Buried peaks in a sea of Martian sand
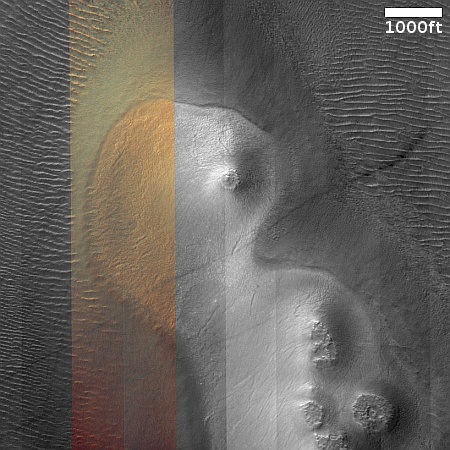
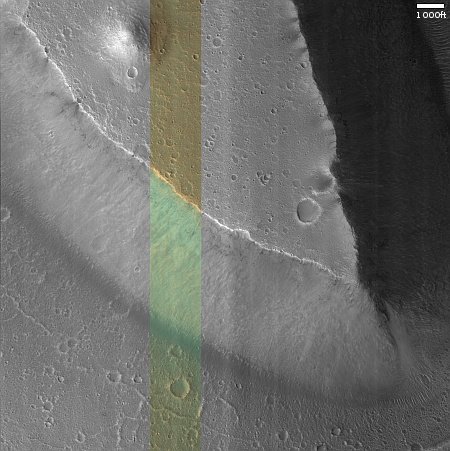
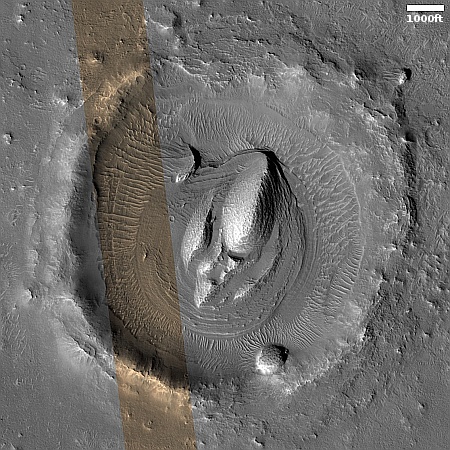
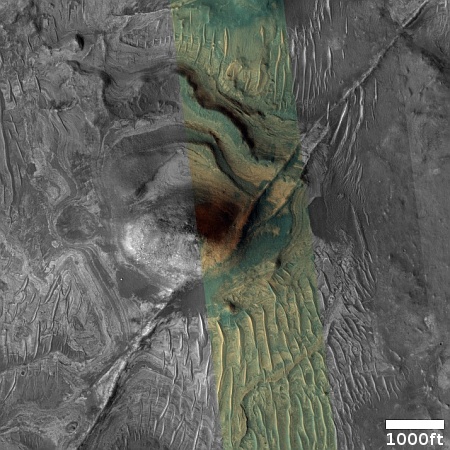
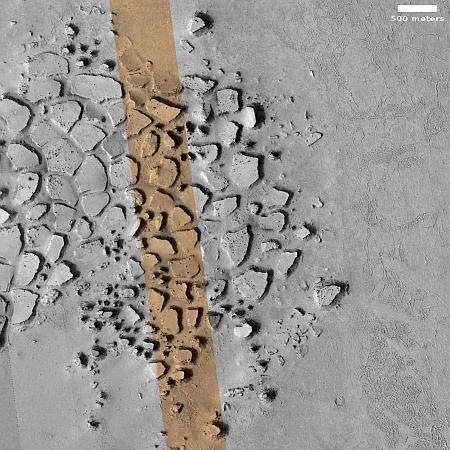
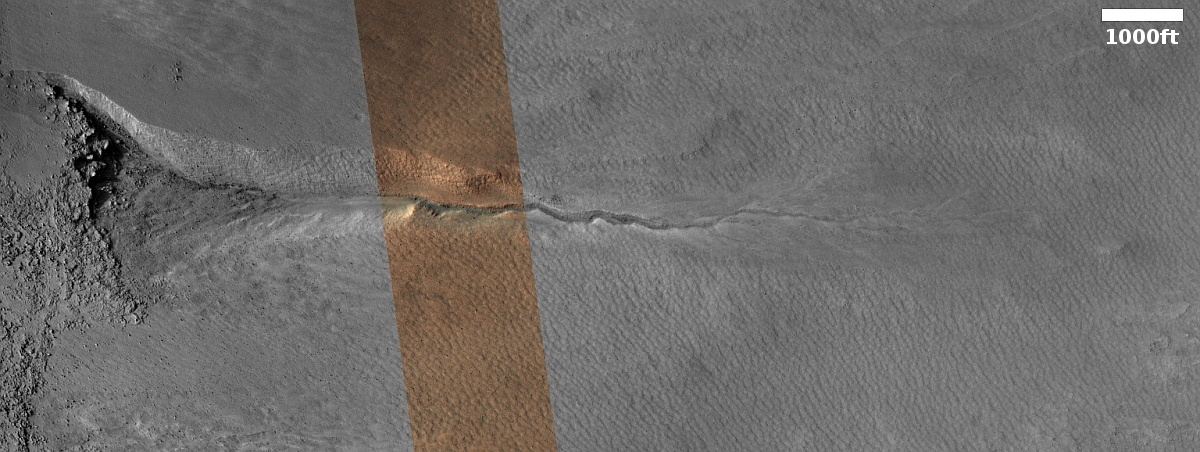
