Three new papers find sugars, “gum,” and lots of stardust in the samples brought back from the asteroid Bennu
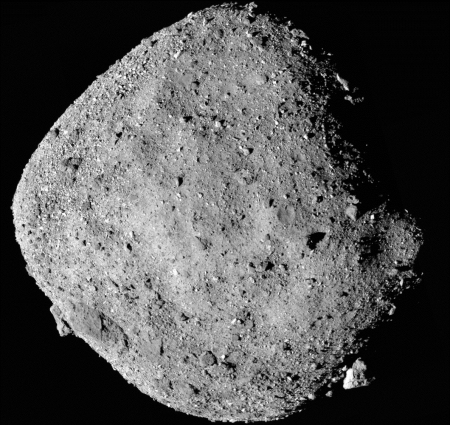

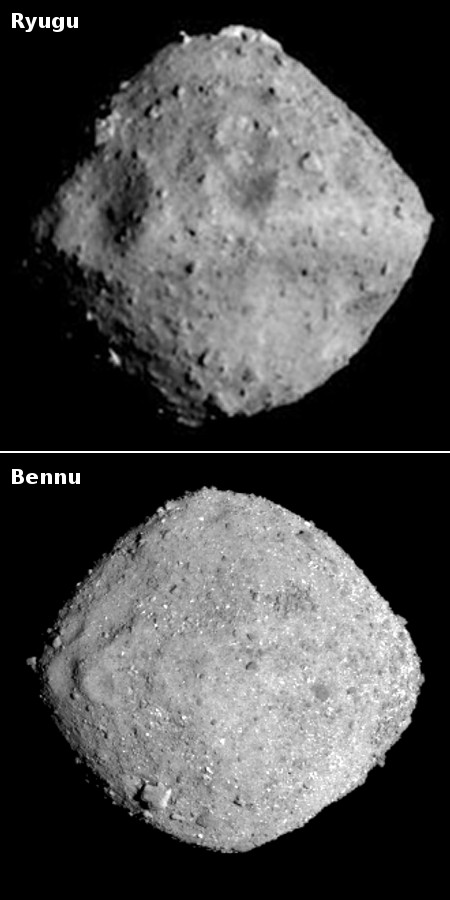
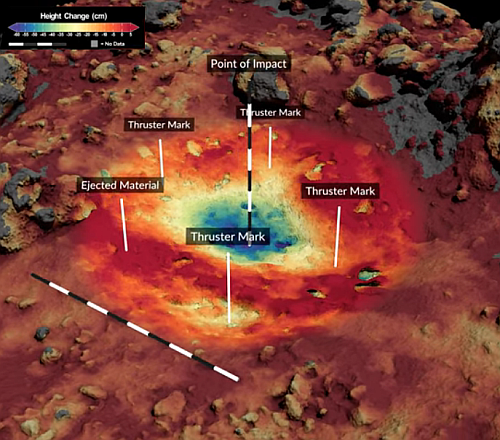
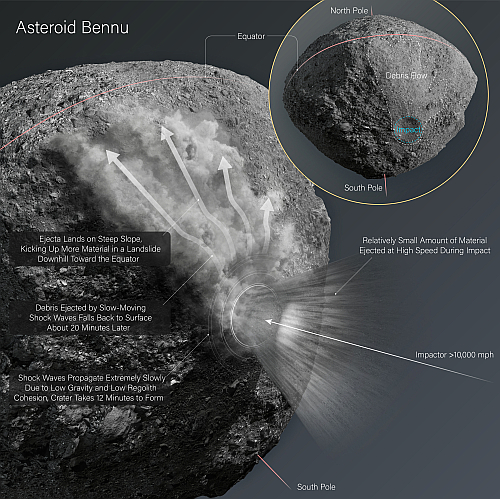
The asteroid Bennu
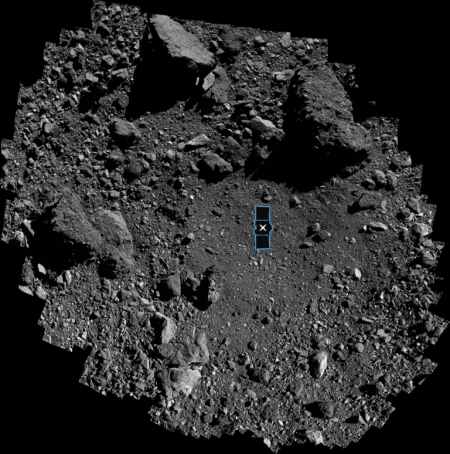
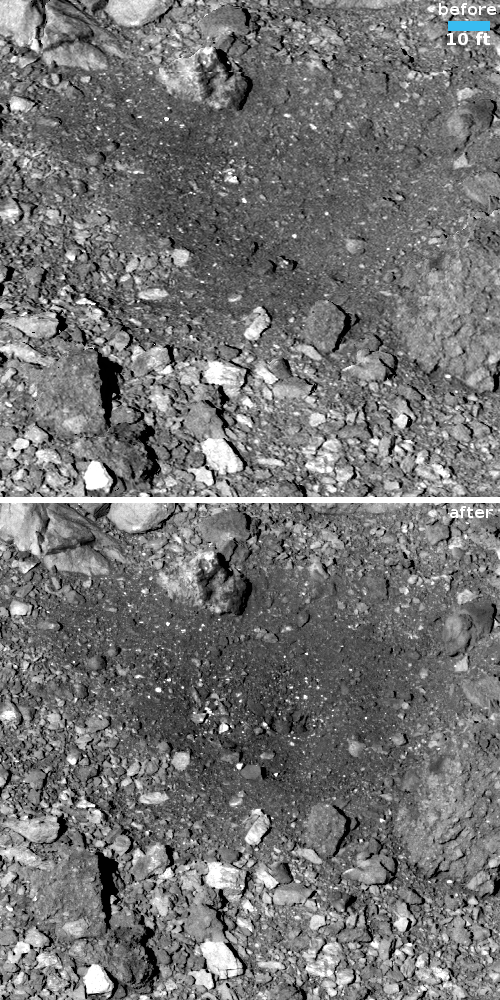
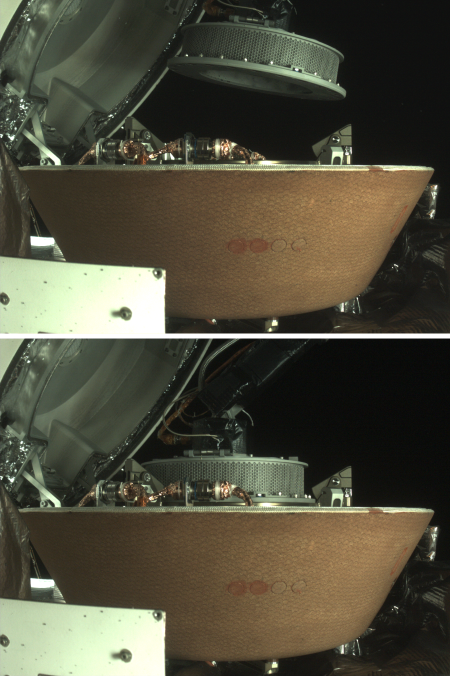
Three new papers published this week have found that the samples brought back by OSIRIS-REx from the asteroid Bennu contained some unexpected or unusual materials, including sugars that are important for biology, a gumlike material never seen before, and a much higher amount of stardust than expected.
The papers can be read here, here, and here.
As the press release notes, describing the sugar discovery:
The five-carbon sugar ribose and, for the first time in an extraterrestrial sample, six-carbon glucose were found. Although these sugars are not evidence of life, their detection, along with previous detections of amino acids, nucleobases, and carboxylic acids in Bennu samples, show building blocks of biological molecules were widespread throughout the solar system.
The stardust results found six-times the abundance previously found in other samples.
As for the “gum”, this was possibly the strangest discovery of all, coming from the solar system’s earliest time period.
» Read more

The asteroid Bennu
Three new papers published this week have found that the samples brought back by OSIRIS-REx from the asteroid Bennu contained some unexpected or unusual materials, including sugars that are important for biology, a gumlike material never seen before, and a much higher amount of stardust than expected.
The papers can be read here, here, and here.
As the press release notes, describing the sugar discovery:
The five-carbon sugar ribose and, for the first time in an extraterrestrial sample, six-carbon glucose were found. Although these sugars are not evidence of life, their detection, along with previous detections of amino acids, nucleobases, and carboxylic acids in Bennu samples, show building blocks of biological molecules were widespread throughout the solar system.
The stardust results found six-times the abundance previously found in other samples.
As for the “gum”, this was possibly the strangest discovery of all, coming from the solar system’s earliest time period.
» Read more