Two launches by China and SpaceX
Both China and SpaceX completed launches today. First, China launched another 11 satellites for its Geely internet-of-things constellation, its Smart Dragon-3 rocket lifting off from a ocean platform off the nation’s eastern coast.
This was the sixth launch for this constellation, bringing the number of satellites in orbit to 64, out of a planned 240. The constellation is designed to provide positioning and communications for trucking and other ground-based businesses.
Next, SpaceX successfully placed three government science satellites into orbit (two for NASA and one for NOAA), its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The first stage completed its second flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic. The two fairings both completed their first flight.
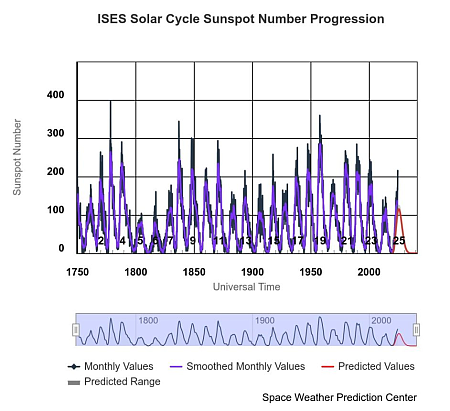
The two NASA satellites were the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP) to study the Sun’s heliosphere at the edge of the solar system and the Carruthers Geocorona Observatory to study the exosphere, the outermost layer of the atmosphere. The NOAA probe, Space Weather Follow On – Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1), will observe the Sun from one million miles from Earth, providing advance knowledge of strong solar flares and eruptions so that utility companies can shield the electric grid appropriately.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
123 SpaceX
55 China
13 Russia
12 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 123 to 94.
Both China and SpaceX completed launches today. First, China launched another 11 satellites for its Geely internet-of-things constellation, its Smart Dragon-3 rocket lifting off from a ocean platform off the nation’s eastern coast.
This was the sixth launch for this constellation, bringing the number of satellites in orbit to 64, out of a planned 240. The constellation is designed to provide positioning and communications for trucking and other ground-based businesses.
Next, SpaceX successfully placed three government science satellites into orbit (two for NASA and one for NOAA), its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The first stage completed its second flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic. The two fairings both completed their first flight.
The two NASA satellites were the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP) to study the Sun’s heliosphere at the edge of the solar system and the Carruthers Geocorona Observatory to study the exosphere, the outermost layer of the atmosphere. The NOAA probe, Space Weather Follow On – Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1), will observe the Sun from one million miles from Earth, providing advance knowledge of strong solar flares and eruptions so that utility companies can shield the electric grid appropriately.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
123 SpaceX
55 China
13 Russia
12 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 123 to 94.