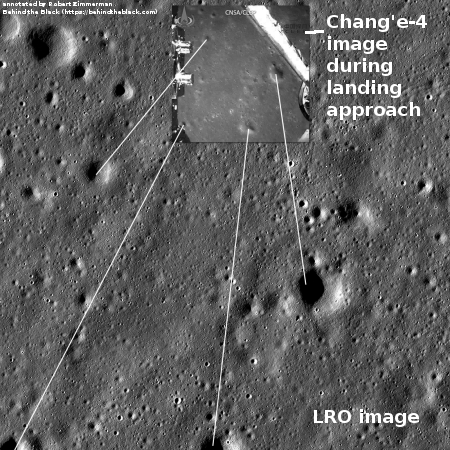
SpaceX successfully launches three satellites
Capitalism in space: SpaceX tonight used its Falcon 9 rocket, including a first stage that had already flown twice before, to launch an Indonesian communications satellite, an Air Force smallsat, and most importantly, the Israeli-built Beresheet lunar lander, the first planetary mission entirely funded from private sources.
You can get some details about Beresheet here. If all goes as planned, it will land on the Moon on April 11 and operate for two Earth days on the surface.
SpaceX was also able to successfully land that first stage, which I think is the first time they have successfully used and recovered a first stage three times. Look for this first stage to fly a fourth time.
The 2019 launch race:
2 China
2 SpaceX
1 ULA
1 Japan
1 India
1 Europe
1 Russia
The U.S. now leads China in the national rankings, 3-2.
Capitalism in space: SpaceX tonight used its Falcon 9 rocket, including a first stage that had already flown twice before, to launch an Indonesian communications satellite, an Air Force smallsat, and most importantly, the Israeli-built Beresheet lunar lander, the first planetary mission entirely funded from private sources.
You can get some details about Beresheet here. If all goes as planned, it will land on the Moon on April 11 and operate for two Earth days on the surface.
SpaceX was also able to successfully land that first stage, which I think is the first time they have successfully used and recovered a first stage three times. Look for this first stage to fly a fourth time.
The 2019 launch race:
2 China
2 SpaceX
1 ULA
1 Japan
1 India
1 Europe
1 Russia
The U.S. now leads China in the national rankings, 3-2.