Looking back from the foothills of Mount Sharp
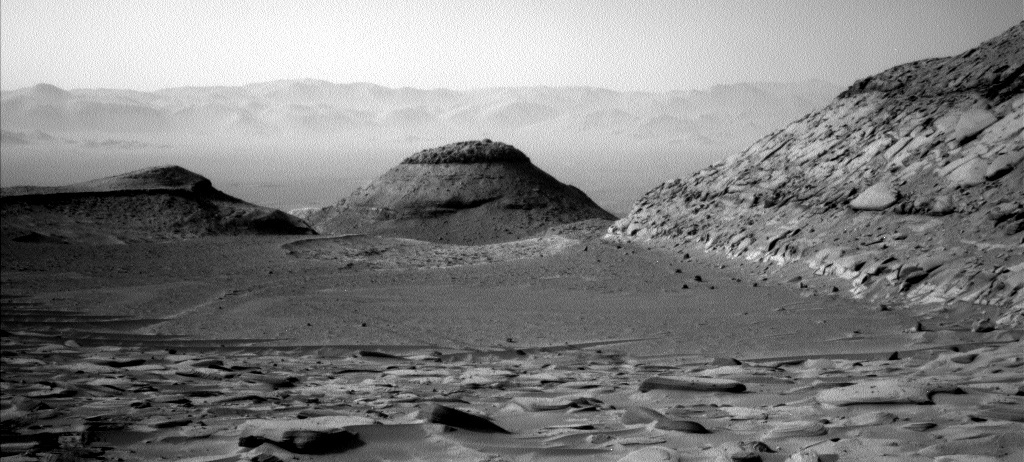
The panorama above, cropped to post here, was taken today by the left navigation camera on the Mars rover Curiosity. It looks back at the rover’s previous travels, though only the terrain traveled in the past few months is visible, the rover having reached this point through the notch to the left of the distinctly dark mesa in the center of the picture. The lower flanks of Mount Sharp the rover traversed to get here are now blocked from view.
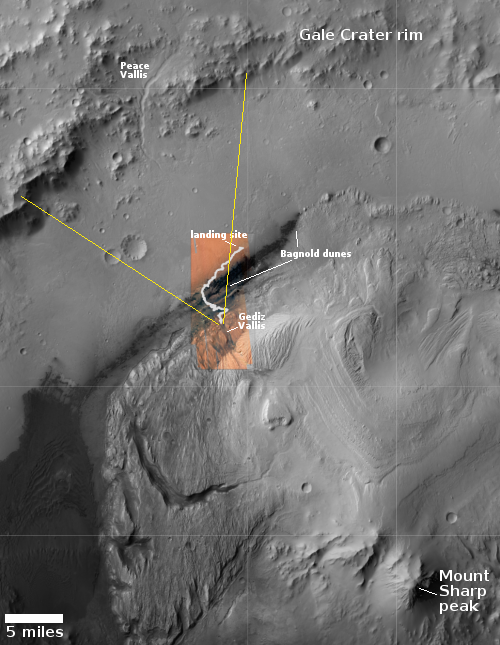
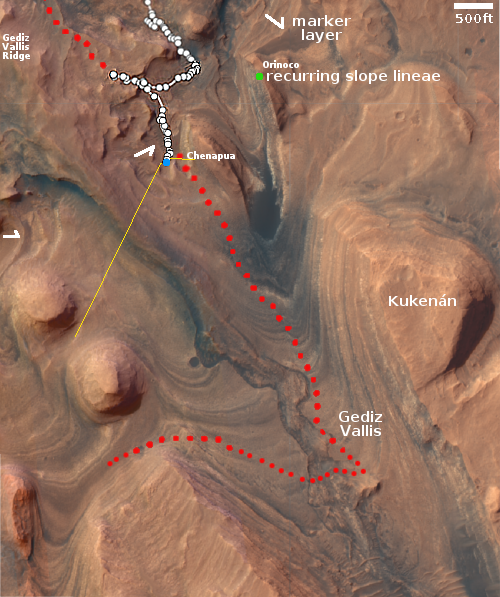
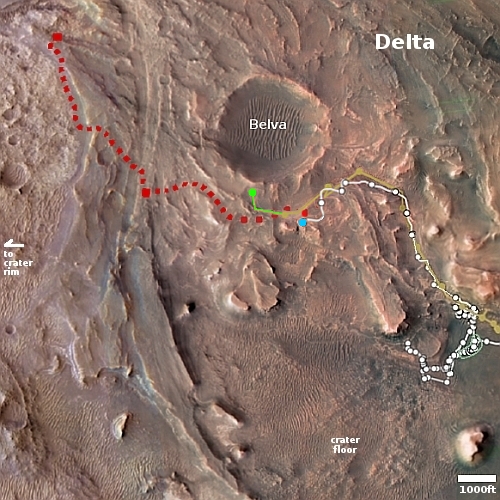
Instead, the image provides a spectacular example of the views north from Curiosity’s present position. The overview map to the right provides us the full context of the entire ten-plus year journey since Curiosity landed safely on Mars on August 5, 2012. The white squiggly line indicates the rover’s route. The yellow lines mark the approximate area covered by the panorama. The rim of Gale Crater is about 20-25 miles away.
As you can see, as spectacular as this view is, the journey up Mount Sharp has barely begun. Mount Sharp’s peak is about 18,000 feet high. The rover at this point has only climbed about 4,600 feet from the floor of Gale Crater.
The panorama above, cropped to post here, was taken today by the left navigation camera on the Mars rover Curiosity. It looks back at the rover’s previous travels, though only the terrain traveled in the past few months is visible, the rover having reached this point through the notch to the left of the distinctly dark mesa in the center of the picture. The lower flanks of Mount Sharp the rover traversed to get here are now blocked from view.
Instead, the image provides a spectacular example of the views north from Curiosity’s present position. The overview map to the right provides us the full context of the entire ten-plus year journey since Curiosity landed safely on Mars on August 5, 2012. The white squiggly line indicates the rover’s route. The yellow lines mark the approximate area covered by the panorama. The rim of Gale Crater is about 20-25 miles away.
As you can see, as spectacular as this view is, the journey up Mount Sharp has barely begun. Mount Sharp’s peak is about 18,000 feet high. The rover at this point has only climbed about 4,600 feet from the floor of Gale Crater.