Ingenuity completes 19th flight
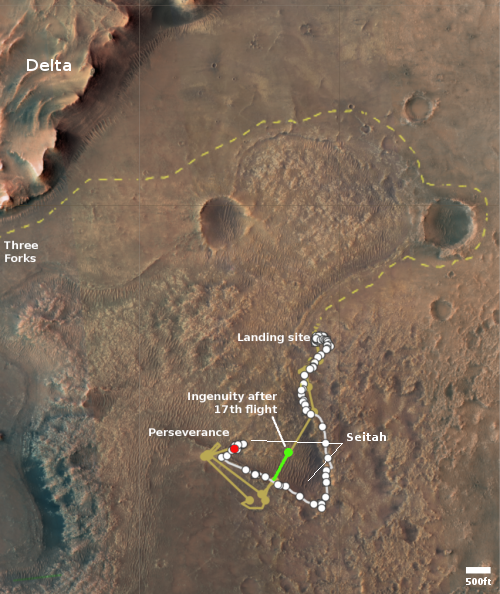
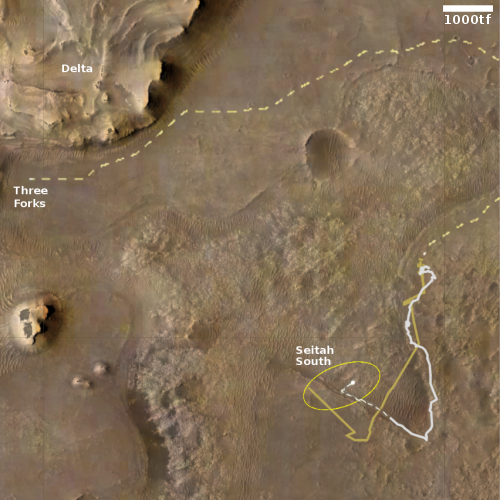
The Mars helicopter Ingenuity yesterday successfully completed its 19th flight on the Martian surface, traveling for 99 seconds about 200 feet to the northeast, landing close to the landing site of its 8th flight back in June 2021.
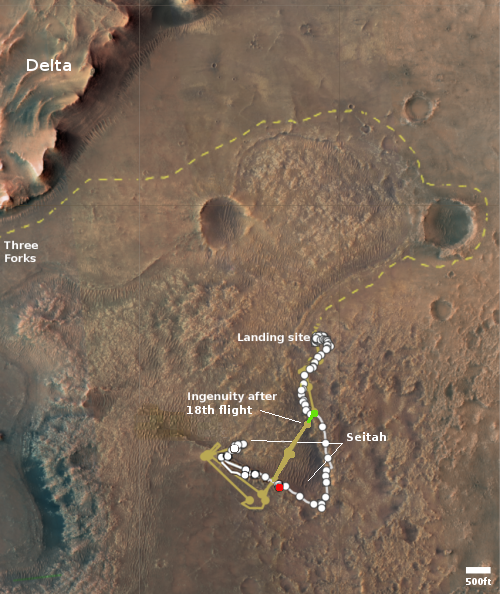
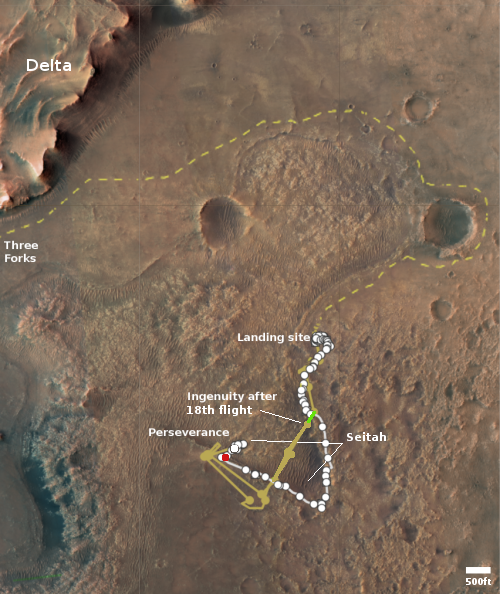
The map to the right shows the helicopter’s overall travels in tan, with the 19th flight path in green. The white line marks Perseverance’s travels, with the red dot indicating its present location. The dashed yellow line indicates the rover’s planned route. To achieve that the rover team is retracing its steps along the path it had previously traveled, with Ingenuity flying in front, along that path.
The flight had been delayed more than a month while waiting for a dust storm to settle as well as making sure Perseverance was in a good position to maintain communications throughout the flight. With Perseverance finally on the move to the east and the dust storm subsiding, the Ingenuity flight was finally possible.
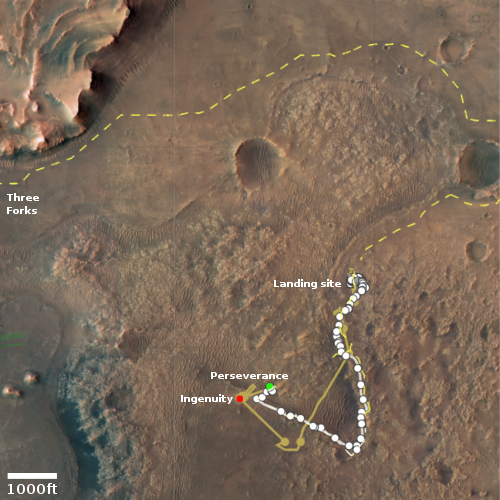
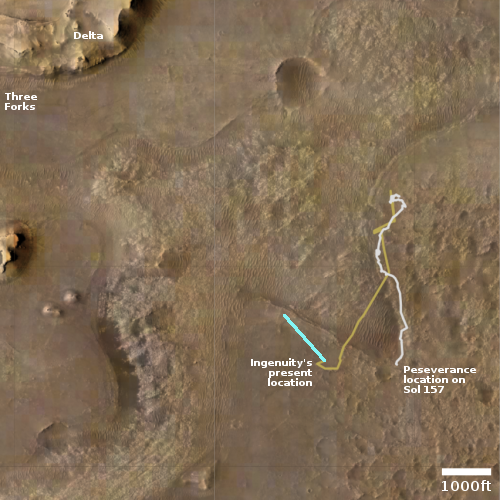
The Mars helicopter Ingenuity yesterday successfully completed its 19th flight on the Martian surface, traveling for 99 seconds about 200 feet to the northeast, landing close to the landing site of its 8th flight back in June 2021.
The map to the right shows the helicopter’s overall travels in tan, with the 19th flight path in green. The white line marks Perseverance’s travels, with the red dot indicating its present location. The dashed yellow line indicates the rover’s planned route. To achieve that the rover team is retracing its steps along the path it had previously traveled, with Ingenuity flying in front, along that path.
The flight had been delayed more than a month while waiting for a dust storm to settle as well as making sure Perseverance was in a good position to maintain communications throughout the flight. With Perseverance finally on the move to the east and the dust storm subsiding, the Ingenuity flight was finally possible.