OSIRIS-REx’s sample grab at Bennu in 2020 proved the rubble-pile asteroid has far less cohesion than predicted
The OSIRIS-REx science team, using data gathered during the spacecraft’s sample grab at Bennu in 2020, has determined that the rubble-pile asteroid has far less cohesion than predicted, with its rubble behaving less like a solid object and more like the playground ball-pits found in amusement parks.
After analyzing data gathered when NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft collected a sample from asteroid Bennu in October 2020, scientists have learned something astonishing: The spacecraft would have sunk into Bennu had it not fired its thrusters to back away immediately after it grabbed dust and rock from the asteroid’s surface.
It turns out that the particles making up Bennu’s exterior are so loosely packed and lightly bound to each other that if a person were to step onto Bennu they would feel very little resistance, as if stepping into a pit of plastic balls that are popular play areas for kids.
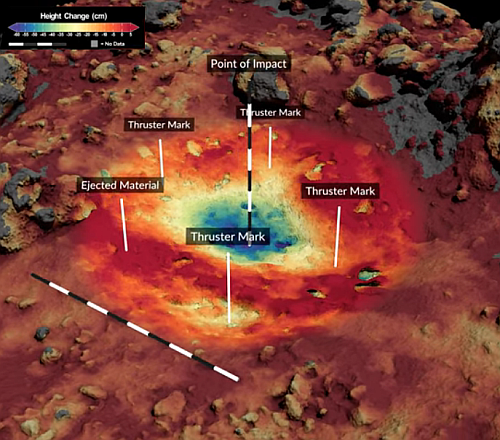
The image above shows what the touch down crater looked like after the sample grab, taken from the video that was part of the press release. The false colors indicate the depth changes produced by the touch down. The final crater was 26 feet across and more than two feet in depth, far larger than expected. Moreover, the energy from the spacecraft’s thrusters as it lifted off had increased the size of that crater further, by about 40%.
These results about the asteroid’s lack of cohesion match the earlier results studying a different impact crater on Bennu.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News

The OSIRIS-REx science team, using data gathered during the spacecraft’s sample grab at Bennu in 2020, has determined that the rubble-pile asteroid has far less cohesion than predicted, with its rubble behaving less like a solid object and more like the playground ball-pits found in amusement parks.
After analyzing data gathered when NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft collected a sample from asteroid Bennu in October 2020, scientists have learned something astonishing: The spacecraft would have sunk into Bennu had it not fired its thrusters to back away immediately after it grabbed dust and rock from the asteroid’s surface.
It turns out that the particles making up Bennu’s exterior are so loosely packed and lightly bound to each other that if a person were to step onto Bennu they would feel very little resistance, as if stepping into a pit of plastic balls that are popular play areas for kids.
The image above shows what the touch down crater looked like after the sample grab, taken from the video that was part of the press release. The false colors indicate the depth changes produced by the touch down. The final crater was 26 feet across and more than two feet in depth, far larger than expected. Moreover, the energy from the spacecraft’s thrusters as it lifted off had increased the size of that crater further, by about 40%.
These results about the asteroid’s lack of cohesion match the earlier results studying a different impact crater on Bennu.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News


I’ve suggested that asteroid habitats providing protection from solar and cosmic radiation could be made made just by burying a “balloon” deep within an asteroid and inflating it, that looks even more practical now.
That is an interesting idea.
Seeing some ballutes are looked at as aerobrakes, might it survive the outer part sintered into a shell?
The inner shell has cells and other rubble piles put inside and inflated into the ice-cube trays, as it were?
Bennu is a bit small for what I’m thinking, in larger asteroids there’s a depth at which the pressure from the material above means the pressure is at about 1 bar, so in principle a relatively light inflatable structure could give an internal atmosphere of that 1 bar.