Weird “What the heck?!” pedestal crater on Mars
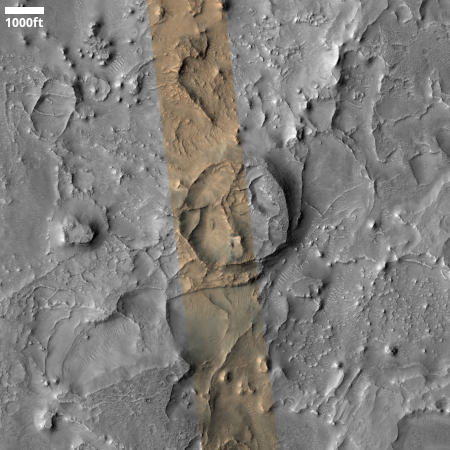
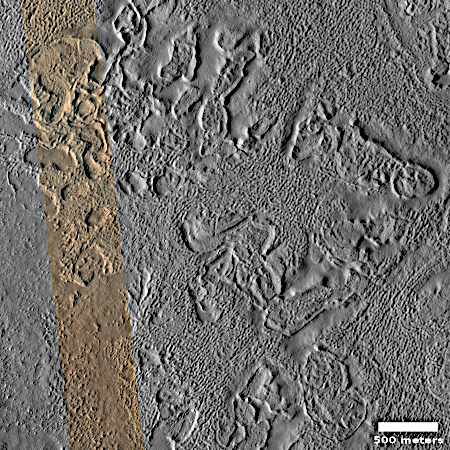
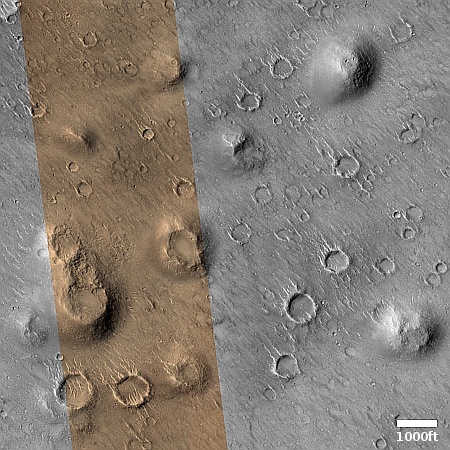
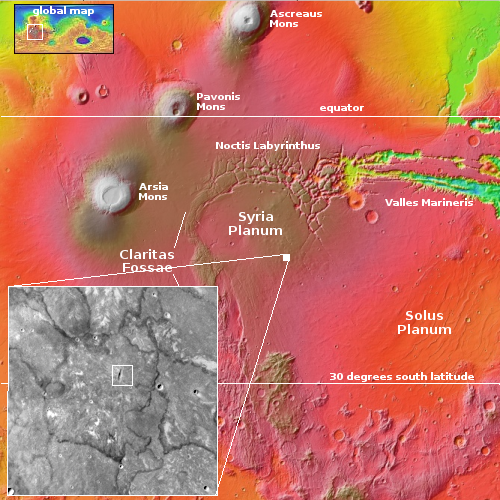
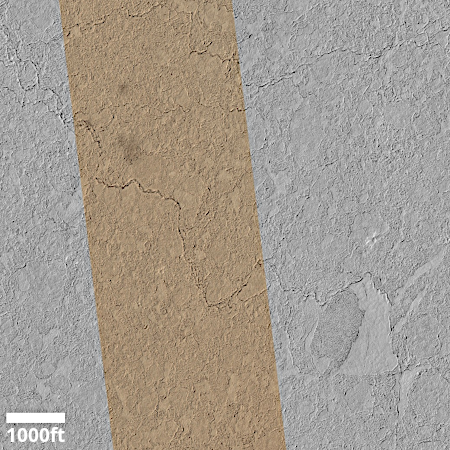
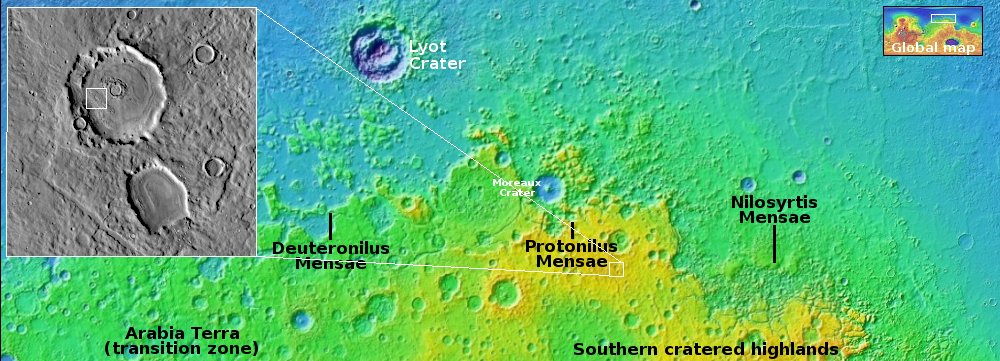
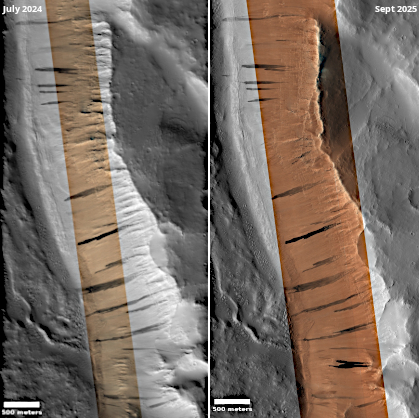
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on August 26, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). While the full image shows what the camera team labels as the “ridges” that cover this area, the most prominent feature in the whole landscape is this half-mile-wide pedestal crater, sitting about 50 to 100 feet above the surrounding terrain.
What makes this strange butte so weird is the plateau on top, criss-crossed with ridges and hollows in a manner that defies any obvious geological explanation.
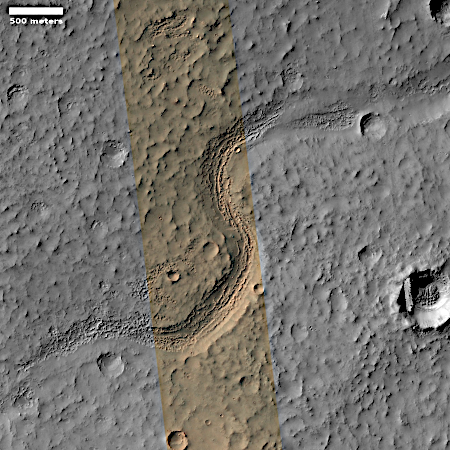
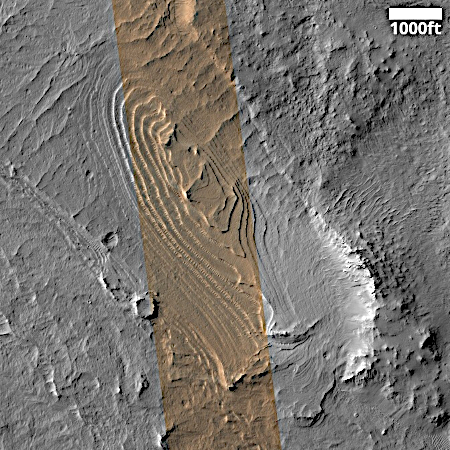
Pedestal craters are not uncommon on Mars, and in fact a bunch of others are found throughout this region. The theory for their formation is that they formed when the surface here was much higher. The impact made the crater floor more dense and resistant to erosion, so as the surrounding terrain wore aware the crater ended up being a butte.
However, pedestal craters usually have relatively smooth tops, making this crater another example of a “What the heck?” image.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on August 26, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). While the full image shows what the camera team labels as the “ridges” that cover this area, the most prominent feature in the whole landscape is this half-mile-wide pedestal crater, sitting about 50 to 100 feet above the surrounding terrain.
What makes this strange butte so weird is the plateau on top, criss-crossed with ridges and hollows in a manner that defies any obvious geological explanation.
Pedestal craters are not uncommon on Mars, and in fact a bunch of others are found throughout this region. The theory for their formation is that they formed when the surface here was much higher. The impact made the crater floor more dense and resistant to erosion, so as the surrounding terrain wore aware the crater ended up being a butte.
However, pedestal craters usually have relatively smooth tops, making this crater another example of a “What the heck?” image.
» Read more