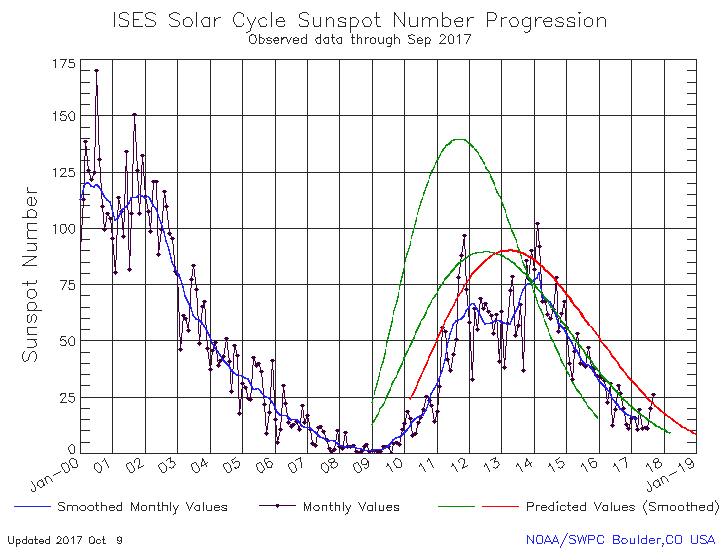
Sunspot update May 2019: The long ramp down
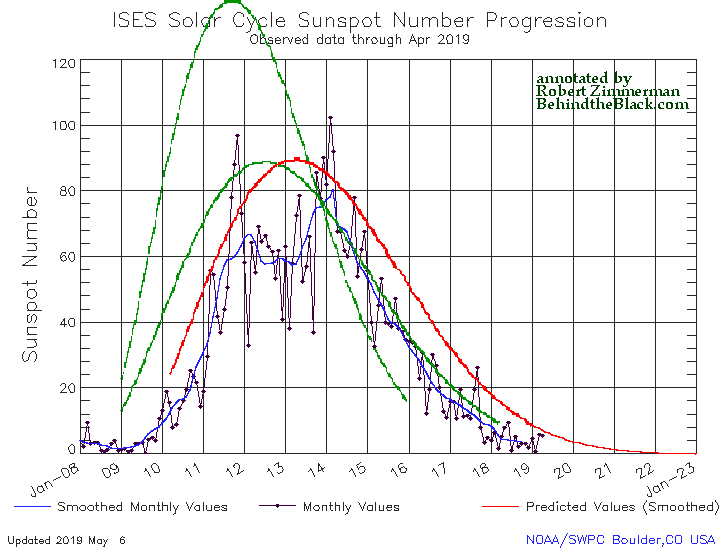
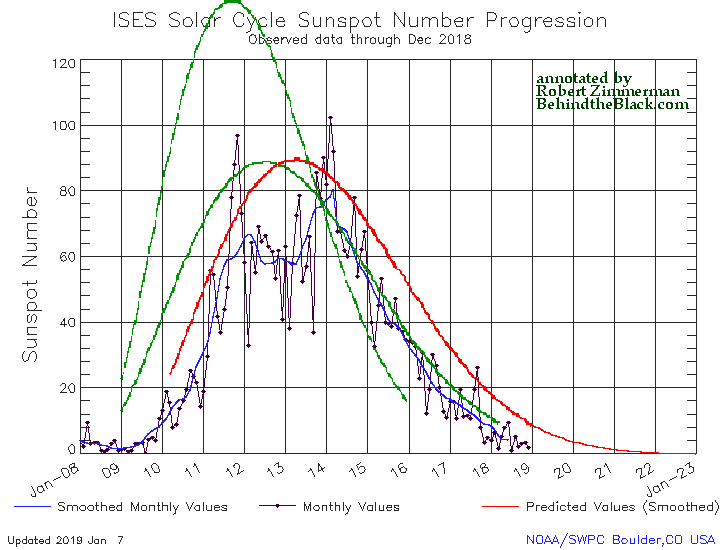
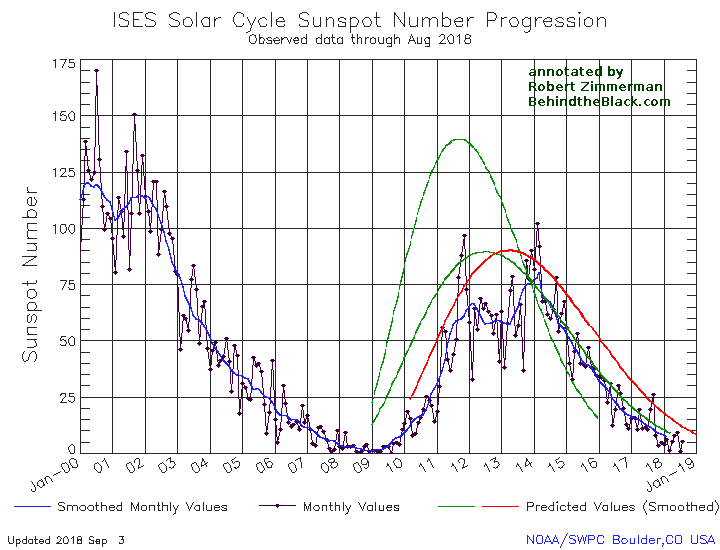
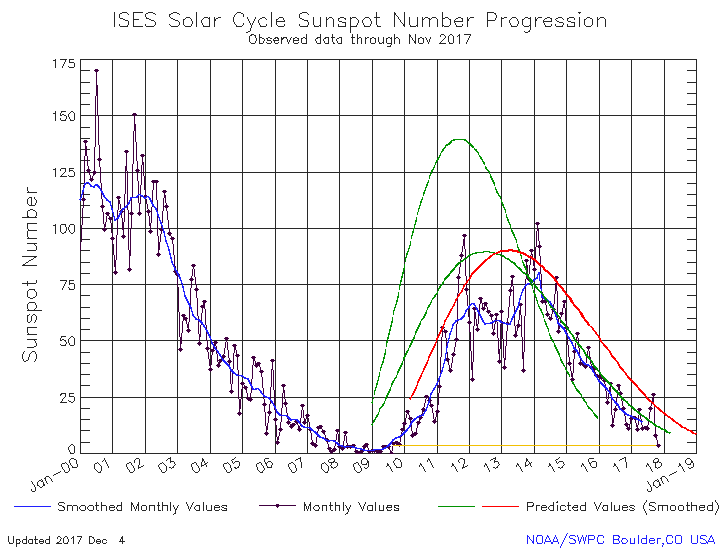
NOAA yesterday released its May update for the Sun’s sunspot cycle. The graph is posted below, annotated by me to give it some context.
The Sun in May continued to show the exact same amount of activity as it had shown for March and April. This steady uptick in sunspot activity once again shows that the ramp down to full solar minimum will be long and extended.
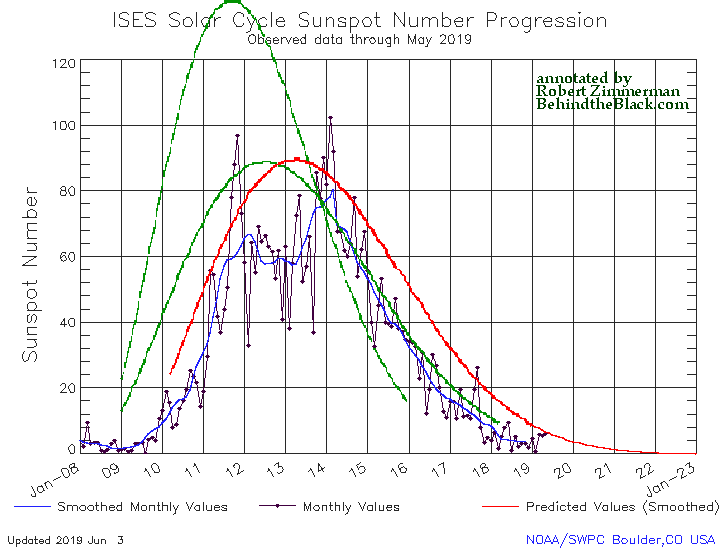
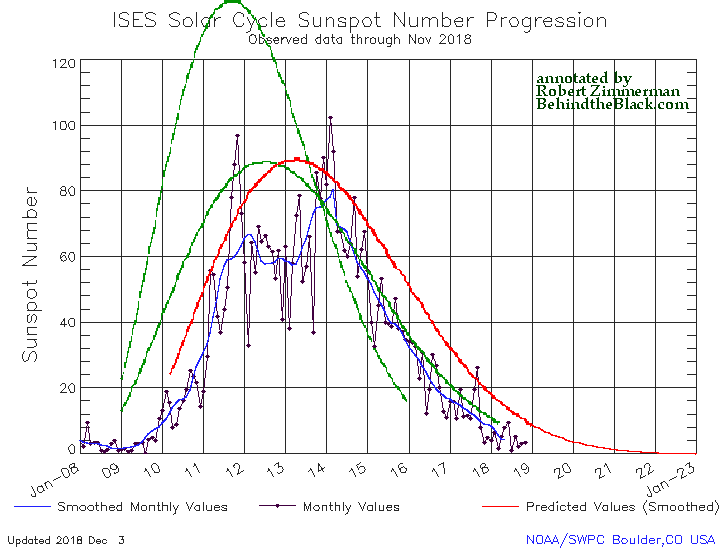
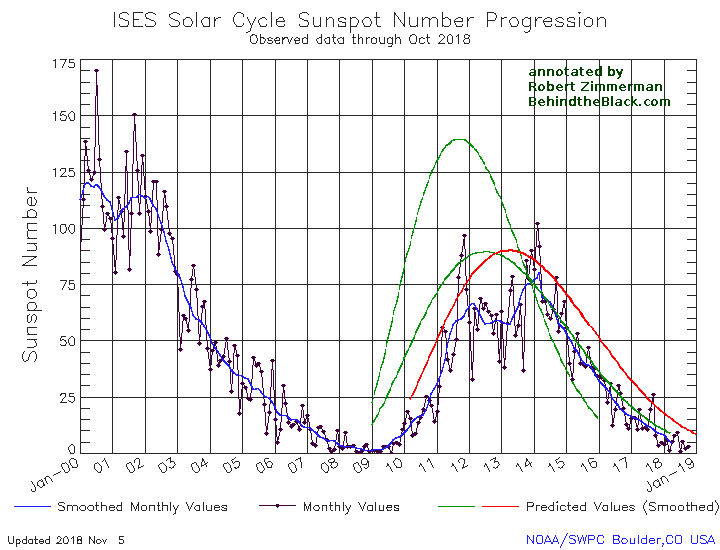
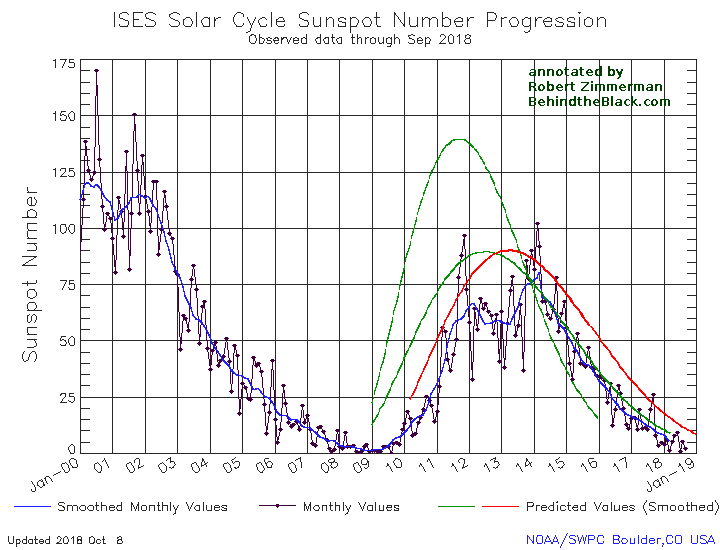
The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community for the previous solar maximum. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction, extended in November 2018 four years into the future.
