Another Webb infrared image of Jupiter released
The science team for the James Webb Space Telescope today released another infrared false-color image of Jupiter, this time processed for science instead of calibration of the telescope after launch.
That image is to the right, reduced to post here. From the caption:
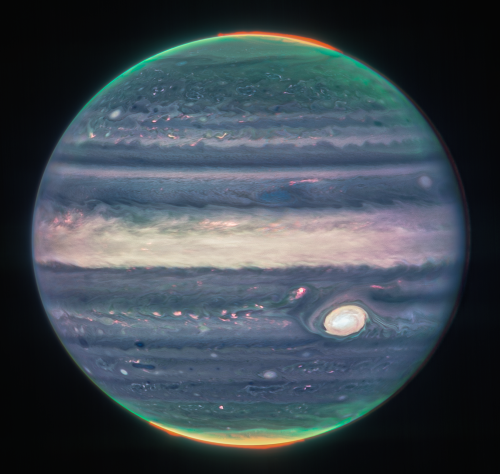
Several exposures in three different filters were assembled to create this mosaic, after being corrected for the rotation of the planet. The combination of filters yields an image whose colors denote the height of the clouds and the intensity of auroral emissions.
The F360M filter (mapped to the red-orange colors) is sensitive to light reflected from the lower clouds and upper hazes. The red features in the polar regions are auroral emissions, caused by ions excited through collisions with charged particles at altitudes up to 1000 km above the cloud level. Auroral emission in red is evident in the northern and southern polar regions and reaches high above the limb of the planet. In the F212N filter (mapped to yellow-green colors), the gaseous methane in Jupiter’s atmosphere absorbs light; the greenish areas around the polar regions come from stratospheric hazes 100-200 km above the cloud level. The stratospheric haze that appears green in this composite is also concentrated in the polar regions, but extends down to equatorial latitudes and can also be seen along the limbs (edges) of the planet. The cyan channel holds the F150W2 filter, which is primarily sensitive to reflected light from the Jupiter’s deeper main cloud level at about one bar.
The Great Red Spot, the hazy equatorial region and myriad small storm systems appear white (or reddish-white) in this false-color image. Regions with little cloud cover appear as dark ribbons north of the equatorial region. Some dark regions — for example, those next to the Great Red Spot and in cyclonic features in the southern hemisphere — are also dark-colored when observed in visible wavelengths.
This image is part of the telescope’s early release science program.
The science team for the James Webb Space Telescope today released another infrared false-color image of Jupiter, this time processed for science instead of calibration of the telescope after launch.
That image is to the right, reduced to post here. From the caption:
Several exposures in three different filters were assembled to create this mosaic, after being corrected for the rotation of the planet. The combination of filters yields an image whose colors denote the height of the clouds and the intensity of auroral emissions.
The F360M filter (mapped to the red-orange colors) is sensitive to light reflected from the lower clouds and upper hazes. The red features in the polar regions are auroral emissions, caused by ions excited through collisions with charged particles at altitudes up to 1000 km above the cloud level. Auroral emission in red is evident in the northern and southern polar regions and reaches high above the limb of the planet. In the F212N filter (mapped to yellow-green colors), the gaseous methane in Jupiter’s atmosphere absorbs light; the greenish areas around the polar regions come from stratospheric hazes 100-200 km above the cloud level. The stratospheric haze that appears green in this composite is also concentrated in the polar regions, but extends down to equatorial latitudes and can also be seen along the limbs (edges) of the planet. The cyan channel holds the F150W2 filter, which is primarily sensitive to reflected light from the Jupiter’s deeper main cloud level at about one bar.
The Great Red Spot, the hazy equatorial region and myriad small storm systems appear white (or reddish-white) in this false-color image. Regions with little cloud cover appear as dark ribbons north of the equatorial region. Some dark regions — for example, those next to the Great Red Spot and in cyclonic features in the southern hemisphere — are also dark-colored when observed in visible wavelengths.
This image is part of the telescope’s early release science program.