Perseverance as seen from orbit
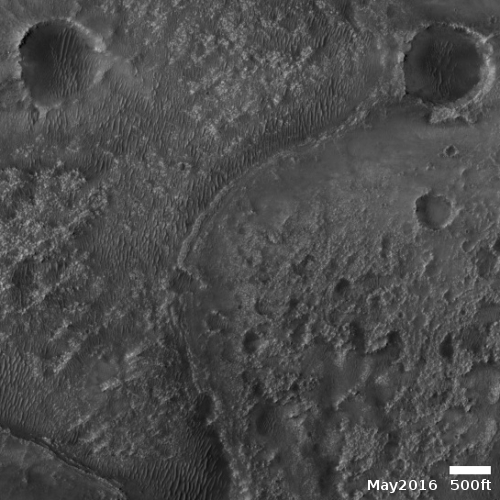
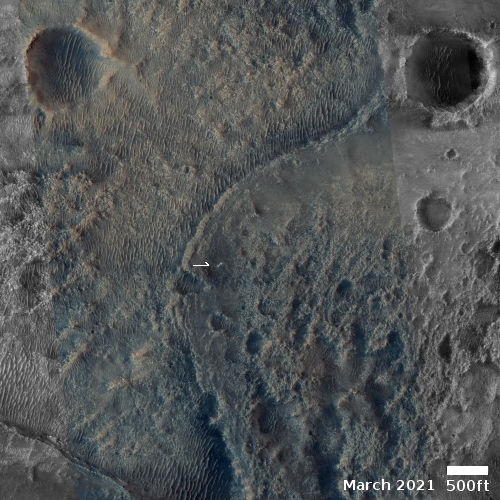
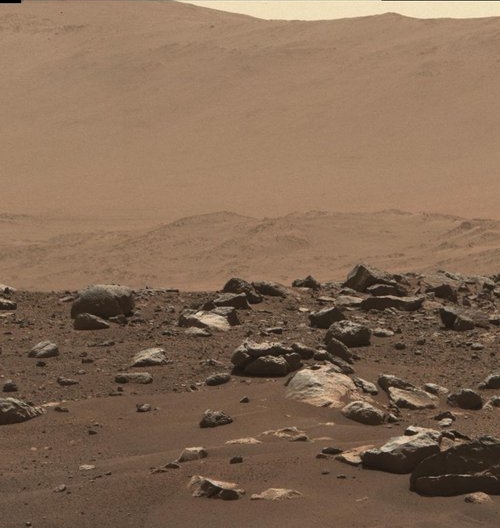
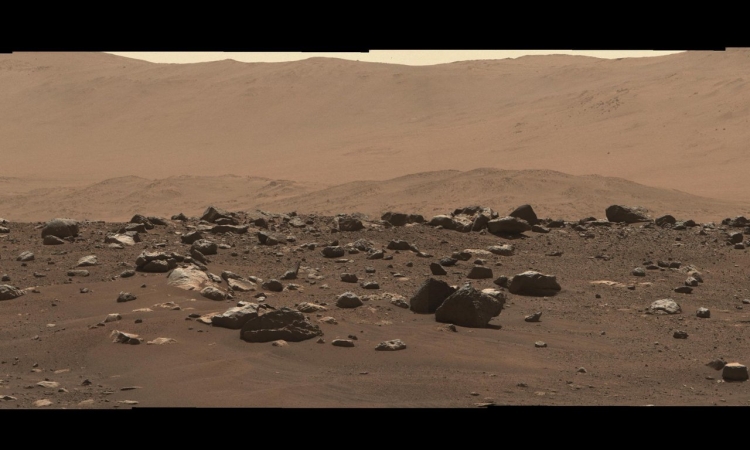
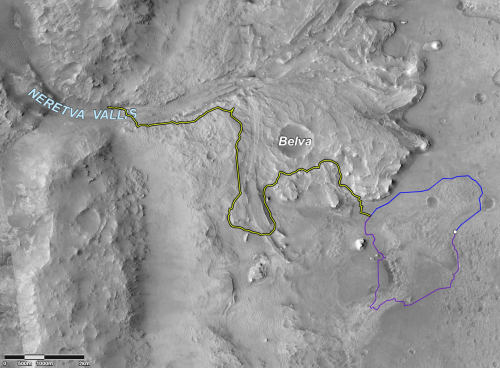
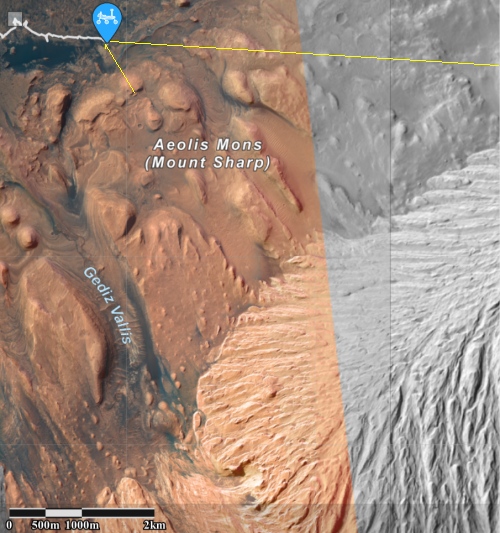
Cool image time! The two photos to the right show the landing site for the Perseverance rover in Jezero Crater on Mars. The first image was taken in 2016 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The second image was made available today in the monthly release of photos taken that camera on MRO.
