German rocket company successfully tests first stage to failure
Capitalism in space: The German startup rocket company Rocket Factory Augsburg has successfully completed a tank pressure test of its rocket’s core first stage, testing that stage to failure.
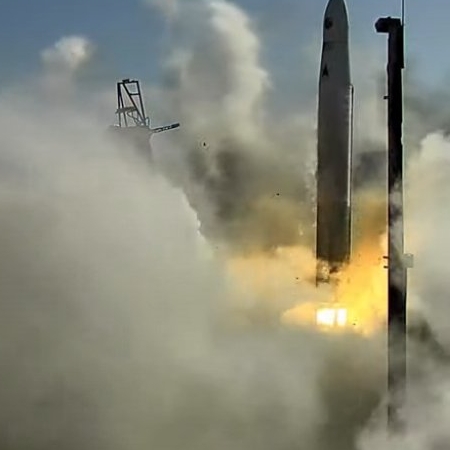
The German startup Rocket Factory Augsburg, or RFA, has concluded another test of their RFA One rocket. In the test, the company performed a destructive cryogenic pressure test of their first stage prototype. The company has shown a video in which the prototype stage broke apart after it was fueled with cryogenic nitrogen to test the quality of the welds and determine the pressure at which the structure fails.
The milestone is the latest for the company which is aiming to develop a reusable launch vehicle for small payloads. The first flight of RFA One is currently slated for late 2022, following more testing and development.
The video of the test, with a dramatic soundtrack (as has sadly become the practice today since all life always has its own soundtrack) can be seen at the link.
This company is one of three German private rocket startups vying to enter the smallsat launch market — Isar, RFA, and HyImpulse — with two hoping to make their first launch next year.
Capitalism in space: The German startup rocket company Rocket Factory Augsburg has successfully completed a tank pressure test of its rocket’s core first stage, testing that stage to failure.
The German startup Rocket Factory Augsburg, or RFA, has concluded another test of their RFA One rocket. In the test, the company performed a destructive cryogenic pressure test of their first stage prototype. The company has shown a video in which the prototype stage broke apart after it was fueled with cryogenic nitrogen to test the quality of the welds and determine the pressure at which the structure fails.
The milestone is the latest for the company which is aiming to develop a reusable launch vehicle for small payloads. The first flight of RFA One is currently slated for late 2022, following more testing and development.
The video of the test, with a dramatic soundtrack (as has sadly become the practice today since all life always has its own soundtrack) can be seen at the link.
This company is one of three German private rocket startups vying to enter the smallsat launch market — Isar, RFA, and HyImpulse — with two hoping to make their first launch next year.