Juno detects the largest volcanic event on Io yet
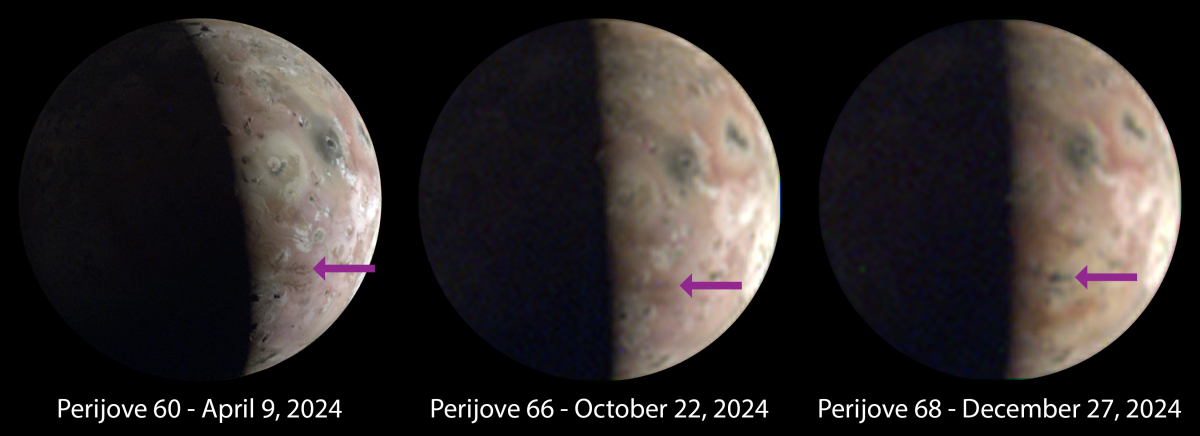

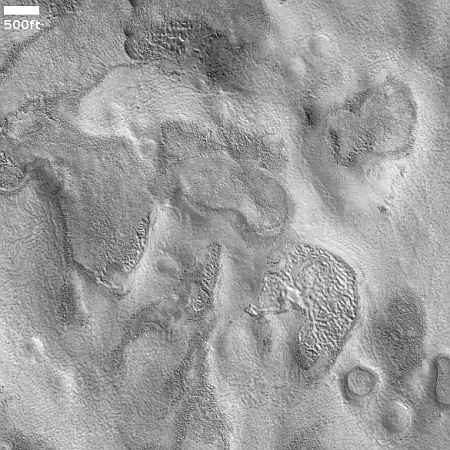
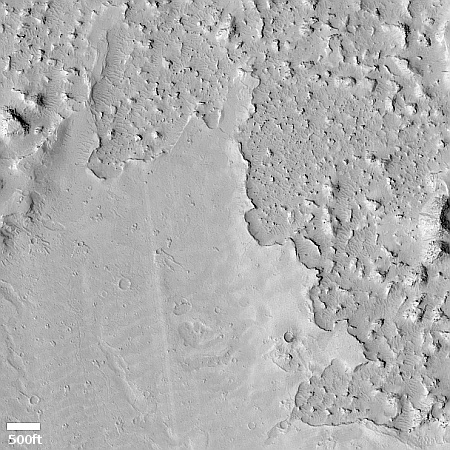
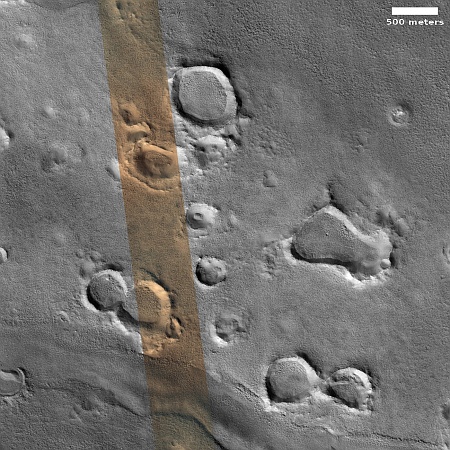
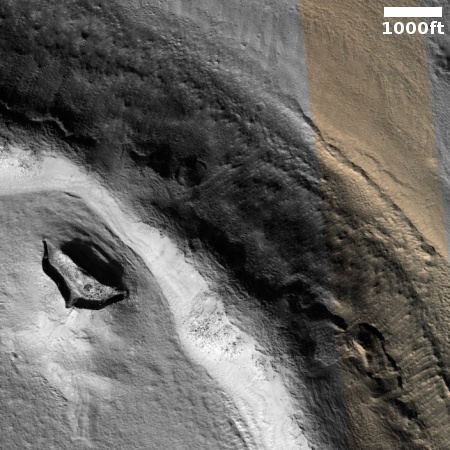