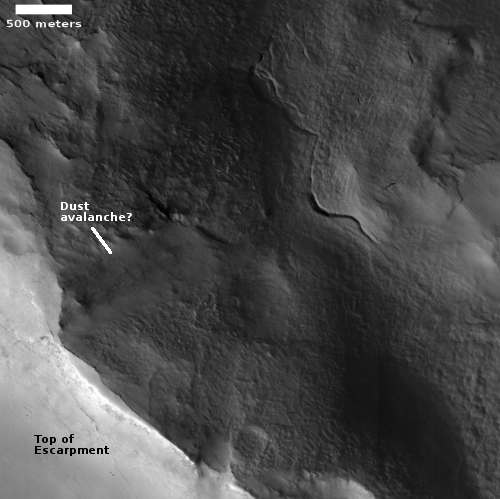
The arrow points to a small white streak that is not visible in the 2016 photo. A closer look reveals that the streak is actually two fanlike white deposits expanding outward in opposite directions from a central point.
What we are seeing are the exhaust fans blown onto the Martian surface by the retro-jets on the Sky crane that was lowering Perseverance to the ground. The rover was put down at the centerpoint, and was still at that spot on March 2nd when this photo was acquired.
The highest resolution version of this image requires special software, so in this version you cannot see the rover itself. Nor can you see the Sky crane after it crashed landed or the parachutes.
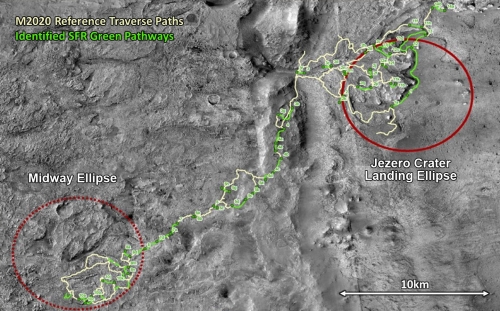
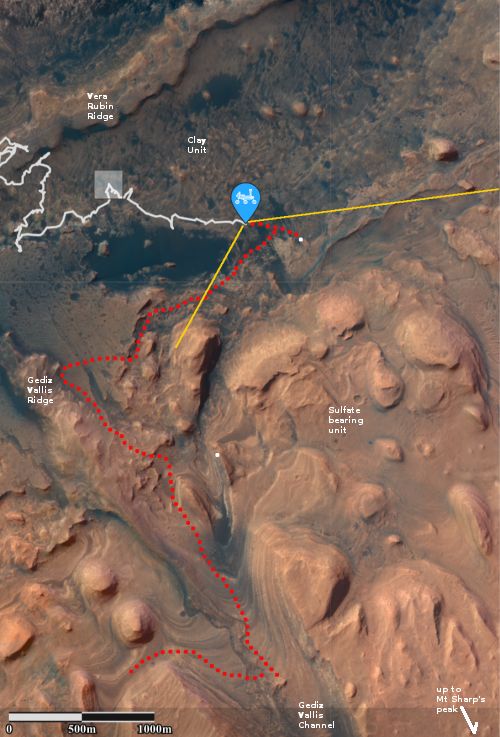
The new photo was taken one week after the first high resolution image from MRO, as part of what will become a routine periodic monitoring of the site, along with obtaining mapping information for picking the rover’s upcoming route They will also probably use both images to try to locate both the Sky crane and parachutes, on the ground.
Cool image time! The two photos to the right show the landing site for the Perseverance rover in Jezero Crater on Mars. The first image was taken in 2016 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The second image was made available today in the monthly release of photos taken that camera on MRO.
The arrow points to a small white streak that is not visible in the 2016 photo. A closer look reveals that the streak is actually two fanlike white deposits expanding outward in opposite directions from a central point.
What we are seeing are the exhaust fans blown onto the Martian surface by the retro-jets on the Sky crane that was lowering Perseverance to the ground. The rover was put down at the centerpoint, and was still at that spot on March 2nd when this photo was acquired.
The highest resolution version of this image requires special software, so in this version you cannot see the rover itself. Nor can you see the Sky crane after it crashed landed or the parachutes.
The new photo was taken one week after the first high resolution image from MRO, as part of what will become a routine periodic monitoring of the site, along with obtaining mapping information for picking the rover’s upcoming route They will also probably use both images to try to locate both the Sky crane and parachutes, on the ground.