Perseverance’s first climb
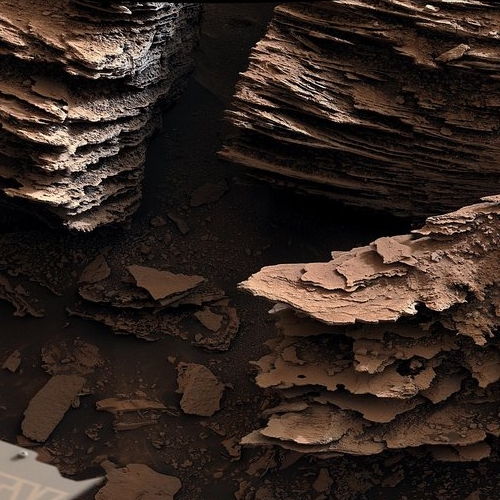
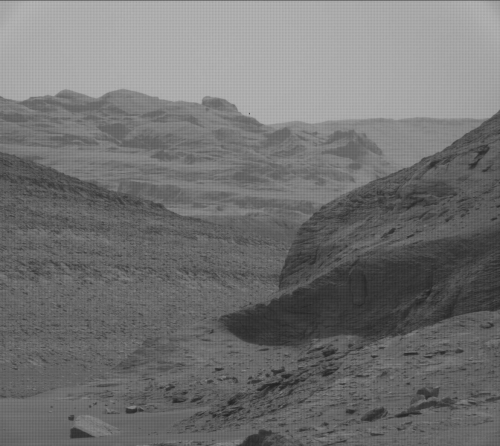
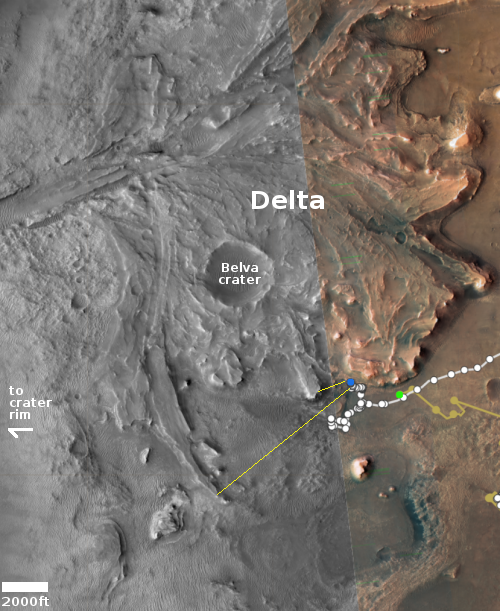
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken by the high resolution camera on the Mars rover Perseverance on June 16, 2022, shortly after it began its first climb up from the generally flat floor of Jezero crater and onto the delta that once in the far past flowed through a gap into that crater.
I have rotated the image about 8.5 degrees to make horizontal the crater floor and the distant rim of the crater (barely visible through the atmosphere’s thick winter dust). This shows that the rover was then climbing what appears to be a relative low angle grade, hardly as challenging as the serious grades that Curiosity has been dealing with now for the past two years in the foothills of Mount Sharp. Nonetheless, Perseverance has begun climbing.
To see where the rover is see the overview map from the start of this week. Unfortunately, I have been unable to determine the direction of this photo. It could be looking west, south, or east, based on features inside Jezero Crater. I therefore cannot tell you the distance to the rim, which depending on the direction, could be from five to twenty-five miles away.
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken by the high resolution camera on the Mars rover Perseverance on June 16, 2022, shortly after it began its first climb up from the generally flat floor of Jezero crater and onto the delta that once in the far past flowed through a gap into that crater.
I have rotated the image about 8.5 degrees to make horizontal the crater floor and the distant rim of the crater (barely visible through the atmosphere’s thick winter dust). This shows that the rover was then climbing what appears to be a relative low angle grade, hardly as challenging as the serious grades that Curiosity has been dealing with now for the past two years in the foothills of Mount Sharp. Nonetheless, Perseverance has begun climbing.
To see where the rover is see the overview map from the start of this week. Unfortunately, I have been unable to determine the direction of this photo. It could be looking west, south, or east, based on features inside Jezero Crater. I therefore cannot tell you the distance to the rim, which depending on the direction, could be from five to twenty-five miles away.