InSight team decides to shorten lander’s life to operate seismometer longer
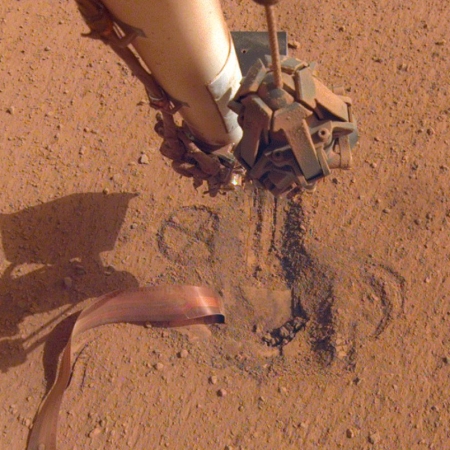
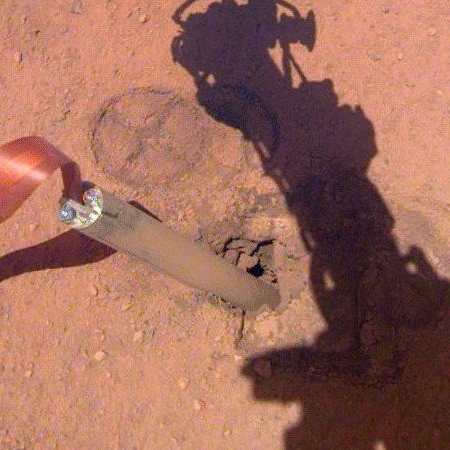
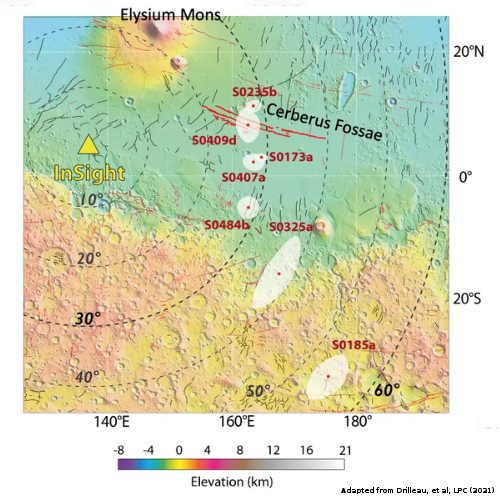
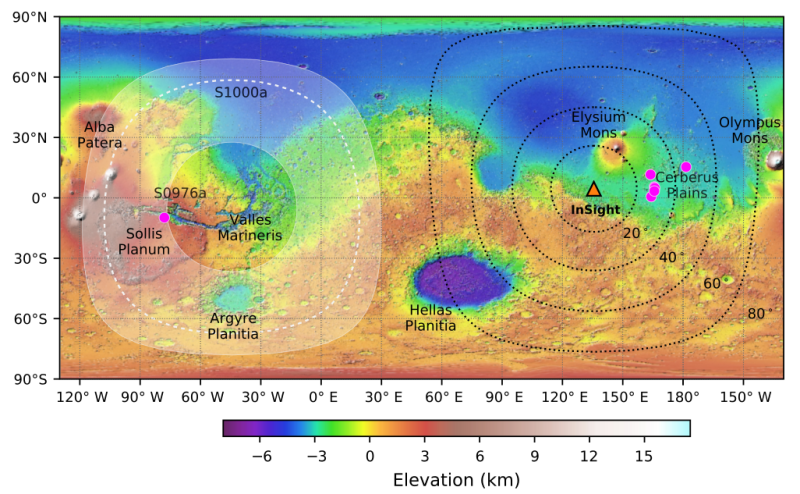
The InSight science team has decided to continue to operate the lander’s seismometer through August rather than turning it off at the end of June, even though that longer use will drain InSight’s batteries sooner and kill the lander shortly thereafter.
The previous plan would have allowed the lander to survive through the end of the year, but would have meant no earthquake data would have been gathered after June.
To enable the seismometer to continue to run for as long as possible, the mission team is turning off InSight’s fault protection system. While this will enable the instrument to operate longer, it leaves the lander unprotected from sudden, unexpected events that ground controllers wouldn’t have time to respond to.
“The goal is to get scientific data all the way to the point where InSight can’t operate at all, rather than conserve energy and operate the lander with no science benefit,” said Chuck Scott, InSight’s project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
Apparently they have realized that it is now very unlikely that a dust devil will come by and clear the dust from InSight’s solar panels, so keeping the spacecraft alive longer — but getting no data — does not make sense.
The InSight science team has decided to continue to operate the lander’s seismometer through August rather than turning it off at the end of June, even though that longer use will drain InSight’s batteries sooner and kill the lander shortly thereafter.
The previous plan would have allowed the lander to survive through the end of the year, but would have meant no earthquake data would have been gathered after June.
To enable the seismometer to continue to run for as long as possible, the mission team is turning off InSight’s fault protection system. While this will enable the instrument to operate longer, it leaves the lander unprotected from sudden, unexpected events that ground controllers wouldn’t have time to respond to.
“The goal is to get scientific data all the way to the point where InSight can’t operate at all, rather than conserve energy and operate the lander with no science benefit,” said Chuck Scott, InSight’s project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
Apparently they have realized that it is now very unlikely that a dust devil will come by and clear the dust from InSight’s solar panels, so keeping the spacecraft alive longer — but getting no data — does not make sense.