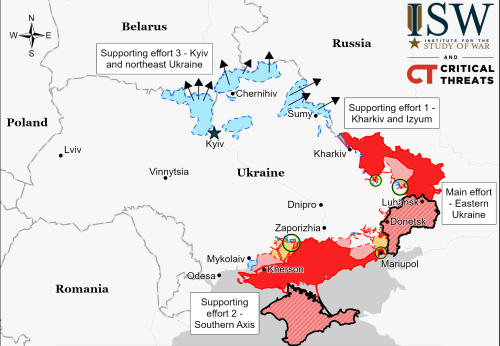
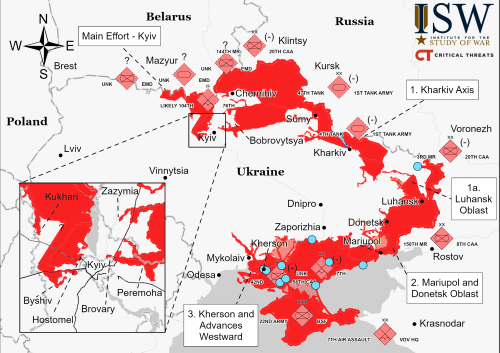
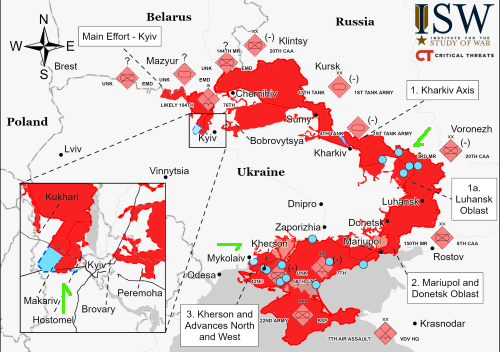
Ukrainian rocket for Nova Scotia spaceport so far unaffected by war
Capitalism in space: According to the CEO of Maritime Launch Services, the Canadian company that is building a spaceport in Nova Scotia, work on the Ukrainian Cyclone-4M rocket that the spaceport wants to offer customers has as yet not been impacted by the invasion by Russia.
Steve Matier, CEO of Maritime Launch Services, says daily planning work continues with the makers of the Cyclone-4M rocket, who are based in Dnipro, Ukraine. Matier said in an interview Tuesday his company still hopes to conduct its first launch sometime in 2023, once it gets final construction and environmental approval from the province for its proposed facilities near Canso, N.S.
However, Matier also said the first launches from the spaceport will not use the Cyclone. Instead, these launches would use smaller unnamed rockets putting smaller payloads in lower orbit. Since the company’s initial business model had been to offer to satellite customers not only the spaceport but the rocket, this statement suggests the company has changed that business model and is now marketing the spaceport to other rocket companies.
Matier’s comments were in connection with the announcement that Maritime has now become a publicly traded company.
Capitalism in space: According to the CEO of Maritime Launch Services, the Canadian company that is building a spaceport in Nova Scotia, work on the Ukrainian Cyclone-4M rocket that the spaceport wants to offer customers has as yet not been impacted by the invasion by Russia.
Steve Matier, CEO of Maritime Launch Services, says daily planning work continues with the makers of the Cyclone-4M rocket, who are based in Dnipro, Ukraine. Matier said in an interview Tuesday his company still hopes to conduct its first launch sometime in 2023, once it gets final construction and environmental approval from the province for its proposed facilities near Canso, N.S.
However, Matier also said the first launches from the spaceport will not use the Cyclone. Instead, these launches would use smaller unnamed rockets putting smaller payloads in lower orbit. Since the company’s initial business model had been to offer to satellite customers not only the spaceport but the rocket, this statement suggests the company has changed that business model and is now marketing the spaceport to other rocket companies.
Matier’s comments were in connection with the announcement that Maritime has now become a publicly traded company.