Fake scientist Michael Mann slapped down hard by DC superior court

Fake leftist scientist Michael Mann
In the never-ending legal battle between fake climate scientist Michael Mann and his critics, Rand Simberg and Mark Steyn, Mann has once again lost badly in an appeal to a higher court, with the Superior Court in DC not only ruling that Mann must immediately pay Simberg and Steyn a total of more than $27K in court costs and fees, but blasting Mann for his lies to the court during the proceedings.
The fact remains that Dr. Mann throughout this litigation complained that he suffered lost grant funding directly stemming from the defamatory statements of Messrs. Simberg and Steyn, while providing very little in the way of specifics about the dollar amounts of his losses directly attributable to the statements (such as corroborating testimony from percipient witnesses), all while promising to illuminate the Court at trial. At trial, Dr. Mann elected through his attorneys to present to the jury a blown-up demonstrative, without redaction or explanation, a demonstrative intentionally prepared for its use at trial, which included a budget (loss) amount of $9,713,924.00, when the correct amount, previously corrected during a third round of discovery, was $112,000.
…the Court simply cannot condone such bad faith litigation tactics, particularly in a case that had been zealously litigated across several years and a case involving complicated facts. Thus, the Court’s ruling must stand. It is the Court’s duty to punish and deter bad faith litigation tactics.
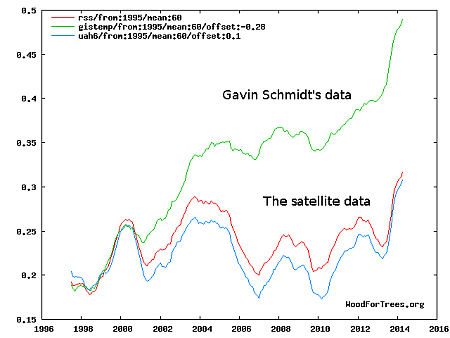
In other words, Mann didn’t simply falsify his scientific results, using false data in his infamous hockey stick graph to create the illusion of human-caused global warming, when Simberg and Steyn called him out on this fake science, he tried to sue them using more fake data that was quickly revealed in discovery to be outright lies.
The court has thankfully decided it cannot tolerate such behavior.
What must be understood about Mann is that he is a very typical leftist radical, who thinks that because his cause is just and good, he is somehow immune from any consequences for bad behavior. Such leftists increasingly believe they are allowed to lie, cheat, defame, and even sometimes commit violence, because anyone who disagrees with them is evil. Mann did not do the last item (though many other leftists now are), but he did all the others, and truly believed he could get away with it. He is now finding out otherwise.

Fake leftist scientist Michael Mann
In the never-ending legal battle between fake climate scientist Michael Mann and his critics, Rand Simberg and Mark Steyn, Mann has once again lost badly in an appeal to a higher court, with the Superior Court in DC not only ruling that Mann must immediately pay Simberg and Steyn a total of more than $27K in court costs and fees, but blasting Mann for his lies to the court during the proceedings.
The fact remains that Dr. Mann throughout this litigation complained that he suffered lost grant funding directly stemming from the defamatory statements of Messrs. Simberg and Steyn, while providing very little in the way of specifics about the dollar amounts of his losses directly attributable to the statements (such as corroborating testimony from percipient witnesses), all while promising to illuminate the Court at trial. At trial, Dr. Mann elected through his attorneys to present to the jury a blown-up demonstrative, without redaction or explanation, a demonstrative intentionally prepared for its use at trial, which included a budget (loss) amount of $9,713,924.00, when the correct amount, previously corrected during a third round of discovery, was $112,000.
…the Court simply cannot condone such bad faith litigation tactics, particularly in a case that had been zealously litigated across several years and a case involving complicated facts. Thus, the Court’s ruling must stand. It is the Court’s duty to punish and deter bad faith litigation tactics.
In other words, Mann didn’t simply falsify his scientific results, using false data in his infamous hockey stick graph to create the illusion of human-caused global warming, when Simberg and Steyn called him out on this fake science, he tried to sue them using more fake data that was quickly revealed in discovery to be outright lies.
The court has thankfully decided it cannot tolerate such behavior.
What must be understood about Mann is that he is a very typical leftist radical, who thinks that because his cause is just and good, he is somehow immune from any consequences for bad behavior. Such leftists increasingly believe they are allowed to lie, cheat, defame, and even sometimes commit violence, because anyone who disagrees with them is evil. Mann did not do the last item (though many other leftists now are), but he did all the others, and truly believed he could get away with it. He is now finding out otherwise.