A Martian mud volcano
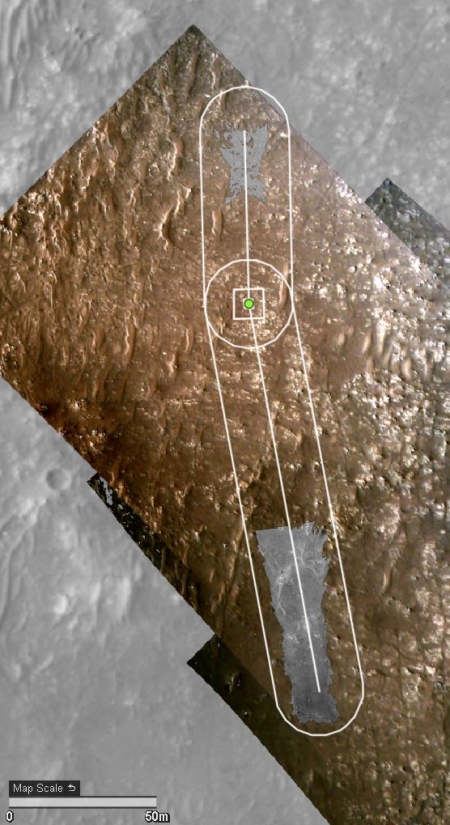
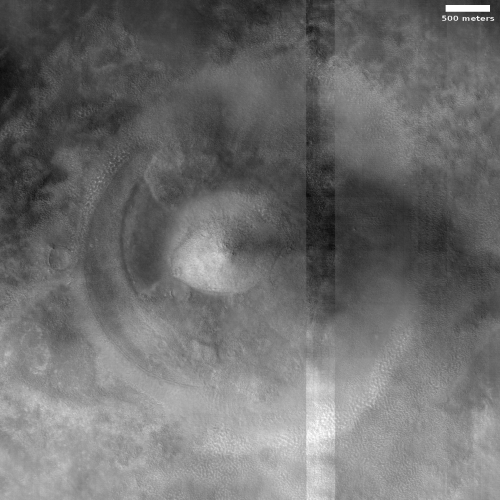
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on January 6, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a distinct conelike knob in an area of the northern lowland plains of Mars dubbed Acidalia Mensa.
According to this paper [pdf], this is possibly a mud volcano.
Bright pitted cones are common in the northern plains of Mars and have been documented to occur in numerous locations including Acidalia Planitia. Various interpretations of these features have been
proposed but growing consensus in recent literature has favored mud volcanism as the most likely formation mechanism. Mud volcanoes are provocative targets for exploration because they bring to the surface sedimentary materials otherwise inaccessible by normal surface exploration and can aid in reconstructing the sedimentary history of the northern plains. Also, by sampling fluids and sediments from deep in the Martian crust, mud volcanoes may be among the best places to search for ancient and extant life.
A previous cool image post, “Baby volcanoes on Mars”, showed another example in the same general area of Mars.
Though this conclusion is not yet confirmed, the multi-layered apron that surrounds the cone certainly suggests repeated eruptions of muddy water over time.
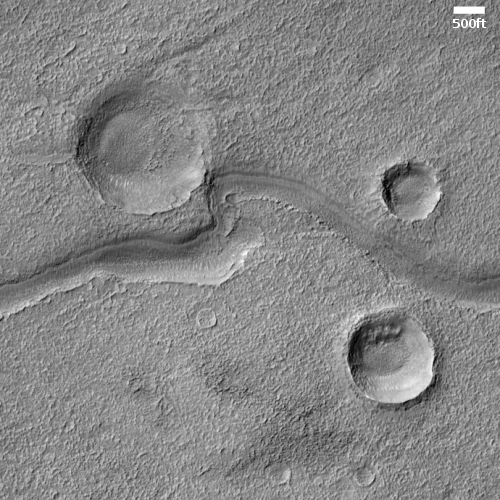
Scientists have taken many images of this area and cone using MRO’s context camera. (See this image as and example.) All show a very rough terrain, with cracks, fissures, and many smaller cones and knobs. This particular knob however dominates the landscape as one of the largest features. The aprons around it are darker, and appear to have been overlain on top of the nearby rough ground.
If such cones are mud volcanoes, they represent a geological process that is pretty much unique to Mars. There are some comparable features on Earth, but they are rare and do not match exactly.
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on January 6, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a distinct conelike knob in an area of the northern lowland plains of Mars dubbed Acidalia Mensa.
According to this paper [pdf], this is possibly a mud volcano.
Bright pitted cones are common in the northern plains of Mars and have been documented to occur in numerous locations including Acidalia Planitia. Various interpretations of these features have been
proposed but growing consensus in recent literature has favored mud volcanism as the most likely formation mechanism. Mud volcanoes are provocative targets for exploration because they bring to the surface sedimentary materials otherwise inaccessible by normal surface exploration and can aid in reconstructing the sedimentary history of the northern plains. Also, by sampling fluids and sediments from deep in the Martian crust, mud volcanoes may be among the best places to search for ancient and extant life.
A previous cool image post, “Baby volcanoes on Mars”, showed another example in the same general area of Mars.
Though this conclusion is not yet confirmed, the multi-layered apron that surrounds the cone certainly suggests repeated eruptions of muddy water over time.
Scientists have taken many images of this area and cone using MRO’s context camera. (See this image as and example.) All show a very rough terrain, with cracks, fissures, and many smaller cones and knobs. This particular knob however dominates the landscape as one of the largest features. The aprons around it are darker, and appear to have been overlain on top of the nearby rough ground.
If such cones are mud volcanoes, they represent a geological process that is pretty much unique to Mars. There are some comparable features on Earth, but they are rare and do not match exactly.