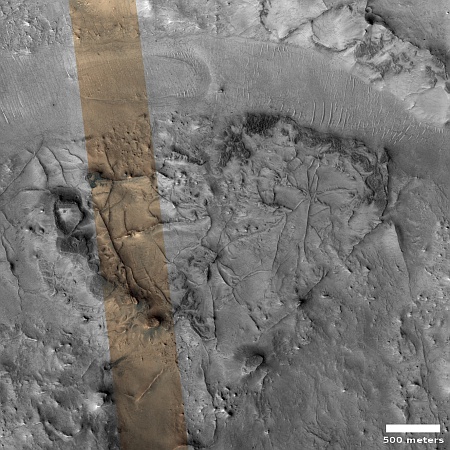
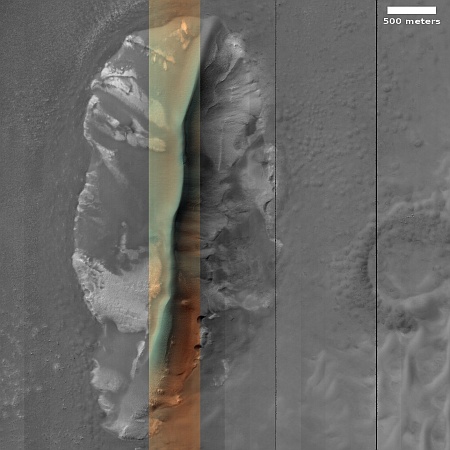
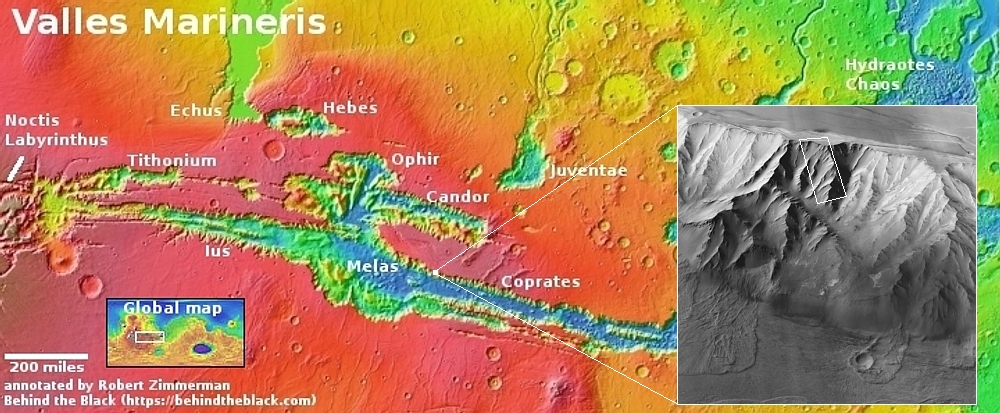
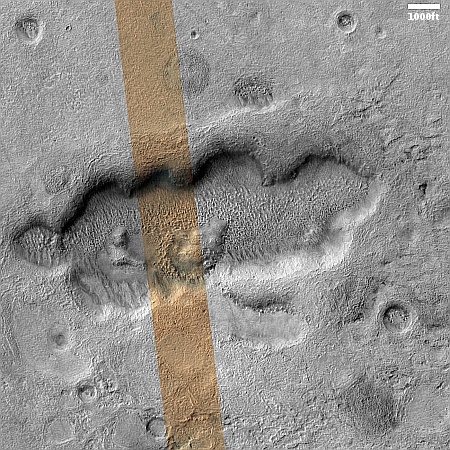
Changes on Io since April 2024. Click for original image.
