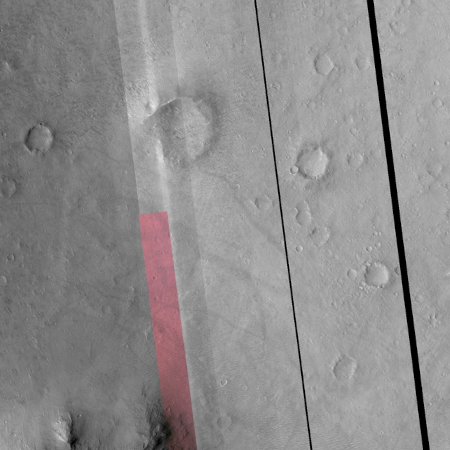
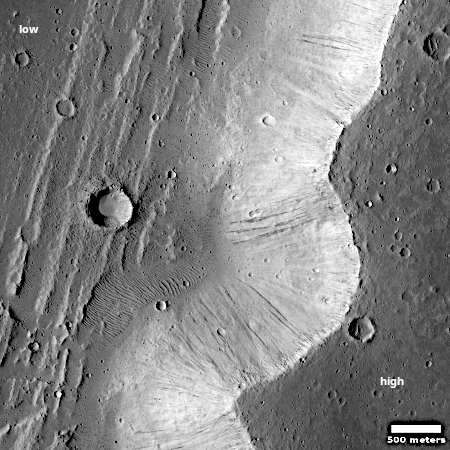
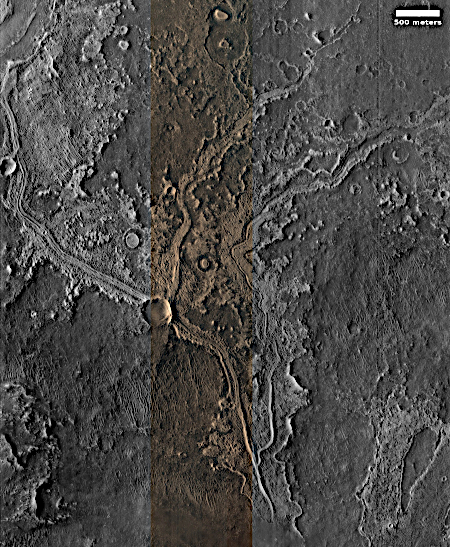
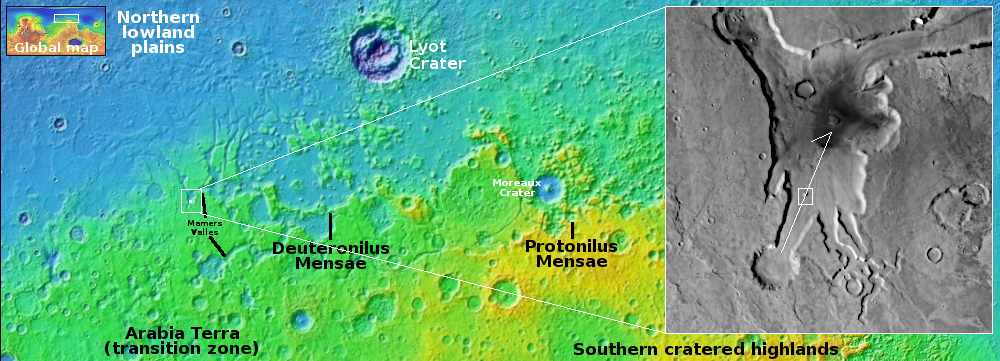
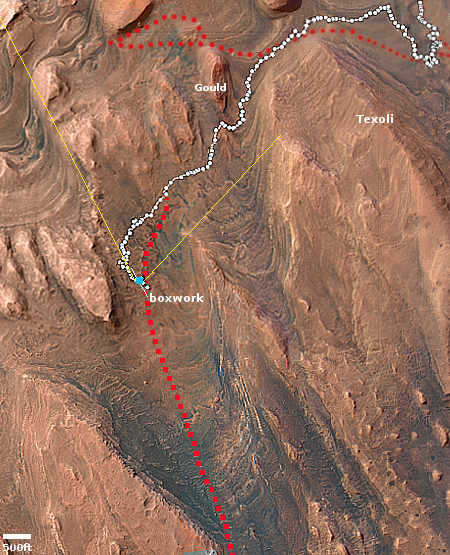
The blue dot on the overview map to the right mark Curiosity’s present position. The yellow lines indicate roughly the area this panorama covers. The red dotted line marks the rover’s approximate planned route, while the white dotted line indicates Curiosity’s actually travels.
