Philippines issues warning about Chinese rocket debris from launch
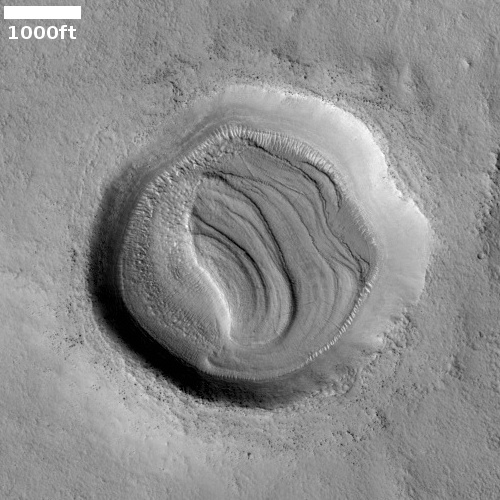
Click for full resolution image.
UPDATE: A tweet from China shows that the strap-on boosters of this rocket crashed near homes in China, though no one was hurt.
Original post:
—————–
The Philippine government issued a statement yesterday warning the public about possible debris from the December 29th launch by China of its Long March 3B rocket.
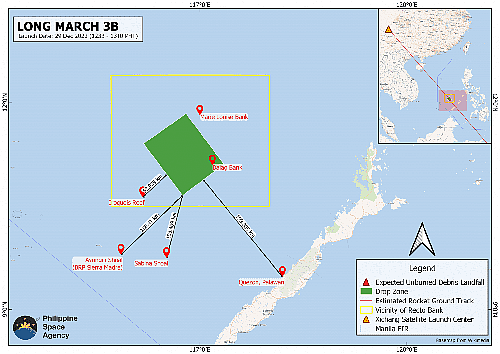
The Philippine Space Agency (PhilSA) is recommending precautionary measures related to expected unburned debris from the Long March 3B rocket scheduled for launch today between 12:33 PM and 01:10 PM Philippine time from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Xichang, Sichuan Province, China. Upon confirmation of planned launch dates, PhilSA immediately issued an advisory to all relevant government agencies on the estimated drop zone area and proposed the issuance of appropriate warnings on air and marine access.
Based on the Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) issued by the Civil Aviation Administration of China (CAAC) to the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines (CAAP), expected unburned debris, such as the rocket boosters and payload fairing, is projected to fall within a drop zone area located within the vicinity of Recto bank, approximately 137 kilometers from Ayungin Shoal and 200 kilometers from Quezon, Palawan. The unburned debris is designed to be discarded as the rocket enters outer space. While not projected to fall on land features or inhabited areas within the Philippine territory, falling debris poses danger and potential risk to ships, aircraft, fishing boats, and other vessels that will pass through the drop zone.
Though the drop zone avoided inhabited areas, it included regions where fisherman worked, and the flight path still flew over inhabited areas. The risk was extremely low, but it appears China also made no effort prior to launch to coordinate this situation with other governments, such as the Philippines. Its warning apparently arrived just before launch. Thus, there was risk that Filipino fisherman were in the drop zone at launch.

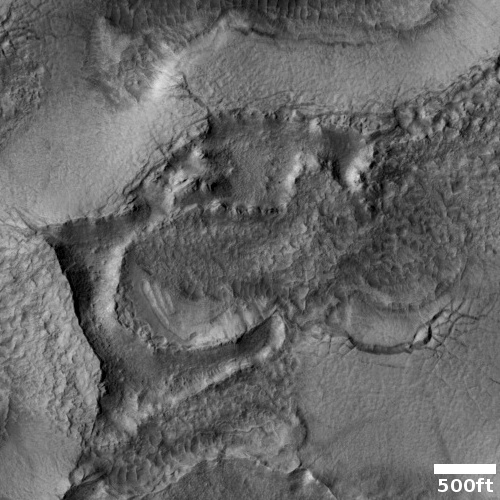
Click for full resolution image.
UPDATE: A tweet from China shows that the strap-on boosters of this rocket crashed near homes in China, though no one was hurt.
Original post:
—————–
The Philippine government issued a statement yesterday warning the public about possible debris from the December 29th launch by China of its Long March 3B rocket.
The Philippine Space Agency (PhilSA) is recommending precautionary measures related to expected unburned debris from the Long March 3B rocket scheduled for launch today between 12:33 PM and 01:10 PM Philippine time from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Xichang, Sichuan Province, China. Upon confirmation of planned launch dates, PhilSA immediately issued an advisory to all relevant government agencies on the estimated drop zone area and proposed the issuance of appropriate warnings on air and marine access.
Based on the Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) issued by the Civil Aviation Administration of China (CAAC) to the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines (CAAP), expected unburned debris, such as the rocket boosters and payload fairing, is projected to fall within a drop zone area located within the vicinity of Recto bank, approximately 137 kilometers from Ayungin Shoal and 200 kilometers from Quezon, Palawan. The unburned debris is designed to be discarded as the rocket enters outer space. While not projected to fall on land features or inhabited areas within the Philippine territory, falling debris poses danger and potential risk to ships, aircraft, fishing boats, and other vessels that will pass through the drop zone.
Though the drop zone avoided inhabited areas, it included regions where fisherman worked, and the flight path still flew over inhabited areas. The risk was extremely low, but it appears China also made no effort prior to launch to coordinate this situation with other governments, such as the Philippines. Its warning apparently arrived just before launch. Thus, there was risk that Filipino fisherman were in the drop zone at launch.