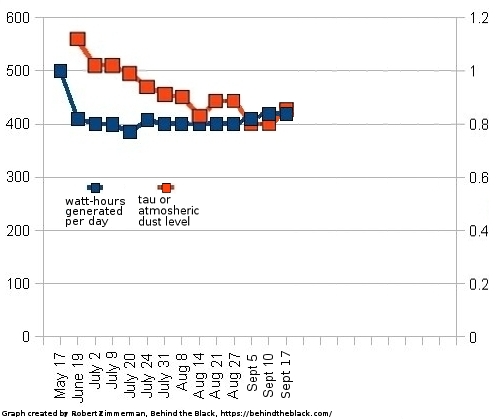
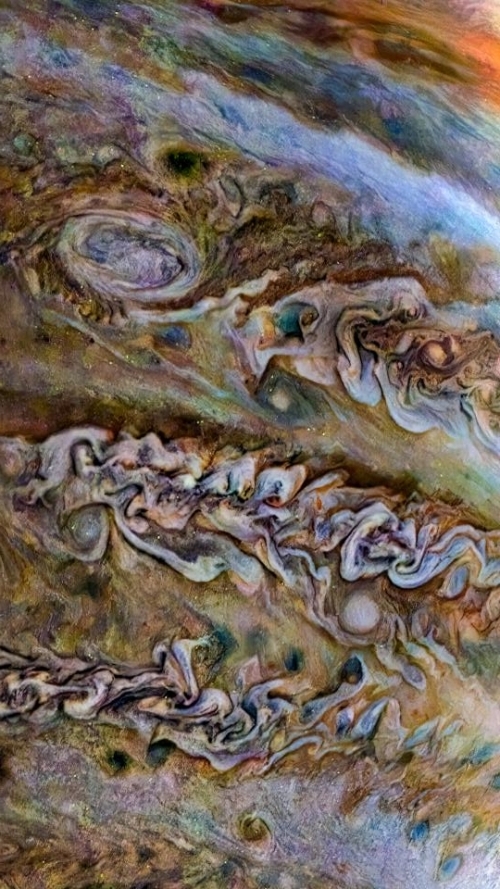
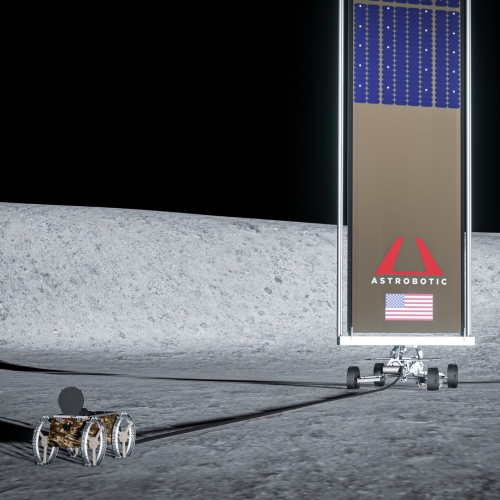
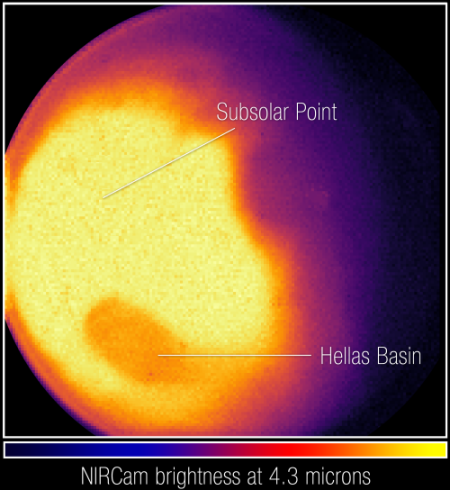
OneWeb announces delivery of 36 satellites to India for launch
Capitalism in space: OneWeb yesterday announced the delivery of 36 satellites to India for launch on that nation’s biggest rocket, the GSLV-Mark3.
Though no date for launch was mentioned, the press release did say this:
One additional launch will take place this year and three more are targeted for early next year to complete the constellation.
This suggests two launches before the end of the year, one by India with the second already contracted to SpaceX. As for the three launches next year, it is unclear yet who will launch them. OneWeb has contracts with SpaceX, Relativity, and NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), the commercial arm of India’s government space program which is doing this year’s GSLV launch. While Relativity has not yet launched, either SpaceX or NSIL could handle those launches for sure next year.
Capitalism in space: OneWeb yesterday announced the delivery of 36 satellites to India for launch on that nation’s biggest rocket, the GSLV-Mark3.
Though no date for launch was mentioned, the press release did say this:
One additional launch will take place this year and three more are targeted for early next year to complete the constellation.
This suggests two launches before the end of the year, one by India with the second already contracted to SpaceX. As for the three launches next year, it is unclear yet who will launch them. OneWeb has contracts with SpaceX, Relativity, and NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), the commercial arm of India’s government space program which is doing this year’s GSLV launch. While Relativity has not yet launched, either SpaceX or NSIL could handle those launches for sure next year.