Kepler’s first discovered exoplanet is spiraling into its aging star
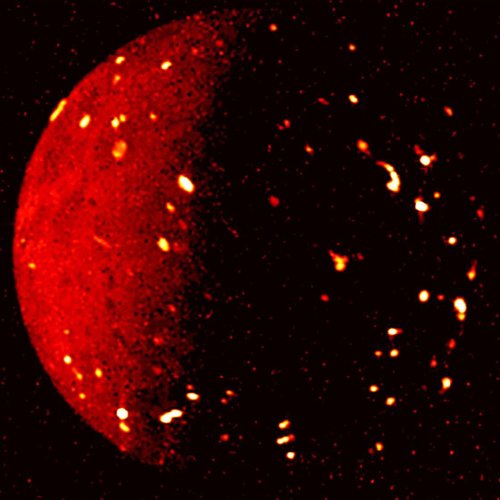
Measurements of the orbit of first exoplanet discovered by the Kepler space telescope have determined that its orbit is very slowly shrinking, and that it will eventually spiral into its aging sun.
In the case of Kepler-1658b, according to the new study, its orbital period is decreasing at the miniscule rate of about 131 milliseconds (thousandths of a second) per year, with a shorter orbit indicating the planet has moved closer to its star.
Detecting this decline required multiple years of careful observation. The watch started with Kepler and then was picked up by the Palomar Observatory’s Hale Telescope in Southern California and finally the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Telescope, or TESS, which launched in 2018. All three instruments captured transits, the term for when an exoplanet crosses the face of its star and causes a very slight dimming of the star’s brightness. Over the past 13 years, the interval between Kepler-1658b’s transits has slightly but steadily decreased.
The scientists think tidal forces are causing the orbit to shrink. The star itself is old and beginning to expand as it evolves towards its own stellar death.
Measurements of the orbit of first exoplanet discovered by the Kepler space telescope have determined that its orbit is very slowly shrinking, and that it will eventually spiral into its aging sun.
In the case of Kepler-1658b, according to the new study, its orbital period is decreasing at the miniscule rate of about 131 milliseconds (thousandths of a second) per year, with a shorter orbit indicating the planet has moved closer to its star.
Detecting this decline required multiple years of careful observation. The watch started with Kepler and then was picked up by the Palomar Observatory’s Hale Telescope in Southern California and finally the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Telescope, or TESS, which launched in 2018. All three instruments captured transits, the term for when an exoplanet crosses the face of its star and causes a very slight dimming of the star’s brightness. Over the past 13 years, the interval between Kepler-1658b’s transits has slightly but steadily decreased.
The scientists think tidal forces are causing the orbit to shrink. The star itself is old and beginning to expand as it evolves towards its own stellar death.