That we are definitely ramping downward to minimum, even with the slight increase in the past three months, is shown by the fact that the Sun has shown no sunspots for the past fifteen days. In fact, all the activity shown in May comes from the first half of the month. This pattern is actually a reflection of the Sun’s 27-day rotation period. As I noted in my February 2017 update,
January’s activity however illustrated a statistical phenomenon that is typical of the sunspot count. That count is determined not by the numbers of sunspots on the entire surface of the Sun, but on the sunspots visible on the side of the Sun facing the Earth. Since it is not unusual for one face to be more active than the other, as we transition from maximum to minimum the sunspot counts will often show a more pronounced up-and-down curve reflecting this fact. Since the Sun’s day equals about 27 Earth days, this means that about every two weeks the active side will dominate our view until it rotates away and the inactive side reveals itself for two weeks.
In 2017 the number of spots were greater, so the period of inactivity was generally less. Now, it is not unusual for the Sun to be blank for weeks at a time. When it does become active, it is also not unusual for that activity to be confined to one hemisphere, so we get two weeks or less of activity, followed by two weeks or more of blankness.
So far there have been no sunspots in June. Expect that to continue for at least another week, when the more active hemisphere of the Sun returns to face us. I would not be surprise however if that other hemisphere arrives with its sunspots gone, so that the present streak of blankness continues unabated.
Meanwhile, solar scientists struggle to figure out what is going to happen next. Unlike climate scientists, who know as little about the climate, the solar science community admits to its ignorance about the Sun, and the uncertainty of its solar models.