SEC goes after Musk
The Securities and Exchange Commission today filed a complaint against Tesla in an effort to force Elon Musk out as head of the company.
The complaint filed by the Securities and Exchange Commission came after a last-minute decision by Mr. Musk and his lawyers to fight the case rather than settle the charges.
The filing by the SEC in federal court in Manhattan threatens to deal a severe blow to the Palo Alto, Calif., electric car maker. Its brand and Mr. Musk are closely intertwined, and analysts have said the company’s roughly $50 billion market value is driven by Wall Street’s appreciation for Mr. Musk’s vision and skill as an innovator.
SEC Sues Elon Musk for Fraud, Seeks Removal From Tesla
Tesla wasn’t named in the suit as a defendant, but the SEC is seeking to bar Mr. Musk, Tesla’s largest shareholder and its top executive, from serving as an officer or director of any U.S. public company. Tesla shares, which have been under intense pressure amid questions about the firm’s financial strength and Mr. Musk’s behavior, tumbled 9.9% to $277 in after-hours trading Thursday on Nasdaq.
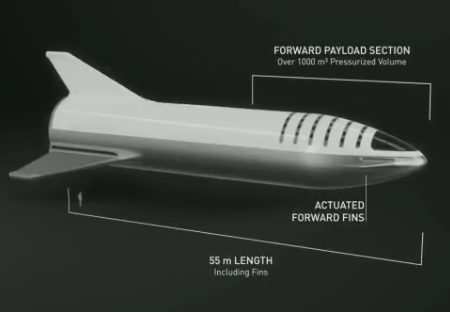
This is very bad news for Tesla. However, it might be good news for SpaceX, as Musk has admitted to being very overworked. If he is forced from Tesla, he will have an enormous load removed from him.
The Securities and Exchange Commission today filed a complaint against Tesla in an effort to force Elon Musk out as head of the company.
The complaint filed by the Securities and Exchange Commission came after a last-minute decision by Mr. Musk and his lawyers to fight the case rather than settle the charges.
The filing by the SEC in federal court in Manhattan threatens to deal a severe blow to the Palo Alto, Calif., electric car maker. Its brand and Mr. Musk are closely intertwined, and analysts have said the company’s roughly $50 billion market value is driven by Wall Street’s appreciation for Mr. Musk’s vision and skill as an innovator.
SEC Sues Elon Musk for Fraud, Seeks Removal From Tesla
Tesla wasn’t named in the suit as a defendant, but the SEC is seeking to bar Mr. Musk, Tesla’s largest shareholder and its top executive, from serving as an officer or director of any U.S. public company. Tesla shares, which have been under intense pressure amid questions about the firm’s financial strength and Mr. Musk’s behavior, tumbled 9.9% to $277 in after-hours trading Thursday on Nasdaq.
This is very bad news for Tesla. However, it might be good news for SpaceX, as Musk has admitted to being very overworked. If he is forced from Tesla, he will have an enormous load removed from him.