More polygons on Mars!
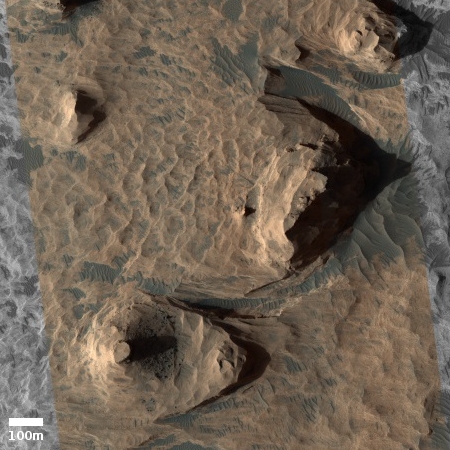
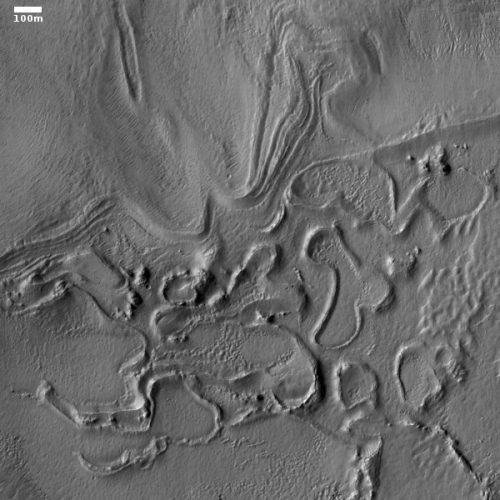
Today’s cool image, rotated, cropped, and contrast-enhanced to post here, focuses on polygons found near the equator of Mars. It was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on May 22, 2020, and shows what the science team labels as “well-preserved polygons.”
Previously I have posted cool images showing polygons (here and here), but those images were located in the northern mid-latitudes, and were thought to have been formed in connection with some form of freeze-melt-drying water process in permafrost.
Today’s image however is likely not related to water. It is located in the equatorial regions, where little water is expected. It also has a more permanent nature, which suggests that it is the result of some sort of volcanic or tectonic process. That the polygons are depressions suggests the latter, since a volcanic process is more likely to have filled cracks and left ridges more resistant to erosion, as explained by this article.
In this case the topography suggests instead some form of spreading and cracking process that left behind these polygon-shaped cracks. In mud, such polygons are found when the mud dries, but once again, these are in a very dry region. If formed in that manner they must have formed a very very long time ago, when the climate here was very different, and were somehow preserved for eons since.
The location, as shown in the overview map below provides some context, though it really doesn’t answer any questions..
» Read more
Today’s cool image, rotated, cropped, and contrast-enhanced to post here, focuses on polygons found near the equator of Mars. It was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on May 22, 2020, and shows what the science team labels as “well-preserved polygons.”
Previously I have posted cool images showing polygons (here and here), but those images were located in the northern mid-latitudes, and were thought to have been formed in connection with some form of freeze-melt-drying water process in permafrost.
Today’s image however is likely not related to water. It is located in the equatorial regions, where little water is expected. It also has a more permanent nature, which suggests that it is the result of some sort of volcanic or tectonic process. That the polygons are depressions suggests the latter, since a volcanic process is more likely to have filled cracks and left ridges more resistant to erosion, as explained by this article.
In this case the topography suggests instead some form of spreading and cracking process that left behind these polygon-shaped cracks. In mud, such polygons are found when the mud dries, but once again, these are in a very dry region. If formed in that manner they must have formed a very very long time ago, when the climate here was very different, and were somehow preserved for eons since.
The location, as shown in the overview map below provides some context, though it really doesn’t answer any questions..
» Read more