Blue Origin negotiating with India to use its rockets and capsule for Orbital Reef space station
According to the head of India’s space agency ISRO, he has been in discussions with Blue Origin about using different versions of that nation’s largest rocket (dubbed LVM-3 or GSLV-Mk3 depending on configuration) and its manned capsule (still under development) for eventually ferrying crew and cargo to Blue Origin’s proposed Orbital Reef space station.
Somanath said: “We are exploring … In fact, we’ve already discussed it with Blue Origin and they are very keen to consider this option of LVM-3 becoming a crew capsule mission to service the Orbital Reef. It is a possibility and we are engaging through IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre).”
On the challenge of integrating a docking system that is compatible, he said standard docking systems are in the public domain. “…Whoever can design a docking system that matches with the US design and standard, can be used. However, we will still need to have agreements with agencies to try it out given that there are multiple interfaces — electrical, mechanical and so on. It is not just one document, we will need to work with them to develop it. We will do that.
It appears Somanath has also had discussions with NASA about also providing the same service to ISS.
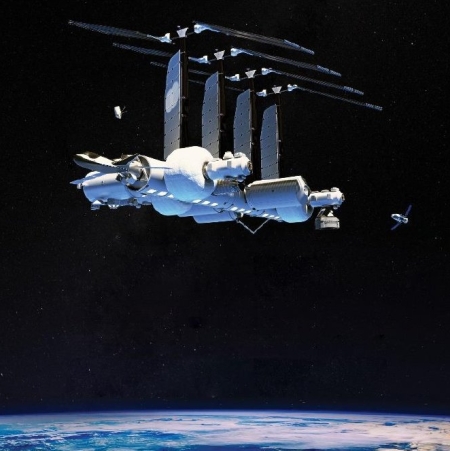
An Orbital Reef deal however suggests something very disturbing about Blue Origin. The plan had been to use Blue Origin’s New Glenn orbital rocket (also still under development but years behind schedule) to launch crew and cargo capsules to the station. That in fact is supposed to be Blue Origin’s main technical contribution to the station. Why would the company then look to India for such capability, unless it recognizes that there are more problems with New Glenn that it has not revealed?
It is also possible that Jeff Bezos is simply expressing his leftwing globalist agenda with these negotiations. Or it could mean some combination of both. This situation bears watching.
According to the head of India’s space agency ISRO, he has been in discussions with Blue Origin about using different versions of that nation’s largest rocket (dubbed LVM-3 or GSLV-Mk3 depending on configuration) and its manned capsule (still under development) for eventually ferrying crew and cargo to Blue Origin’s proposed Orbital Reef space station.
Somanath said: “We are exploring … In fact, we’ve already discussed it with Blue Origin and they are very keen to consider this option of LVM-3 becoming a crew capsule mission to service the Orbital Reef. It is a possibility and we are engaging through IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre).”
On the challenge of integrating a docking system that is compatible, he said standard docking systems are in the public domain. “…Whoever can design a docking system that matches with the US design and standard, can be used. However, we will still need to have agreements with agencies to try it out given that there are multiple interfaces — electrical, mechanical and so on. It is not just one document, we will need to work with them to develop it. We will do that.
It appears Somanath has also had discussions with NASA about also providing the same service to ISS.
An Orbital Reef deal however suggests something very disturbing about Blue Origin. The plan had been to use Blue Origin’s New Glenn orbital rocket (also still under development but years behind schedule) to launch crew and cargo capsules to the station. That in fact is supposed to be Blue Origin’s main technical contribution to the station. Why would the company then look to India for such capability, unless it recognizes that there are more problems with New Glenn that it has not revealed?
It is also possible that Jeff Bezos is simply expressing his leftwing globalist agenda with these negotiations. Or it could mean some combination of both. This situation bears watching.