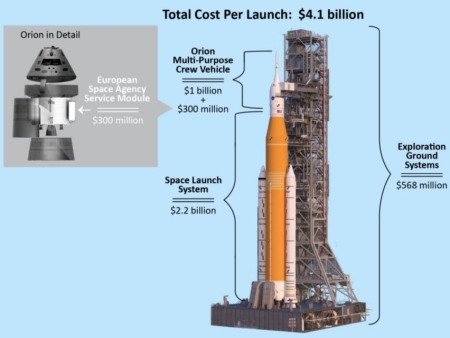
SpaceX raises launch prices
Capitalism in space: Though most of the press has focused on the Starlink announcement on March 22nd that it was raising its subscriber rates, that same day SpaceX announced that it too was raising its prices, increasing its launch fees by 8% to 10%.
The starting prices for a Falcon 9 or Falcon Heavy rocket will each increase by about 8%. A Falcon 9 launch will cost $67 million, up from $62 million, and a Falcon Heavy launch will now run $97 million, up from $90 million. A footnote on SpaceX’s pricing page notes that “missions purchased in 2022 but flown beyond 2023 may be subject to additional adjustments due to inflation.”
..The company also adjusted its prices for its small satellite rideshare program. Those flights will now start at $1.1 million to fly a payload weighing 200 kilograms to a sun-synchronous orbit, up from a base price of $1 million. SpaceX increased the cost of additional payload mass by 10% as well and will now charge $5,500 per extra kilogram, up from a previous $5,000 per kilogram.
As with the Starlink announcement, SpaceX officials stated that the price increase was due entirely by inflation.
The irony here is that SpaceX could easily raise its rocket prices by 20%, and still be undercutting its entire competition. Even with these increases it is still by far the cheapest game in town.
Nonetheless, when it comes to inflation we have only just begun. The consequences of the Ukraine war, the sanctions against Russia, the Biden administration’s restrictions on domestic oil production, and the various COVID regulations restricting commerce are all still in effect, and are all putting pressure on supply. Prices will continue to rise.
Capitalism in space: Though most of the press has focused on the Starlink announcement on March 22nd that it was raising its subscriber rates, that same day SpaceX announced that it too was raising its prices, increasing its launch fees by 8% to 10%.
The starting prices for a Falcon 9 or Falcon Heavy rocket will each increase by about 8%. A Falcon 9 launch will cost $67 million, up from $62 million, and a Falcon Heavy launch will now run $97 million, up from $90 million. A footnote on SpaceX’s pricing page notes that “missions purchased in 2022 but flown beyond 2023 may be subject to additional adjustments due to inflation.”
..The company also adjusted its prices for its small satellite rideshare program. Those flights will now start at $1.1 million to fly a payload weighing 200 kilograms to a sun-synchronous orbit, up from a base price of $1 million. SpaceX increased the cost of additional payload mass by 10% as well and will now charge $5,500 per extra kilogram, up from a previous $5,000 per kilogram.
As with the Starlink announcement, SpaceX officials stated that the price increase was due entirely by inflation.
The irony here is that SpaceX could easily raise its rocket prices by 20%, and still be undercutting its entire competition. Even with these increases it is still by far the cheapest game in town.
Nonetheless, when it comes to inflation we have only just begun. The consequences of the Ukraine war, the sanctions against Russia, the Biden administration’s restrictions on domestic oil production, and the various COVID regulations restricting commerce are all still in effect, and are all putting pressure on supply. Prices will continue to rise.