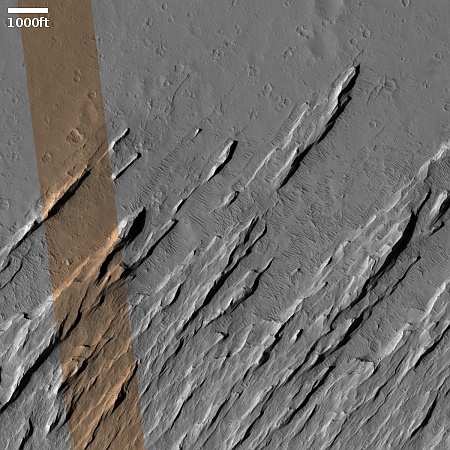
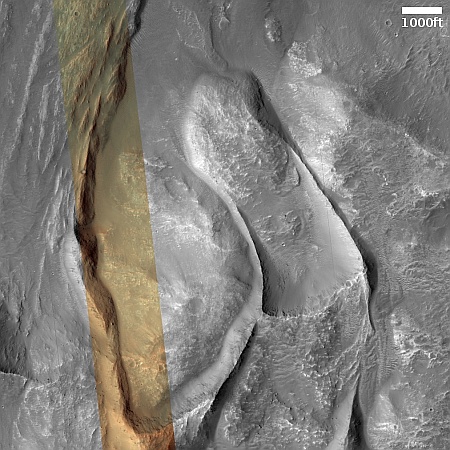
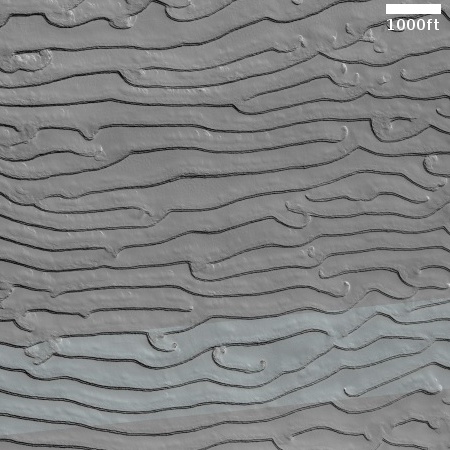
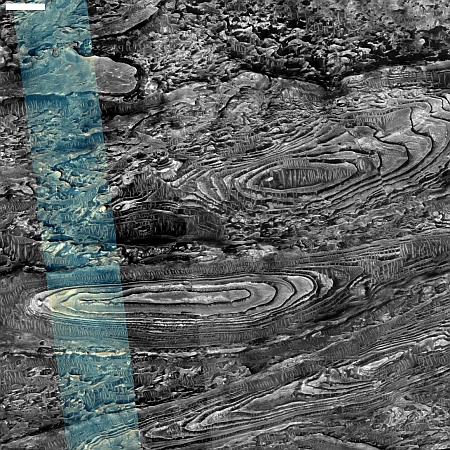
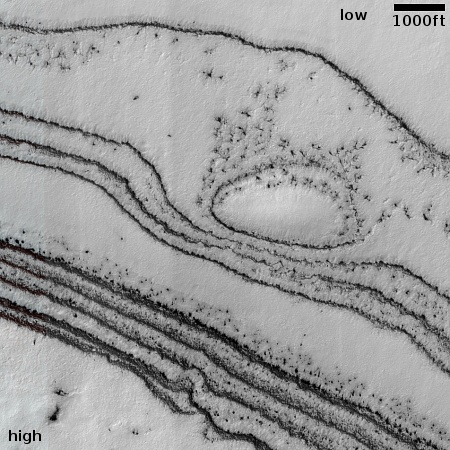
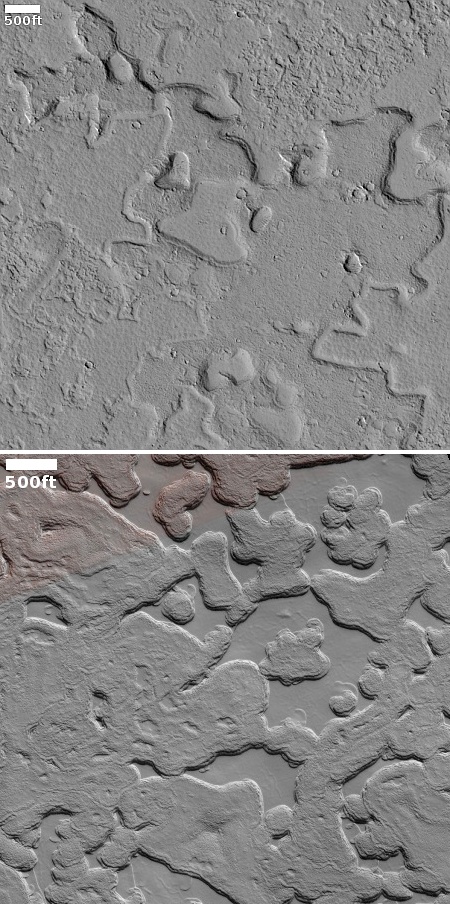
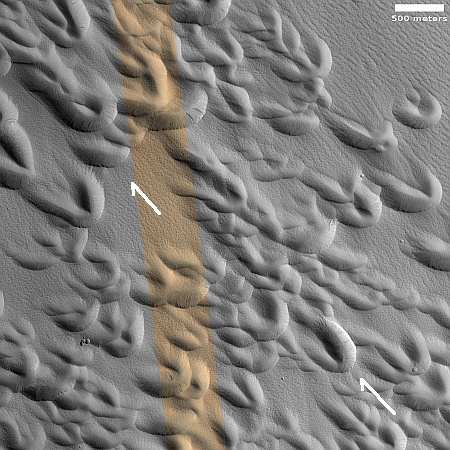