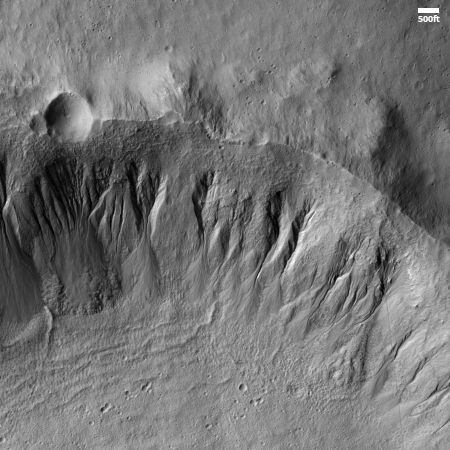
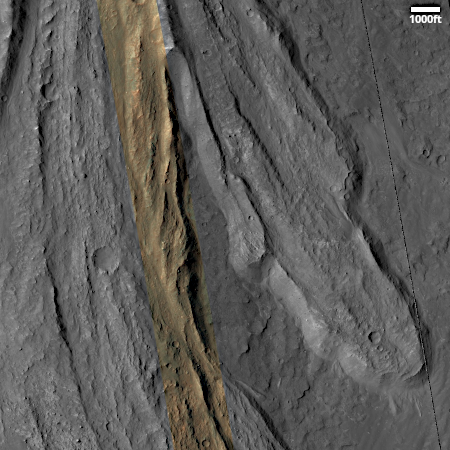
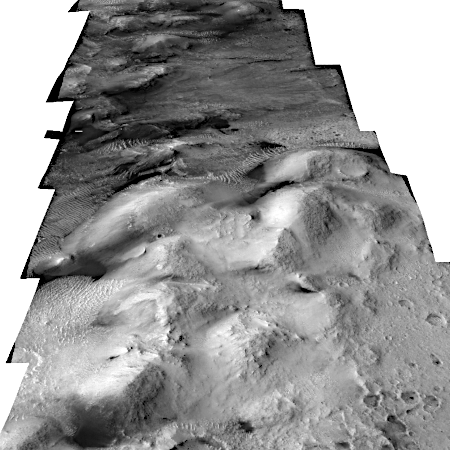
Right now Curiosity is traveling through a geological layer the scientists have dubbed the sulfate unit. The lighter colored hills seen on the horizon have also been identified as sulfate, but believed to be much more pure. The geology there should be very different. Instead of rough and rocky it could be like traveling over soft porous sand. This however is merely a guess on my part, based on imagery of those light-colored hills.
The actual route through those hills however remains unknown. Either the science team has not yet released it, or is still trying to figure out the best way through.
Cool image time! Since May 2025 Curiosity has been exploring in great detail the boxwork formations located on the lower slopes of Mount Sharp. It is now about to complete those investigations, with the Curiosity science team beginning their planning for moving onward and upward.
The panorama above, enhanced to post here, was taken on March 2, 2026 by the rover’s right navigation camera. It looks uphill along the valley that Curiosity is in toward the mountainous region the rover is targeting. Note that the peak of Mount Sharp is not visible, being more than 25 miles away beyond the horizon and about 15,000 feet higher up.
The blue dot on the overview map to the right mark Curiosity’s present position. The yellow lines indicate roughly the area this panorama covers. The red dotted line marks the rover’s approximate planned route, while the white dotted line indicates Curiosity’s actually travels.
Right now Curiosity is traveling through a geological layer the scientists have dubbed the sulfate unit. The lighter colored hills seen on the horizon have also been identified as sulfate, but believed to be much more pure. The geology there should be very different. Instead of rough and rocky it could be like traveling over soft porous sand. This however is merely a guess on my part, based on imagery of those light-colored hills.
The actual route through those hills however remains unknown. Either the science team has not yet released it, or is still trying to figure out the best way through.