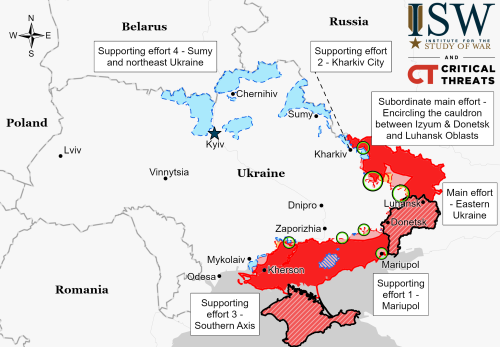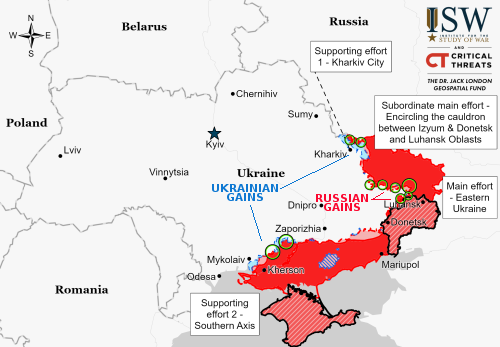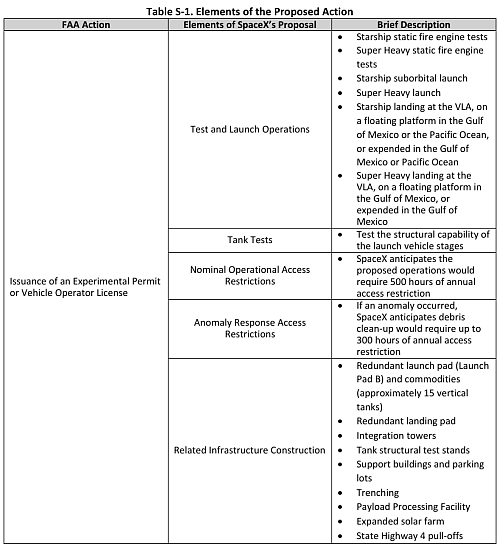
After almost a half year of delays, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) today released its environmental reassessment of SpaceX’s operations in Boca Chica, Texas, possibly recommending that future launches of Starship/Superheavy be allowed at that location but also leaving open the continuing ability of the federal government to block further flight tests.
The FAA determined that the Proposed Action would not result in significant environmental consequences and has issued a Mitigated Finding of No Significant Impact/Record of Decision (FONSI/ROD). … Required mitigation measures are listed throughout Chapter 3 of the final PEA [the environmental reassessment]. Should any future license or permit be issued to SpaceX to perform any aspect of the Proposed Action, the FAA will ensure that SpaceX implements these mitigation measures as conditions for licensure.
You can read the executive summary here [pdf]. The actual reassessment [referred to as the PEA] can be read here [pdf]. The key quote, on page 2 of the reassessment, is this:
The applicant has provided the FAA with a mission profile of proposed launch operations that is
analyzed in this PEA. The FAA’s Federal Action is to issue experimental permit(s) and/or a vehicle operator license to SpaceX for this mission profile, which is described in more detail in Section 2.1. If SpaceX modifies or adds operations as part of its Starship/Super Heavy program in the future, the FAA would analyze the environmental impacts of those activities in a tiered environmental document, which would summarize the issues discussed in this PEA that remain applicable (e.g., the environment around the Boca Chica launch site) and concentrate on the issues specific to the subsequent action (e.g., a mission profile involving a new landing site).
The completion of the environmental review process does not guarantee that the FAA will issue an experimental permit or vehicle operator license to SpaceX for Starship/Super Heavy launches at the launch site. [emphasis mine]
Essentially, SpaceX — after some revisions based on public comments — provided the FAA a detailed outline of its proposed operations, as summarized by the graph above (taken from the executive summary), and the FAA agreed to that program. However, this agreement by the FAA does not include any actual permits for flights or tests.
Furthermore, this recommendation by the FAA is not final. The reassessment also included in great detail a second option, dubbed the “No Action Alternative”:
Under the No Action Alternative, the FAA would not issue new experimental permits or licenses to SpaceX for any test or launch operations at the Boca Chica Launch Site. In this situation, SpaceX’s production and manufacturing that that do not require a license from the FAA or approval by any other federal agencies would continue at its existing facilities and production and manufacturing infrastructure would expand. Testing operations, including tank tests and static fire engine tests, that do not require approval by the FAA or other federal agencies would also continue at the VLA. In addition, SpaceX could conduct missions of the Starship prototype launch vehicle as authorized by the current license (LRLO 20‐119). 6 The license expires on May 27, 2023. This alternative provides the basis for comparing the environmental consequences of the Proposed Action.
Under this alternative, SpaceX operations at Boca Chica would be severely limited, and would essentially end in May ’23.
In reviewing both documents, it appears that the FAA has given SpaceX a go-ahead with this reassessment, but done so with many caveats. It will issue SpaceX its launch permits, probably on a per launch basis, each of which will require SpaceX to meet more than 130 pages of further environmental and social justice requirements. As noted in the first quote above, should SpaceX fail to meet any of those mitigation measures, future permits will be blocked.
Furthermore, the reassessment appears to have left it open for the White House to choose the “No Action Alternative.”
In either case this reassessment appears to have given any number of agencies within the federal government — including the White House — the clear ability to block SpaceX’s operations repeatedly, after each test flight.
I suspect SpaceX will immediately apply for a launch permit, and hope that political pressure will force the federal agencies to approve that permit.
NOTE: This analysis is based on a first quick review. The documents are long and purposely written to make it hard to figure out what is being proposed. More review is still required.