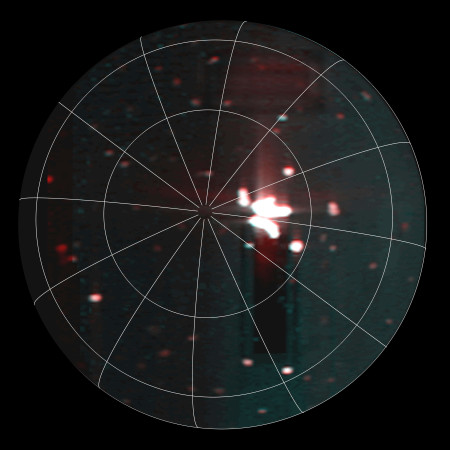
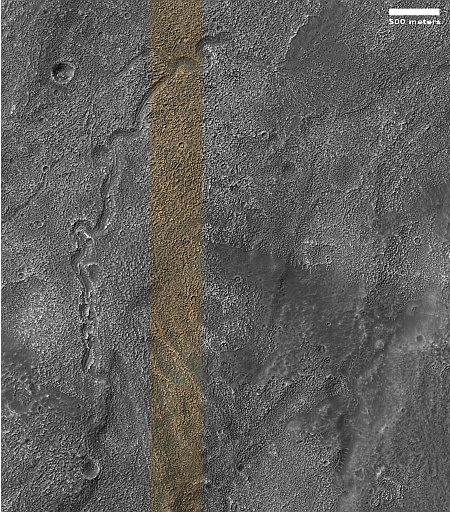
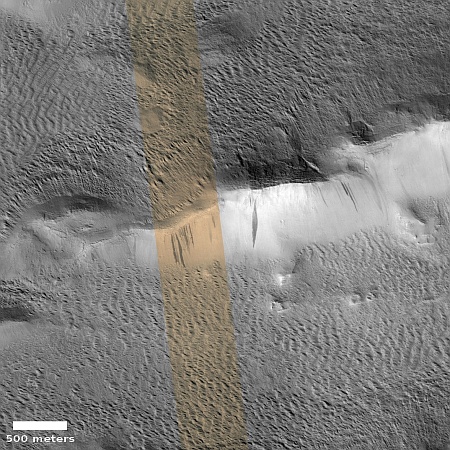
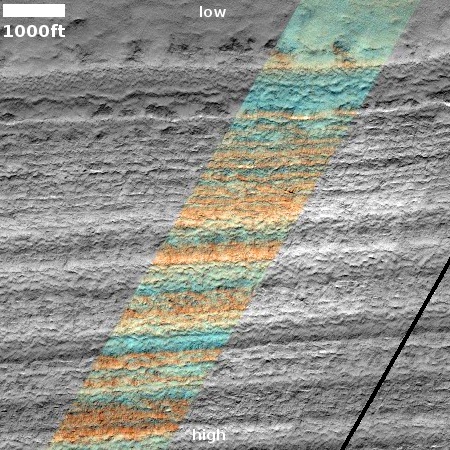
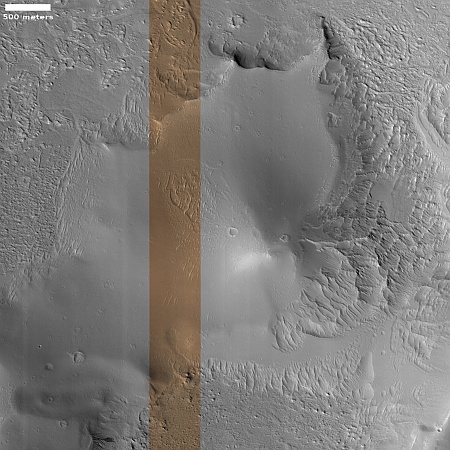
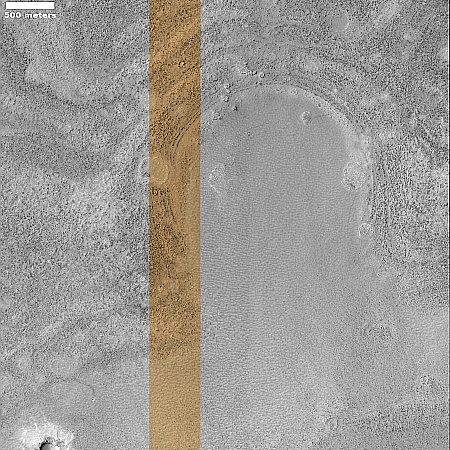
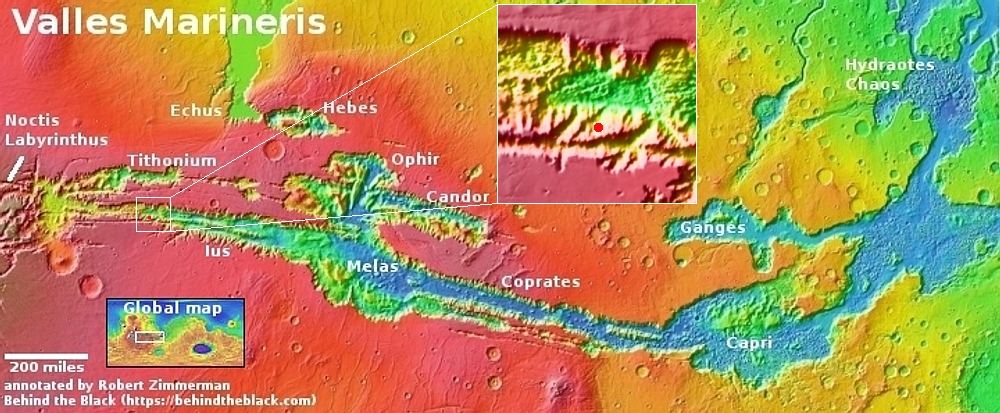
Infrared detection of volcanic hot spot.
