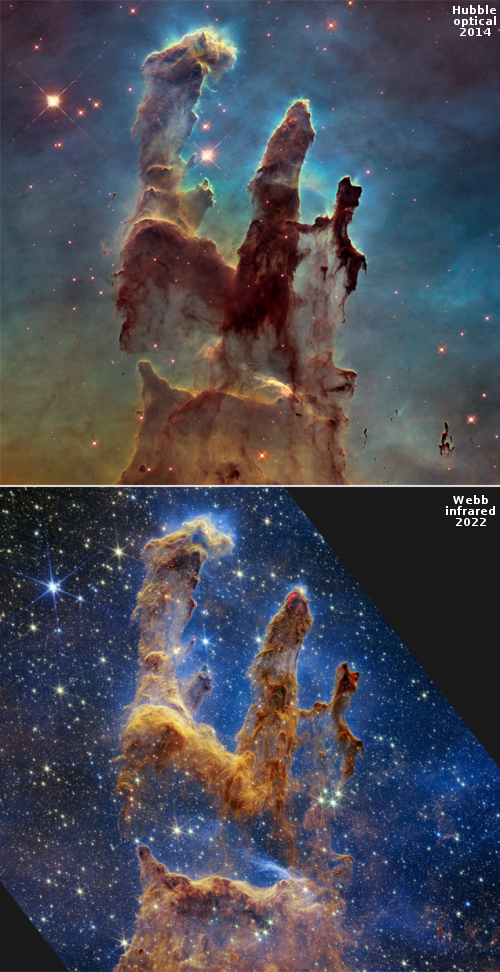
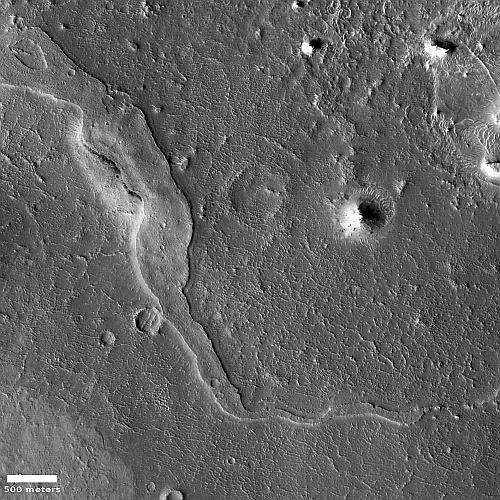
Hubble spots double tail of debris from DART impact of Dimorphus
A series of images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope of the ejecta released when DART crashed into the small 525-foot-wide asteroid Dimorphus has found that debris forming a double tail trailing away from the Sun.
The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on October 11, 2022 by Hubble, and shows those two tails as close parallel debris trails.
Repeated observations from Hubble over the last several weeks have allowed scientists to present a more complete picture of how the system’s debris cloud has evolved over time. The observations show that the ejected material, or “ejecta,” has expanded and faded in brightness as time went on after impact, largely as expected. The twin tail is an unexpected development, although similar behavior is commonly seen in comets and active asteroids. The Hubble observations provide the best-quality image of the double-tail to date.
Following impact, Hubble made 18 observations of the system. Imagery indicates the second tail formed between 2-8 October 2022.
Though observations by telescope will continue for the years to follow, the real punchline to this event will be when the European probe Hera rendezvouses with the Didymous-Dimorphus pair in 2026 to perform several years of very close observations.
A series of images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope of the ejecta released when DART crashed into the small 525-foot-wide asteroid Dimorphus has found that debris forming a double tail trailing away from the Sun.
The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on October 11, 2022 by Hubble, and shows those two tails as close parallel debris trails.
Repeated observations from Hubble over the last several weeks have allowed scientists to present a more complete picture of how the system’s debris cloud has evolved over time. The observations show that the ejected material, or “ejecta,” has expanded and faded in brightness as time went on after impact, largely as expected. The twin tail is an unexpected development, although similar behavior is commonly seen in comets and active asteroids. The Hubble observations provide the best-quality image of the double-tail to date.
Following impact, Hubble made 18 observations of the system. Imagery indicates the second tail formed between 2-8 October 2022.
Though observations by telescope will continue for the years to follow, the real punchline to this event will be when the European probe Hera rendezvouses with the Didymous-Dimorphus pair in 2026 to perform several years of very close observations.