Colliding glaciers
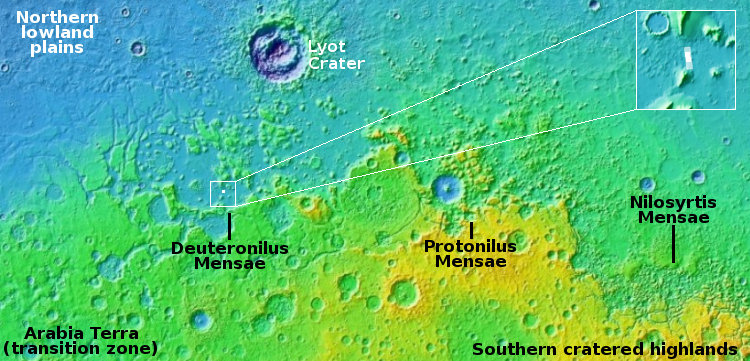
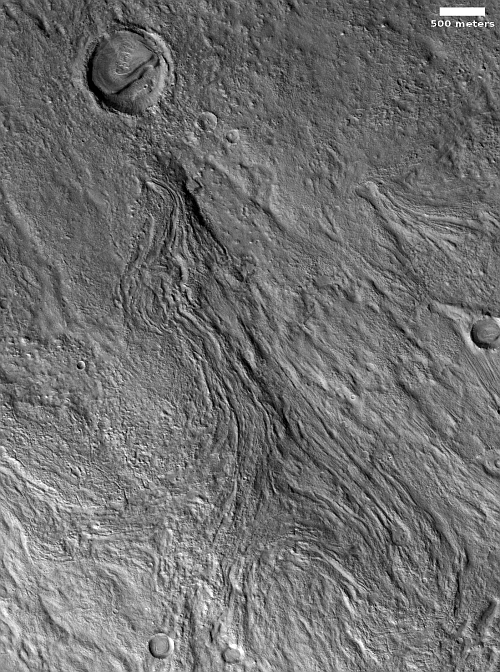
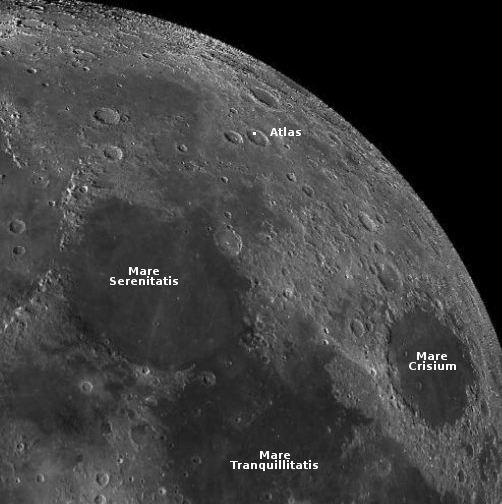
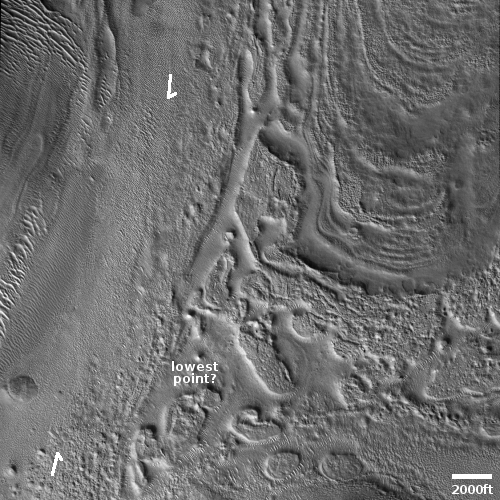
For today’s cool image we return once again to glacier country in the northern mid-latitudes of Mars. The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on August 28, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a spot where I think glacial flows coming from the north and south have collided at a low point. The white dot in the box on the overview map above marks its location, with the inset showing the mesas to the north and south that suggest this flow pattern.
What makes these colliding flows especially cool is the source of the northern flow. It appears that came out of the impact heat from that crater, which caused the ice on the downhill side to flow. You can also see the same phenomenon a short distance to the east, with a much smaller crater, likely a secondary impact from the first.
Note also the glacial fill inside the larger crater. This impact happened on top of older glaciers, but later climate cycles caused more ice to be deposited within the crater afterward. That this glacial fill appears terraced and thus layered also suggests that there were several if not many such later climate cycles.

For today’s cool image we return once again to glacier country in the northern mid-latitudes of Mars. The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on August 28, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a spot where I think glacial flows coming from the north and south have collided at a low point. The white dot in the box on the overview map above marks its location, with the inset showing the mesas to the north and south that suggest this flow pattern.
What makes these colliding flows especially cool is the source of the northern flow. It appears that came out of the impact heat from that crater, which caused the ice on the downhill side to flow. You can also see the same phenomenon a short distance to the east, with a much smaller crater, likely a secondary impact from the first.
Note also the glacial fill inside the larger crater. This impact happened on top of older glaciers, but later climate cycles caused more ice to be deposited within the crater afterward. That this glacial fill appears terraced and thus layered also suggests that there were several if not many such later climate cycles.