Click for original image.
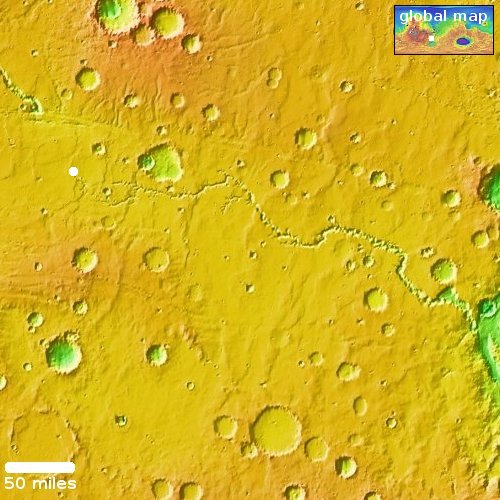
Using Juno’s Italian JIRAM infrared instrument image as well as its optical camera, scientists have detected what appears to be the largest volcanic event yet measured on the Jupiter moon Io, covering an area larger than Lake Superior,
Scientists with NASA’s Juno mission have discovered a volcanic hot spot in the southern hemisphere of Jupiter’s moon Io. The hot spot is not only larger than Earth’s Lake Superior, but it also belches out eruptions six times the total energy of all the world’s power plants.
…The JIRAM science team estimates the as-yet-unnamed feature spans 40,000 square miles (100,000 square kilometers). The previous record holder was Io’s Loki Patera, a lava lake of about 7,700 square miles (20,000 square kilometers). The total power value of the new hot spot’s radiance measured well above 80 trillion watts.
The pictures above were taken by Juno’s optical camera during the last three close flyby’s, looking down at the south pole, with the red arrows indicating the change to the pole’s right during each pass. The infrared image to the right shows a similar view during the fly-by, and shows that same hot spot as the bright area to the pole’s right.
Juno will do another fly-by of Io in March, though from a greater distance. Scientists plan to use both instruments to see how this hot spot has changed again since the end of December.

Changes on Io since April 2024. Click for original image.

Infrared detection of volcanic hot spot.
Click for original image.
Using Juno’s Italian JIRAM infrared instrument image as well as its optical camera, scientists have detected what appears to be the largest volcanic event yet measured on the Jupiter moon Io, covering an area larger than Lake Superior,
Scientists with NASA’s Juno mission have discovered a volcanic hot spot in the southern hemisphere of Jupiter’s moon Io. The hot spot is not only larger than Earth’s Lake Superior, but it also belches out eruptions six times the total energy of all the world’s power plants.
…The JIRAM science team estimates the as-yet-unnamed feature spans 40,000 square miles (100,000 square kilometers). The previous record holder was Io’s Loki Patera, a lava lake of about 7,700 square miles (20,000 square kilometers). The total power value of the new hot spot’s radiance measured well above 80 trillion watts.
The pictures above were taken by Juno’s optical camera during the last three close flyby’s, looking down at the south pole, with the red arrows indicating the change to the pole’s right during each pass. The infrared image to the right shows a similar view during the fly-by, and shows that same hot spot as the bright area to the pole’s right.
Juno will do another fly-by of Io in March, though from a greater distance. Scientists plan to use both instruments to see how this hot spot has changed again since the end of December.