Buried glaciers flowing off of Martian mesa
Cool image time! Planetary geologists now think that the mid-latitudes of Mars contain many buried and inactive glaciers, formed several million years ago when the planet’s inclination was more than 50 degrees [pdf], rather than the 25 degrees it is now. At that time the mid-latitudes were actually colder than the poles, and water would sublimate from the poles to the colder mid-latitudes to pile up as snow and glaciers.
With today’s 25 degree inclination those mid-latitude glaciers are inactive, and have been so for several million years. It might even be that Mars’ water is beginning a shift back to the poles, but this is uncertain. If anything the planet is presently in a balance, and won’t start transferring water back to the poles until its inclination drops closer to zero.
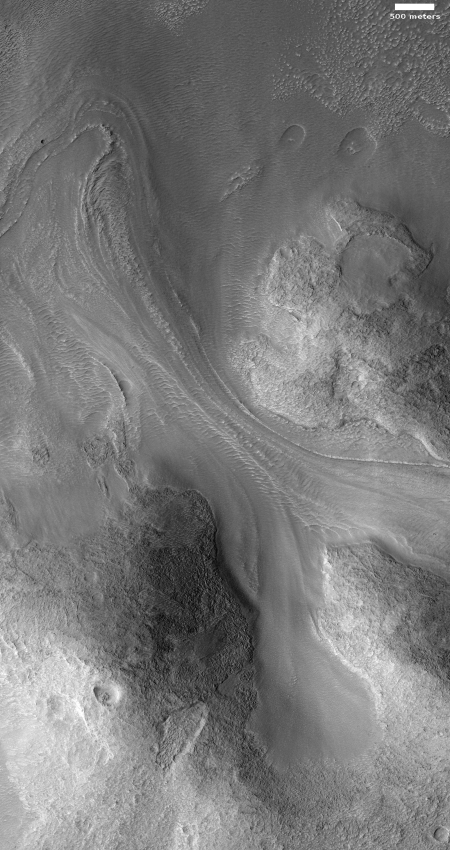
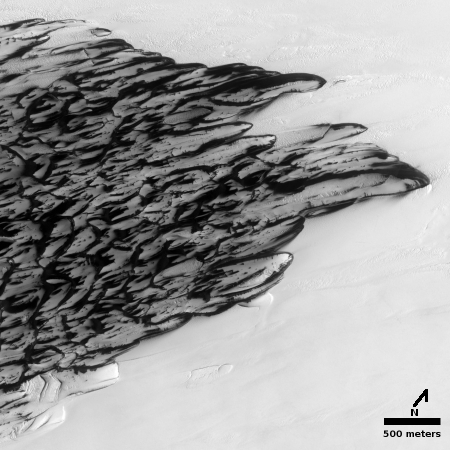
The image to the right, taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on September 23, 2019, is of one of those glacial flows, coming off a mesa in a region called Protonilus Mensae, located in the transition zone between the southern highlands and the northern lowland plains where an intermittent ocean might have once existed.
Much of the geology of Protonilus Mensae is chaos terrain, places where the surface has eroded along angled fissures to form many mesas. The overview map below focuses in on the particular mesa where this flow is located. The red boxes indicate all the MRO images taken of this mesa, with the image above indicated by the black dot.
» Read more
Cool image time! Planetary geologists now think that the mid-latitudes of Mars contain many buried and inactive glaciers, formed several million years ago when the planet’s inclination was more than 50 degrees [pdf], rather than the 25 degrees it is now. At that time the mid-latitudes were actually colder than the poles, and water would sublimate from the poles to the colder mid-latitudes to pile up as snow and glaciers.
With today’s 25 degree inclination those mid-latitude glaciers are inactive, and have been so for several million years. It might even be that Mars’ water is beginning a shift back to the poles, but this is uncertain. If anything the planet is presently in a balance, and won’t start transferring water back to the poles until its inclination drops closer to zero.
The image to the right, taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on September 23, 2019, is of one of those glacial flows, coming off a mesa in a region called Protonilus Mensae, located in the transition zone between the southern highlands and the northern lowland plains where an intermittent ocean might have once existed.
Much of the geology of Protonilus Mensae is chaos terrain, places where the surface has eroded along angled fissures to form many mesas. The overview map below focuses in on the particular mesa where this flow is located. The red boxes indicate all the MRO images taken of this mesa, with the image above indicated by the black dot.
» Read more