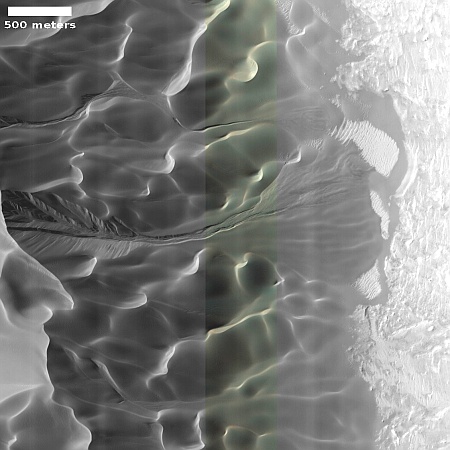
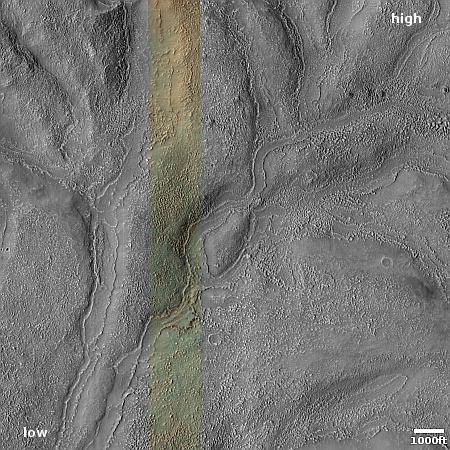
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on April 13, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the MRO science team labels as “streamlined features”, though that doesn’t seem to me to be the best description.
