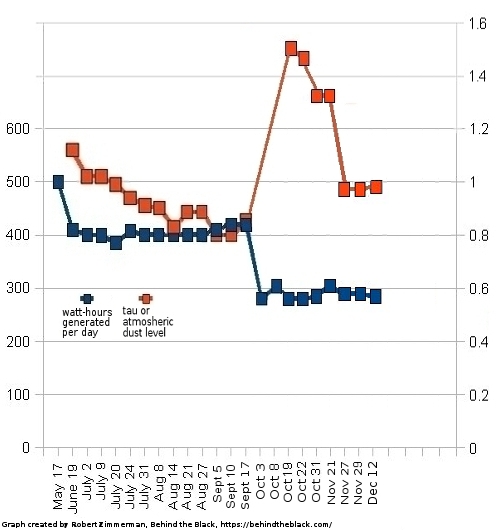
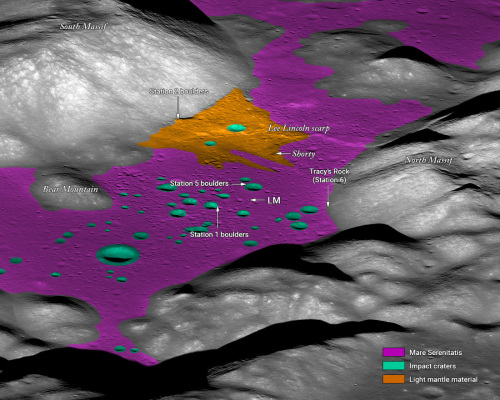
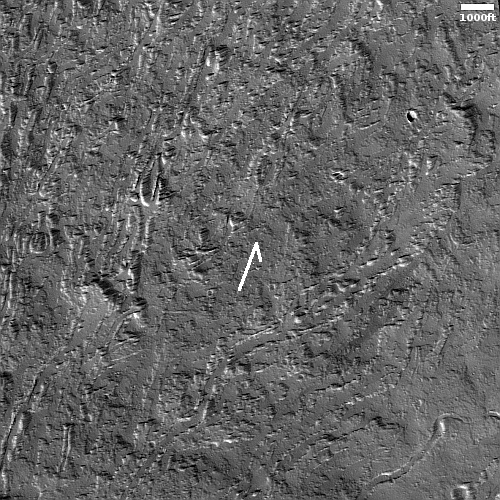
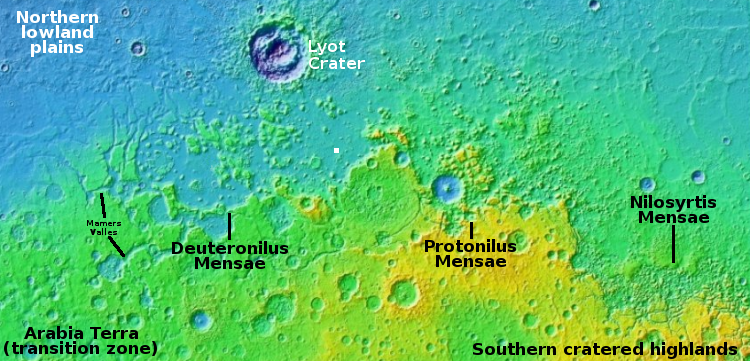
NASA approves $1.2 billion asteroid-hunting space telescope
NASA has given the go-ahead to build NEO-Surveyor for $1.2 billion, more than twice the cost of its original proposal, to launch by 2028 and then look for potentially dangerous asteroids.
Notably, NEO Surveyor was earlier estimated to cost between $500 million and $600 million, or around half of the new commitment. The NASA statement said that the cost and schedule commitments outlined align the mission with “program management best practices that account for potential technical risks and budgetary uncertainty beyond the development project’s control.” Earlier this year, the project’s launch was delayed two years, from 2026, due to agency budget concerns.
The mission is designed to discover 90% of potentially Earth-threatening asteroids and comets 460 feet (140 meters) or larger that come within 30 million miles (48 million kilometers) of Earth’s orbit. The spacecraft will carry out the survey while from Earth-sun Lagrange Point 1, a gravitationally stable spot in space about 930,000 miles (1.5 million kilometers) inside the Earth’s orbit around the sun.
A prediction: It will cost more, and not launch on time. NASA’s decision to double the budget and delay the launch two years suggests it did not trust the JPL cost and time estimates. Based on most NASA-centered projects, however, it is likely the new numbers will still be insufficient.
NASA has given the go-ahead to build NEO-Surveyor for $1.2 billion, more than twice the cost of its original proposal, to launch by 2028 and then look for potentially dangerous asteroids.
Notably, NEO Surveyor was earlier estimated to cost between $500 million and $600 million, or around half of the new commitment. The NASA statement said that the cost and schedule commitments outlined align the mission with “program management best practices that account for potential technical risks and budgetary uncertainty beyond the development project’s control.” Earlier this year, the project’s launch was delayed two years, from 2026, due to agency budget concerns.
The mission is designed to discover 90% of potentially Earth-threatening asteroids and comets 460 feet (140 meters) or larger that come within 30 million miles (48 million kilometers) of Earth’s orbit. The spacecraft will carry out the survey while from Earth-sun Lagrange Point 1, a gravitationally stable spot in space about 930,000 miles (1.5 million kilometers) inside the Earth’s orbit around the sun.
A prediction: It will cost more, and not launch on time. NASA’s decision to double the budget and delay the launch two years suggests it did not trust the JPL cost and time estimates. Based on most NASA-centered projects, however, it is likely the new numbers will still be insufficient.