Dusty Gale Crater in the winter

Click on image for full resolution panorama. For original photos, go here, here, here, here, and here.
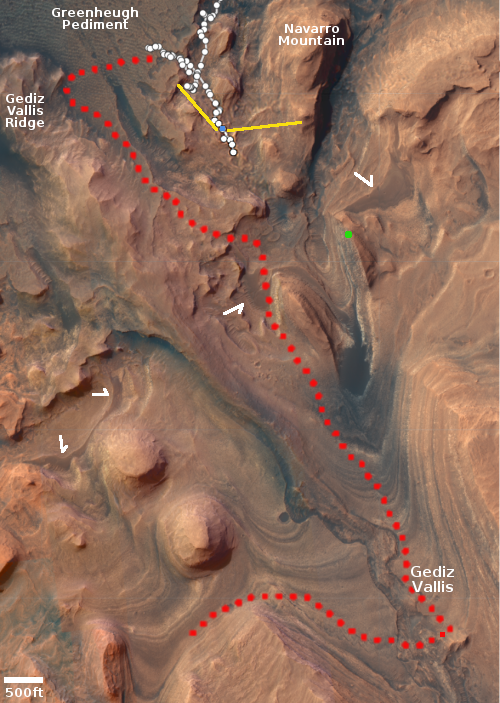
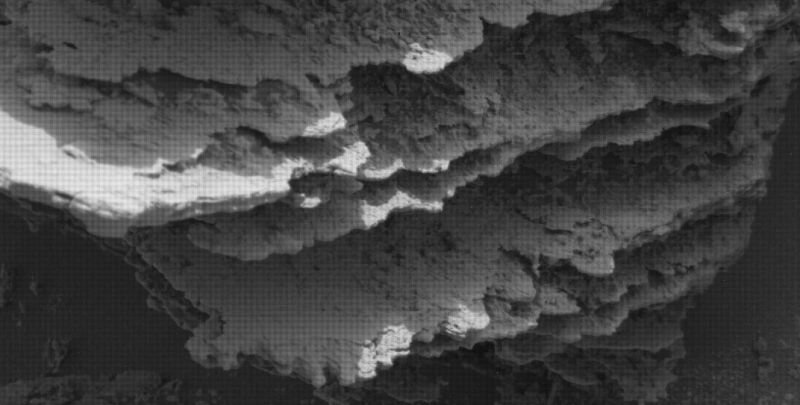
Cool image time! The panorama above, created from five images taken by Curiosity’s left navigation camera on May 25, 2022, looks north across the floor of Gale Crater at its rim about 25 miles away.
The butte on the left I think (though I am not certain) is the backside of the same butte seen from the front in December 2021. Then, Curiosity was below it looking up. Now, Curiosity is above it looking down.
For scale, that butte is about ten feet high. Navarro Mountain on the right is about 450 feet high, but looks less impressive because it is farther away.
It is now winter in Gale Crater, a time period when there is more dust in the atmosphere. This fact becomes very evident if you compare this panorama with a similar one taken in December 2021 in the Martian fall. Then, the air is crystal clear, and the rim can be seen in great detail. Now, though visible (barely) on the left, the haze makes the more distant peaks on the right almost invisible.
Curiosity has climbed about 1,750 feet since it landed in 2012. It is still about 12,600 feet below the peak of Mount Sharp. The blue dot and yellow lines in the overview map to the right indicates Curiosity’s location when the panorama was taken, and the approximate area covered by it.
Be sure and look at the full resolution panorama, especially the section near the middle, where the dramatic nature of this terrain is most evident.

Click on image for full resolution panorama. For original photos, go here, here, here, here, and here.
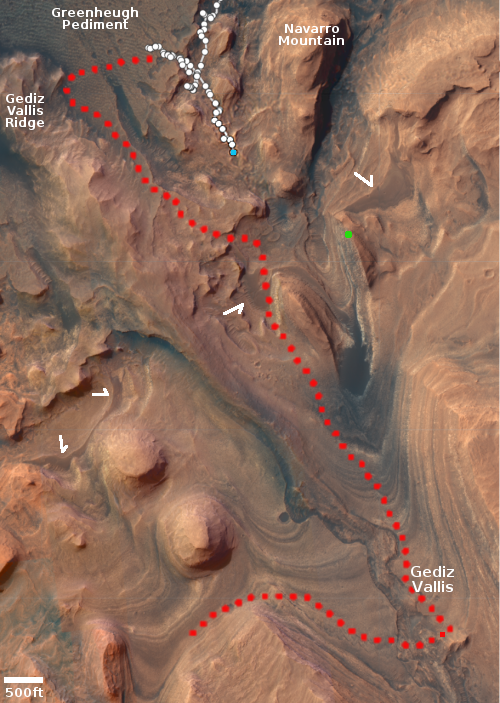
Cool image time! The panorama above, created from five images taken by Curiosity’s left navigation camera on May 25, 2022, looks north across the floor of Gale Crater at its rim about 25 miles away.
The butte on the left I think (though I am not certain) is the backside of the same butte seen from the front in December 2021. Then, Curiosity was below it looking up. Now, Curiosity is above it looking down.
For scale, that butte is about ten feet high. Navarro Mountain on the right is about 450 feet high, but looks less impressive because it is farther away.
It is now winter in Gale Crater, a time period when there is more dust in the atmosphere. This fact becomes very evident if you compare this panorama with a similar one taken in December 2021 in the Martian fall. Then, the air is crystal clear, and the rim can be seen in great detail. Now, though visible (barely) on the left, the haze makes the more distant peaks on the right almost invisible.
Curiosity has climbed about 1,750 feet since it landed in 2012. It is still about 12,600 feet below the peak of Mount Sharp. The blue dot and yellow lines in the overview map to the right indicates Curiosity’s location when the panorama was taken, and the approximate area covered by it.
Be sure and look at the full resolution panorama, especially the section near the middle, where the dramatic nature of this terrain is most evident.