Chang’e-4 and Yutu-2 complete 12th lunar day
Chinese engineers have put both Chang’e-4 and Yutu-2 into dormant mode after completed their twelve lunar day on the far side of the Moon.
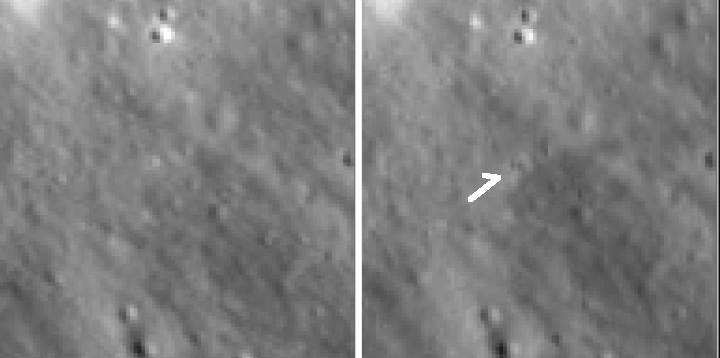
The article from the Chinese state-run press provides very little information, other than telling us that Yutu-2 traveled 345 meters, written in a way to imply that was the distance the rover traveled in this last lunar day. I think that is wrong, however. Based on the distances traversed during previous lunar days, and that the rover had traveled a total of 290 meters at the end of its tenth lunar day, I think this new number is the total distance traveled.
The article also does not say what the consequences will be for these two spacecraft now that the priority of their communications relay has shifted from communications to being a radio telescope.
It could be that the consequences will be minor, considering that both spacecraft are in sleep mode during the lunar nights and for high noon of the lunar day. During those periods the relay satellite could be devoted full time to radio astronomy and have no impact on the lander and rover.
Unfortunately China has not said.
Chinese engineers have put both Chang’e-4 and Yutu-2 into dormant mode after completed their twelve lunar day on the far side of the Moon.
The article from the Chinese state-run press provides very little information, other than telling us that Yutu-2 traveled 345 meters, written in a way to imply that was the distance the rover traveled in this last lunar day. I think that is wrong, however. Based on the distances traversed during previous lunar days, and that the rover had traveled a total of 290 meters at the end of its tenth lunar day, I think this new number is the total distance traveled.
The article also does not say what the consequences will be for these two spacecraft now that the priority of their communications relay has shifted from communications to being a radio telescope.
It could be that the consequences will be minor, considering that both spacecraft are in sleep mode during the lunar nights and for high noon of the lunar day. During those periods the relay satellite could be devoted full time to radio astronomy and have no impact on the lander and rover.
Unfortunately China has not said.