Granted, the prevailing winds, from the northeast to the southwest, appear to pushing the sand dune fields to the southwest. The dark line — created recently by a dust devil — indicates the wind direction. The mesas, from 100 to 200 feet high, do not however appear very streamlined. Instead, they simply look like they are poking up through this sea of sand and dunes, with the wind able over time to successfully push that sand uphill a hundred-plus feet into the saddle between the mesas.
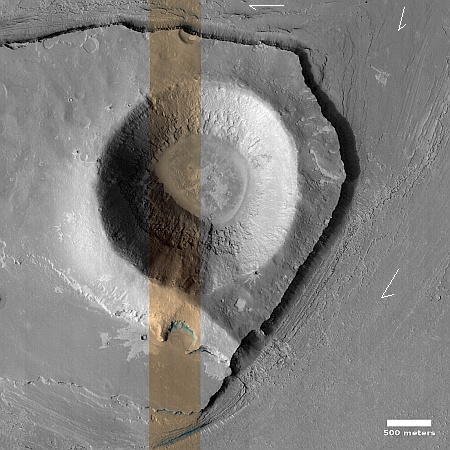
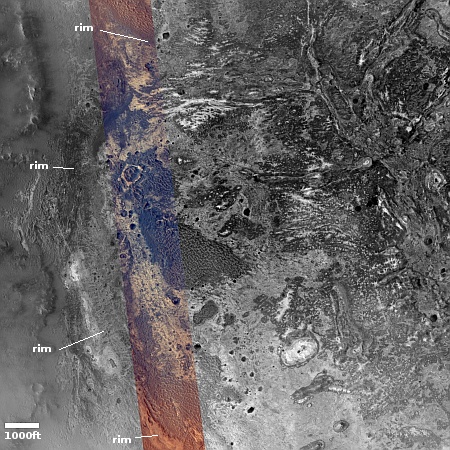
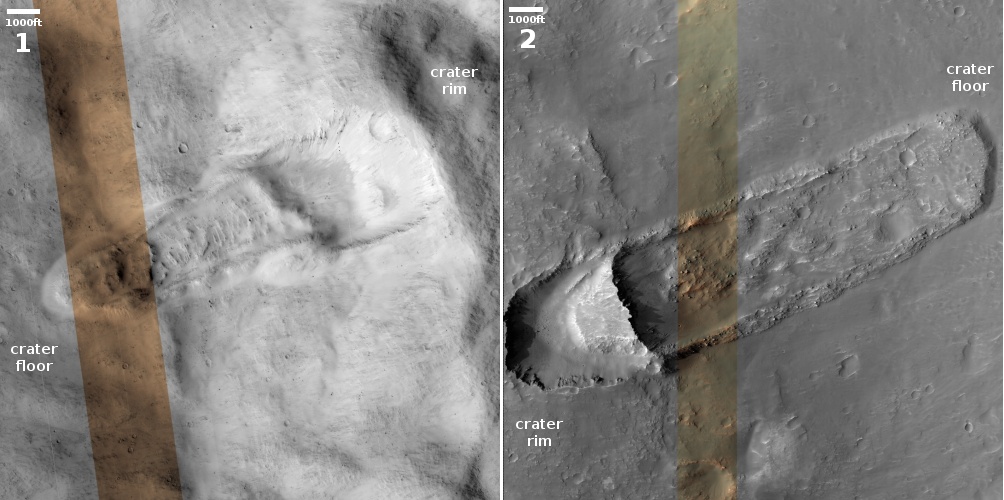
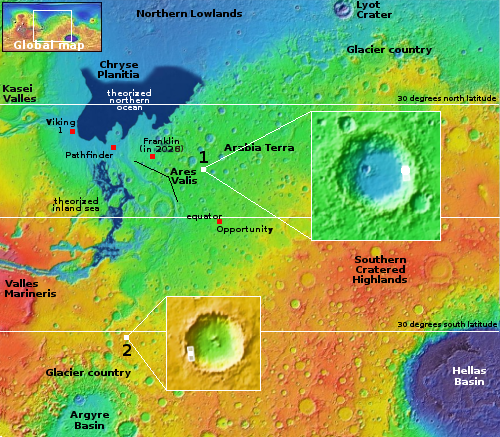
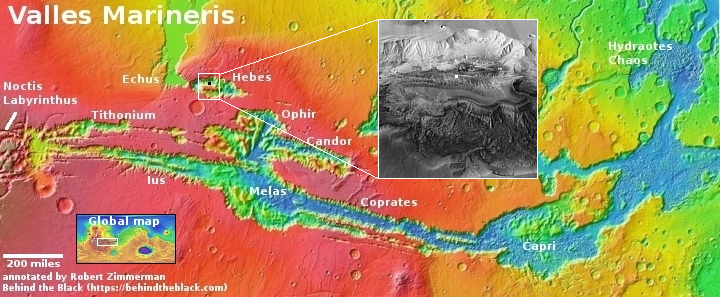
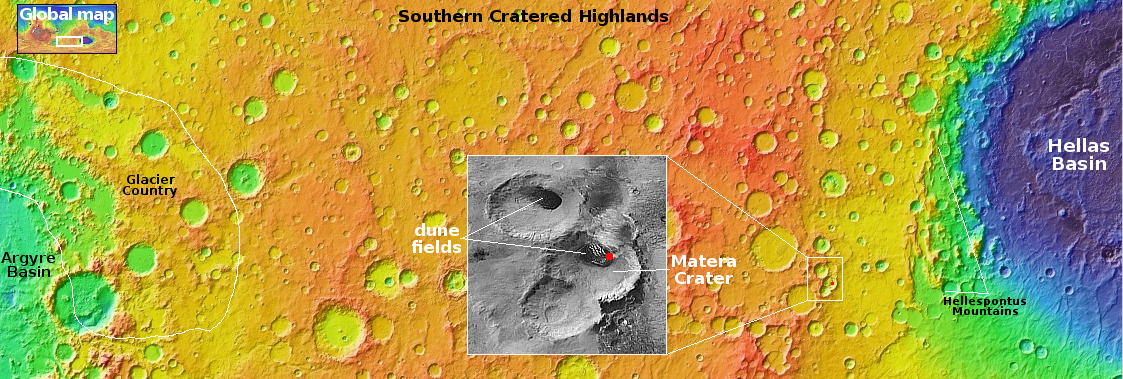
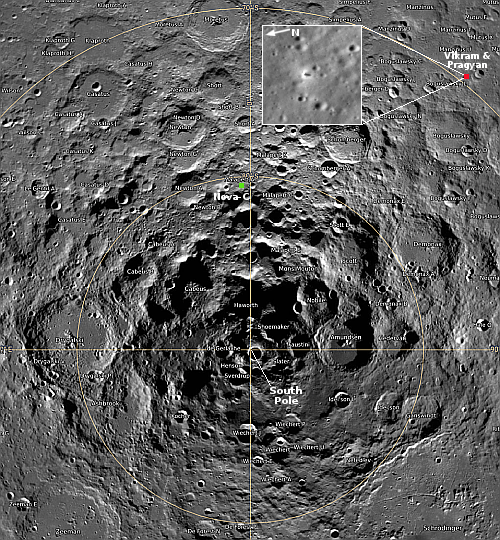
The overview map below provides some context and possibly an explanation, though not a very conclusive one.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on April 13, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the MRO science team labels as “streamlined features”, though that doesn’t seem to me to be the best description.
Granted, the prevailing winds, from the northeast to the southwest, appear to pushing the sand dune fields to the southwest. The dark line — created recently by a dust devil — indicates the wind direction. The mesas, from 100 to 200 feet high, do not however appear very streamlined. Instead, they simply look like they are poking up through this sea of sand and dunes, with the wind able over time to successfully push that sand uphill a hundred-plus feet into the saddle between the mesas.
The overview map below provides some context and possibly an explanation, though not a very conclusive one.
» Read more