Ancient fossil river in the very dry equatorial regions of Mars
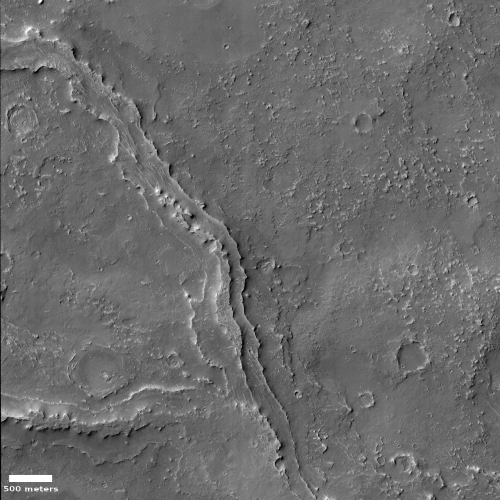
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on August 29, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the scientists label an “inverted channel in Arabia Terra,” a small example of the more than 10,000 miles of fossilized rivers in this region on Mars that scientists have identified using MRO.
They are made of sand and gravel deposited by a river and when the river becomes dry, the channels are left upstanding as the surrounding material erodes. On Earth, inverted channels often occur in dry, desert environments like Oman, Egypt, or Utah, where erosion rates are low – in most other environments, the channels are worn away before they can become inverted. “The networks of inverted channels in Arabia Terra are about 30m high and up to 1–2km wide, so we think they are probably the remains of giant rivers that flowed billions of years ago. [emphasis mine]
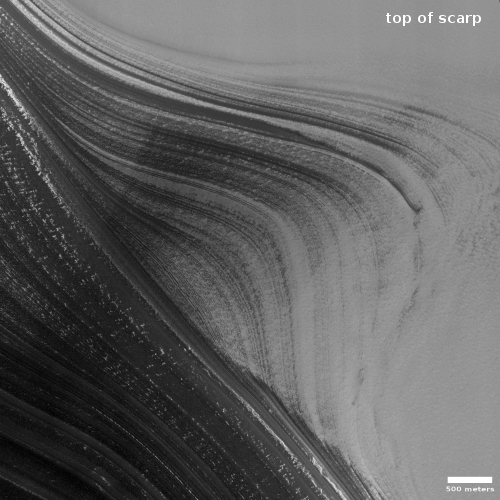
Since this fossilized river is located at 11 degrees north latitude, smack in the middle of the dry equatorial regions of Mars, it has certainly been a dry desert for a very long time. You can see how barren the terrain appears by looking at the wider view afforded by MRO’s context camera below.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on August 29, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the scientists label an “inverted channel in Arabia Terra,” a small example of the more than 10,000 miles of fossilized rivers in this region on Mars that scientists have identified using MRO.
They are made of sand and gravel deposited by a river and when the river becomes dry, the channels are left upstanding as the surrounding material erodes. On Earth, inverted channels often occur in dry, desert environments like Oman, Egypt, or Utah, where erosion rates are low – in most other environments, the channels are worn away before they can become inverted. “The networks of inverted channels in Arabia Terra are about 30m high and up to 1–2km wide, so we think they are probably the remains of giant rivers that flowed billions of years ago. [emphasis mine]
Since this fossilized river is located at 11 degrees north latitude, smack in the middle of the dry equatorial regions of Mars, it has certainly been a dry desert for a very long time. You can see how barren the terrain appears by looking at the wider view afforded by MRO’s context camera below.
» Read more