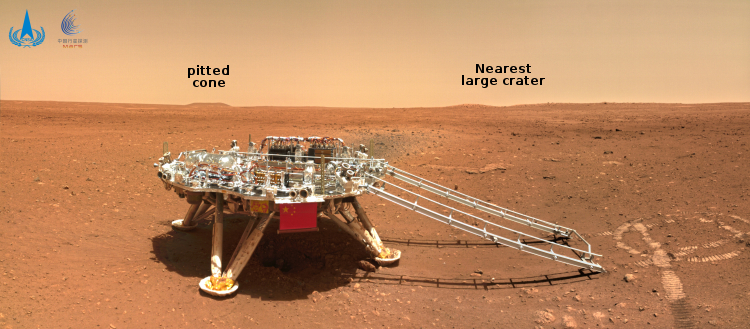
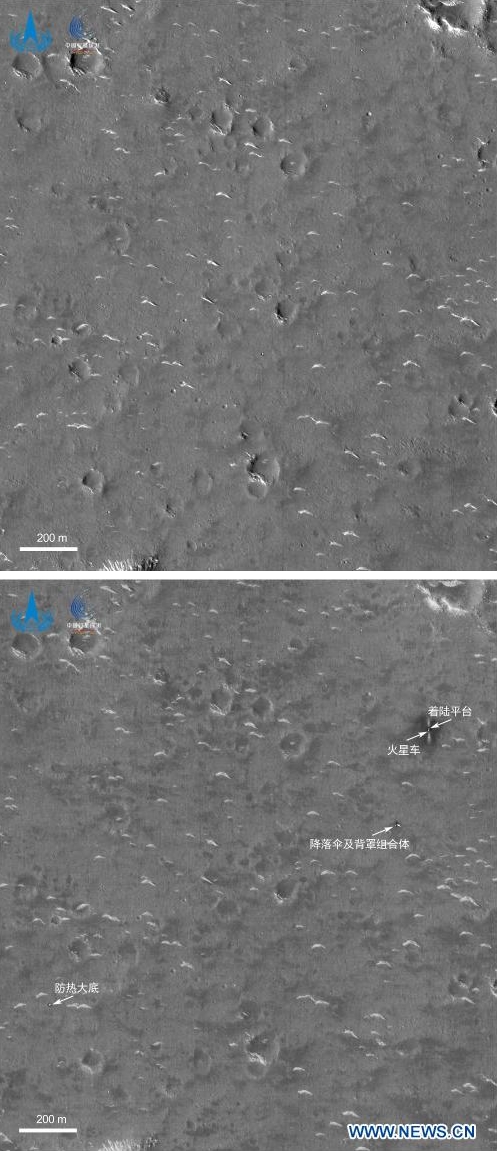
Brazil signs Artemis Accords
Brazil on June 15th became the first South American country to sign the Artemis Accords, designed to bypass the limitations placed on property rights created by the Outer Space Treaty.
U.S. policy requires any nation that wishes to participate in its Artemis program to go back to the Moon to agree to the accords. Brazil is now the eleventh country to sign, joining Australia, Canada, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, New Zealand, South Korea, the United Kingdom, the United Arab Emirates, Ukraine, and the United States.
Russia and China oppose the accords, which causes a problem for Russia as it desperately needs to partner with someone because it can’t on its own afford to build much. It is negotiating possible partnerships with China at its new space station as well as building a base on the Moon, but those agreements are not firm. And continues to send out feelers, including statements by Putin, calling for continuing cooperation with the U.S. in space.
Whether the Biden administration will make an exception for Russia in regards to the Artemis Accords remains unclear. That twelve countries have agreed to the accords however gives the U.S. greater leverage with those countries that have not yet signed.
Brazil on June 15th became the first South American country to sign the Artemis Accords, designed to bypass the limitations placed on property rights created by the Outer Space Treaty.
U.S. policy requires any nation that wishes to participate in its Artemis program to go back to the Moon to agree to the accords. Brazil is now the eleventh country to sign, joining Australia, Canada, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, New Zealand, South Korea, the United Kingdom, the United Arab Emirates, Ukraine, and the United States.
Russia and China oppose the accords, which causes a problem for Russia as it desperately needs to partner with someone because it can’t on its own afford to build much. It is negotiating possible partnerships with China at its new space station as well as building a base on the Moon, but those agreements are not firm. And continues to send out feelers, including statements by Putin, calling for continuing cooperation with the U.S. in space.
Whether the Biden administration will make an exception for Russia in regards to the Artemis Accords remains unclear. That twelve countries have agreed to the accords however gives the U.S. greater leverage with those countries that have not yet signed.